|
Accelerated Failure Time Model
In the statistical area of survival analysis, an accelerated failure time model (AFT model) is a parametric model that provides an alternative to the commonly used proportional hazards models. Whereas a proportional hazards model assumes that the effect of a covariate is to multiply the hazard by some constant, an AFT model assumes that the effect of a covariate is to accelerate or decelerate the life course of a disease by some constant. This is especially appealing in a technical context where the 'disease' is a result of some mechanical process with a known sequence of intermediary stages. Model specification In full generality, the accelerated failure time model can be specified as :: \lambda(t, \theta)=\theta\lambda_0(\theta t) where \theta denotes the joint effect of covariates, typically \theta=\exp(- beta_1X_1 + \cdots + \beta_pX_p. (Specifying the regression coefficients with a negative sign implies that high values of the covariates ''increase'' the survival time, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth (LEB), which can be defined in two ways. ''Cohort'' LEB is the mean length of life of a birth cohort (all individuals born in a given year) and can be computed only for cohorts born so long ago that all their members have died. ''Period'' LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year. National LEB figures reported by national agencies and international organizations for human populations are estimates of ''period'' LEB. In the Bronze Age and the Iron Age, human LEB was 26 years; in 2010, world LEB was 67.2 years. In recent years, LEB in Eswatini (formerly Swaziland) is 49, while LEB in Japan is 83. The combination of high infant mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Gaussian Distribution
In probability theory, the inverse Gaussian distribution (also known as the Wald distribution) is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions with support on (0,∞). Its probability density function is given by : f(x;\mu,\lambda) = \sqrt\frac \exp\biggl(-\frac\biggr) for ''x'' > 0, where \mu > 0 is the mean and \lambda > 0 is the shape parameter. The inverse Gaussian distribution has several properties analogous to a Gaussian distribution. The name can be misleading: it is an "inverse" only in that, while the Gaussian describes a Brownian motion's level at a fixed time, the inverse Gaussian describes the distribution of the time a Brownian motion with positive drift takes to reach a fixed positive level. Its cumulant generating function (logarithm of the characteristic function) is the inverse of the cumulant generating function of a Gaussian random variable. To indicate that a random variable ''X'' is inverse Gaussian-distributed with mean μ and sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
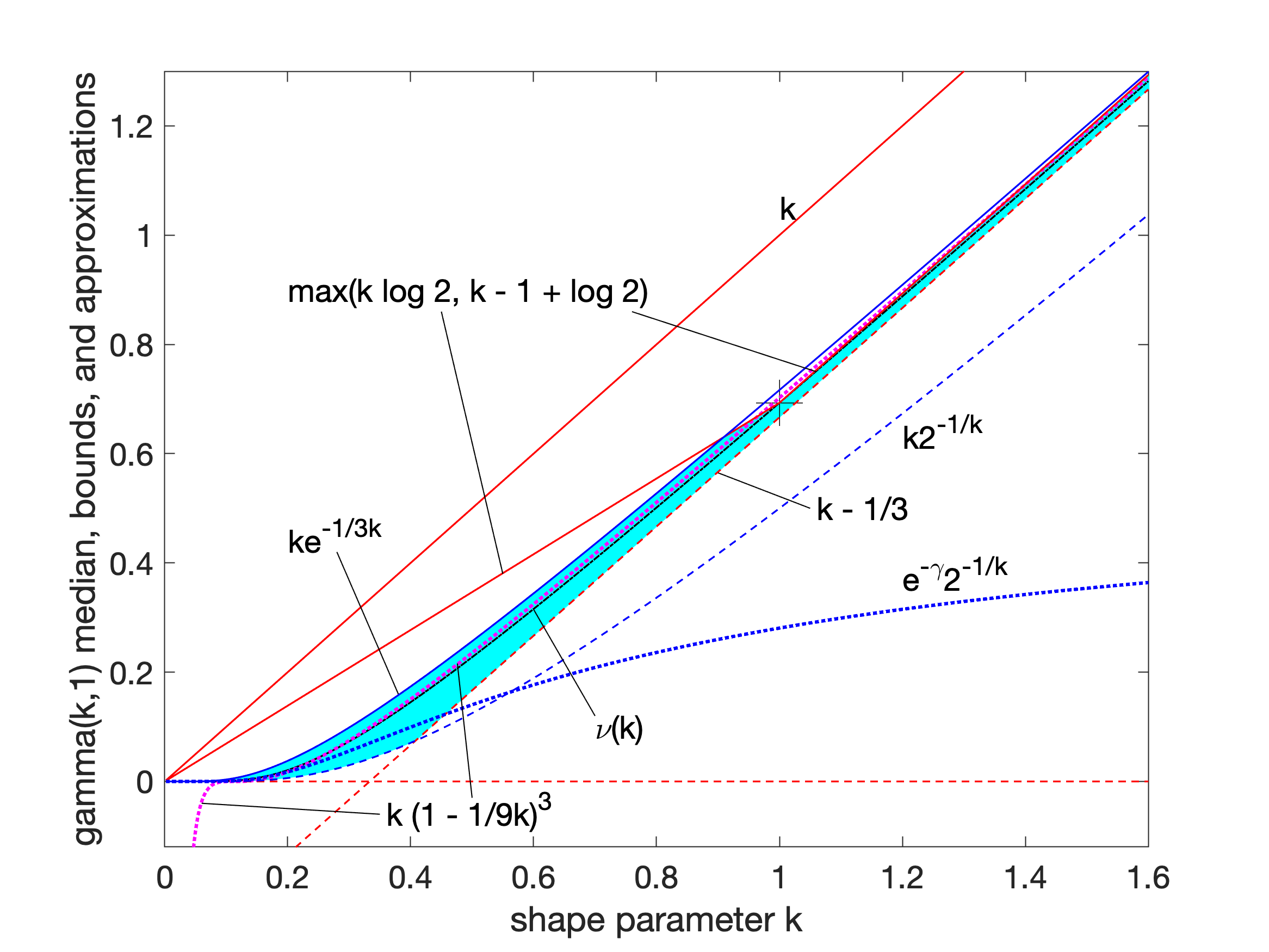
Gamma Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the gamma distribution is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. The exponential distribution, Erlang distribution, and chi-square distribution are special cases of the gamma distribution. There are two equivalent parameterizations in common use: #With a shape parameter k and a scale parameter \theta. #With a shape parameter \alpha = k and an inverse scale parameter \beta = 1/ \theta , called a rate parameter. In each of these forms, both parameters are positive real numbers. The gamma distribution is the maximum entropy probability distribution (both with respect to a uniform base measure and a 1/x base measure) for a random variable X for which E 'X''= ''kθ'' = ''α''/''β'' is fixed and greater than zero, and E n(''X'')= ''ψ''(''k'') + ln(''θ'') = ''ψ''(''α'') − ln(''β'') is fixed (''ψ'' is the digamma function). Definitions The parameterization with ''k'' and ''θ'' appears to be more common in econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the exponential distribution is the probability distribution of the time between events in a Poisson point process, i.e., a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average rate. It is a particular case of the gamma distribution. It is the continuous analogue of the geometric distribution, and it has the key property of being memoryless. In addition to being used for the analysis of Poisson point processes it is found in various other contexts. The exponential distribution is not the same as the class of exponential families of distributions. This is a large class of probability distributions that includes the exponential distribution as one of its members, but also includes many other distributions, like the normal, binomial, gamma, and Poisson distributions. Definitions Probability density function The probability density function (pdf) of an exponential distribution is : f(x;\lambda) = \begin \lambda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Censoring (statistics)
In statistics, censoring is a condition in which the value of a measurement or observation is only partially known. For example, suppose a study is conducted to measure the impact of a drug on mortality rate. In such a study, it may be known that an individual's age at death is ''at least'' 75 years (but may be more). Such a situation could occur if the individual withdrew from the study at age 75, or if the individual is currently alive at the age of 75. Censoring also occurs when a value occurs outside the range of a measuring instrument. For example, a bathroom scale might only measure up to 140 kg. If a 160-kg individual is weighed using the scale, the observer would only know that the individual's weight is at least 140 kg. The problem of censored data, in which the observed value of some variable is partially known, is related to the problem of missing data, where the observed value of some variable is unknown. Censoring should not be confused with the related idea tru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed-form Expression
In mathematics, a closed-form expression is a mathematical expression that uses a finite number of standard operations. It may contain constants, variables, certain well-known operations (e.g., + − × ÷), and functions (e.g., ''n''th root, exponent, logarithm, trigonometric functions, and inverse hyperbolic functions), but usually no limit, differentiation, or integration. The set of operations and functions may vary with author and context. Example: roots of polynomials The solutions of any quadratic equation with complex coefficients can be expressed in closed form in terms of addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and square root extraction, each of which is an elementary function. For example, the quadratic equation :ax^2+bx+c=0, is tractable since its solutions can be expressed as a closed-form expression, i.e. in terms of elementary functions: :x=\frac. Similarly, solutions of cubic and quartic (third and fourth degree) equations can be expresse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulative Distribution Function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x. Every probability distribution supported on the real numbers, discrete or "mixed" as well as continuous, is uniquely identified by an ''upwards continuous'' ''monotonic increasing'' cumulative distribution function F : \mathbb R \rightarrow ,1/math> satisfying \lim_F(x)=0 and \lim_F(x)=1. In the case of a scalar continuous distribution, it gives the area under the probability density function from minus infinity to x. Cumulative distribution functions are also used to specify the distribution of multivariate random variables. Definition The cumulative distribution function of a real-valued random variable X is the function given by where the right-hand side represents the probability that the random variable X takes on a value less tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Log-normal Distribution
In probability theory, a log-normal (or lognormal) distribution is a continuous probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm is normally distributed. Thus, if the random variable is log-normally distributed, then has a normal distribution. Equivalently, if has a normal distribution, then the exponential function of , , has a log-normal distribution. A random variable which is log-normally distributed takes only positive real values. It is a convenient and useful model for measurements in exact and engineering sciences, as well as medicine, economics and other topics (e.g., energies, concentrations, lengths, prices of financial instruments, and other metrics). The distribution is occasionally referred to as the Galton distribution or Galton's distribution, after Francis Galton. The log-normal distribution has also been associated with other names, such as McAlister, Gibrat and Cobb–Douglas. A log-normal process is the statistical realization of the multipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotonic
In mathematics, a monotonic function (or monotone function) is a function between ordered sets that preserves or reverses the given order. This concept first arose in calculus, and was later generalized to the more abstract setting of order theory. In calculus and analysis In calculus, a function f defined on a subset of the real numbers with real values is called ''monotonic'' if and only if it is either entirely non-increasing, or entirely non-decreasing. That is, as per Fig. 1, a function that increases monotonically does not exclusively have to increase, it simply must not decrease. A function is called ''monotonically increasing'' (also ''increasing'' or ''non-decreasing'') if for all x and y such that x \leq y one has f\!\left(x\right) \leq f\!\left(y\right), so f preserves the order (see Figure 1). Likewise, a function is called ''monotonically decreasing'' (also ''decreasing'' or ''non-increasing'') if, whenever x \leq y, then f\!\left(x\right) \geq f\!\left(y\ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weibull Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Weibull distribution is a continuous probability distribution. It is named after Swedish mathematician Waloddi Weibull, who described it in detail in 1951, although it was first identified by Maurice René Fréchet and first applied by to describe a particle size distribution. Definition Standard parameterization The probability density function of a Weibull random variable is : f(x;\lambda,k) = \begin \frac\left(\frac\right)^e^, & x\geq0 ,\\ 0, & x 0 is the ''shape parameter'' and λ > 0 is the ''scale parameter'' of the distribution. Its complementary cumulative distribution function is a stretched exponential function. The Weibull distribution is related to a number of other probability distributions; in particular, it interpolates between the exponential distribution (''k'' = 1) and the Rayleigh distribution (''k'' = 2 and \lambda = \sqrt\sigma ). If the quantity ''X'' is a "time-to-failure", the Weibull distribution gives a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Log-logistic Distribution
In probability and statistics, the log-logistic distribution (known as the Fisk distribution in economics) is a continuous probability distribution for a non-negative random variable. It is used in survival analysis as a parametric model for events whose rate increases initially and decreases later, as, for example, mortality rate from cancer following diagnosis or treatment. It has also been used in hydrology to model stream flow and precipitation, in economics as a simple model of the distribution of wealth or income, and in networking to model the transmission times of data considering both the network and the software. The log-logistic distribution is the probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm has a logistic distribution. It is similar in shape to the log-normal distribution but has heavier tails. Unlike the log-normal, its cumulative distribution function can be written in closed form. Characterization There are several different parameterizations of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |