|
Access Time
Access time is the time delay or latency between a request to an electronic system, and the access being completed or the requested data returned * In a computer, it is the time interval between the instant at which an instruction control unit initiates a call for data or a request to store data, and the instant at which delivery of the data is completed or the storage is started. See also * Memory latency * Mechanical latency * Rotational latency * Seek time Higher performance in hard disk drives comes from devices which have better performance characteristics. These performance characteristics can be grouped into two categories: access time and data transfer time (or rate). Access time The ''access ... References Network access {{compu-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latency (engineering)
Latency, from a general point of view, is a time delay between the cause and the effect of some physical change in the system being observed. Lag, as it is known in gaming circles, refers to the latency between the input to a simulation and the visual or auditory response, often occurring because of network delay in online games. Latency is physically a consequence of the limited velocity at which any physical interaction can propagate. The magnitude of this velocity is always less than or equal to the speed of light. Therefore, every physical system with any physical separation (distance) between cause and effect will experience some sort of latency, regardless of the nature of the stimulation at which it has been exposed to. The precise definition of latency depends on the system being observed or the nature of the simulation. In communications, the lower limit of latency is determined by the medium being used to transfer information. In reliable two-way communication syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as Computer program, programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the Computer hardware, hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of Programmable logic controller, industrial and Consumer electronics, consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instruction (computer Science)
In computer science, an instruction set architecture (ISA), also called computer architecture, is an abstract model of a computer. A device that executes instructions described by that ISA, such as a central processing unit (CPU), is called an ''implementation''. In general, an ISA defines the supported instructions, data types, registers, the hardware support for managing main memory, fundamental features (such as the memory consistency, addressing modes, virtual memory), and the input/output model of a family of implementations of the ISA. An ISA specifies the behavior of machine code running on implementations of that ISA in a fashion that does not depend on the characteristics of that implementation, providing binary compatibility between implementations. This enables multiple implementations of an ISA that differ in characteristics such as performance, physical size, and monetary cost (among other things), but that are capable of running the same machine code, so that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete values that convey information, describing quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted. A datum is an individual value in a collection of data. Data is usually organized into structures such as tables that provide additional context and meaning, and which may themselves be used as data in larger structures. Data may be used as variables in a computational process. Data may represent abstract ideas or concrete measurements. Data is commonly used in scientific research, economics, and in virtually every other form of human organizational activity. Examples of data sets include price indices (such as consumer price index), unemployment rates, literacy rates, and census data. In this context, data represents the raw facts and figures which can be used in such a manner in order to capture the useful information out of it. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
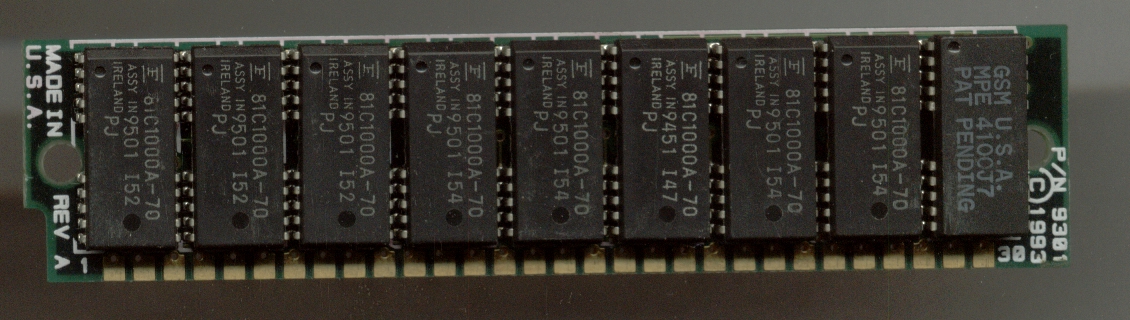
Computer Storage
Computer data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers. The central processing unit (CPU) of a computer is what manipulates data by performing computations. In practice, almost all computers use a storage hierarchy, which puts fast but expensive and small storage options close to the CPU and slower but less expensive and larger options further away. Generally, the fast volatile technologies (which lose data when off power) are referred to as "memory", while slower persistent technologies are referred to as "storage". Even the first computer designs, Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine and Percy Ludgate's Analytical Machine, clearly distinguished between processing and memory (Babbage stored numbers as rotations of gears, while Ludgate stored numbers as displacements of rods in shuttles). This distinction was extended in the Von Neumann a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Latency
''Memory latency'' is the time (the latency) between initiating a request for a byte or word in memory until it is retrieved by a processor. If the data are not in the processor's cache, it takes longer to obtain them, as the processor will have to communicate with the external memory cells. Latency is therefore a fundamental measure of the speed of memory: the less the latency, the faster the reading operation. Latency should not be confused with memory bandwidth, which measures the throughput of memory. Latency can be expressed in clock cycles or in time measured in nanoseconds. Over time, memory latencies expressed in clock cycles have been fairly stable, but they have improved in time.Crucial Technology, "Speed ''vs.'' Latency: Why CAS latency isn't an accurate measure of memory performance/ref> See also * Burst mode (computing) * CAS latency * Multi-channel memory architecture * Interleaved memory * SDRAM burst ordering * SDRAM latency Memory timings or RAM timings descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latency (engineering)
Latency, from a general point of view, is a time delay between the cause and the effect of some physical change in the system being observed. Lag, as it is known in gaming circles, refers to the latency between the input to a simulation and the visual or auditory response, often occurring because of network delay in online games. Latency is physically a consequence of the limited velocity at which any physical interaction can propagate. The magnitude of this velocity is always less than or equal to the speed of light. Therefore, every physical system with any physical separation (distance) between cause and effect will experience some sort of latency, regardless of the nature of the stimulation at which it has been exposed to. The precise definition of latency depends on the system being observed or the nature of the simulation. In communications, the lower limit of latency is determined by the medium being used to transfer information. In reliable two-way communication syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotational Latency
Higher performance in hard disk drives comes from devices which have better performance characteristics. These performance characteristics can be grouped into two categories: access time and data transfer time (or rate). Access time The ''access time'' or ''response time'' of a rotating drive is a measure of the time it takes before the drive can actually transfer data. The factors that control this time on a rotating drive are mostly related to the mechanical nature of the rotating disks and moving heads. It is composed of a few independently measurable elements that are added together to get a single value when evaluating the performance of a storage device. The access time can vary significantly, so it is typically provided by manufacturers or measured in benchmarks as an average. The key components that are typically added together to obtain the access time are: * Seek time * Rotational latency * Command processing time * Settle time Seek time With rotating drives, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seek Time
Higher performance in hard disk drives comes from devices which have better performance characteristics. These performance characteristics can be grouped into two categories: access time and data transfer time (or rate). Access time The ''access time'' or ''response time'' of a rotating drive is a measure of the time it takes before the drive can actually transfer data. The factors that control this time on a rotating drive are mostly related to the mechanical nature of the rotating disks and moving heads. It is composed of a few independently measurable elements that are added together to get a single value when evaluating the performance of a storage device. The access time can vary significantly, so it is typically provided by manufacturers or measured in benchmarks as an average. The key components that are typically added together to obtain the access time are: * Seek time * Rotational latency * Command processing time * Settle time Seek time With rotating drives, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |