|
Acamapitzin
Acamapichtli ( nci-IPA, Ācamāpichtli, aːkamaːˈpit͡ʃt͡ɬi, meaning "Handful of reeds") was the first '' Tlatoani'', or king, of the Aztecs (or Mexica) of Tenochtitlan, and founder of the Aztec imperial dynasty. Chronicles differ as to the dates of his reign: according to the Codex Chimalpahin, he reigned from 1367 to 1387; according to the Codex Aubin, he reigned from 1376 to 1395; and according to the Codex Chimalpopoca, he reigned from 1350 to 1403.Simon, Z (2021). "Ten Chronologies of Ancient Mexico" Biography Family and early life Acamapichtli was not a native of Tenochtitlan. Blood relationships between rulers were an important aspect of politics in 14th century Mexico, and as relative newcomers, the Mexicans were at a disadvantage. On the death of Tenoch, the elders of the Mexica '' calpultin'' decided to elect a ''tlatoani'' who could secure the fledgling city's position through ties to powerful groups in the region. They sent a delegation to the leaders of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Tenochtitlan Rulers
This is a list of Mesoamerican rulers of the ''altepetl'' of Tenochtitlan (modern Mexico City) from its foundation in 1325 until the end of the line of indigenous rulers. From c. 1375 onwards, the rulers of Tenochtitlan were monarchs and used the title ''tlatoani''. From 1427 to 1521, the ''tlatoque'' of Tenochtitlan were alongside those of the cities Tetzcoco and Tlacopan the leaders of the powerful Triple Alliance, commonly known as the Aztec Empire. The rulers of Tenochtitlan were always pre-eminent and gradually transitioned into the sole rulers of the empire; under either Tizoc (1481–1486) or Ahuitzotl (1486–1502), the ''tlatoque'' of Tenochtitlan assumed the grander title ''huehuetlatoani'' ("supreme ''tlatoani''") to indicate their superiority over the other ''tlatoque'' in the alliance. The evolution into full autocracy was finished by 1502, when Moctezuma II was elected as ''huehuetlatoani'' of Tenochtitlan without the traditional input from Tetzoco and Tlacopan. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
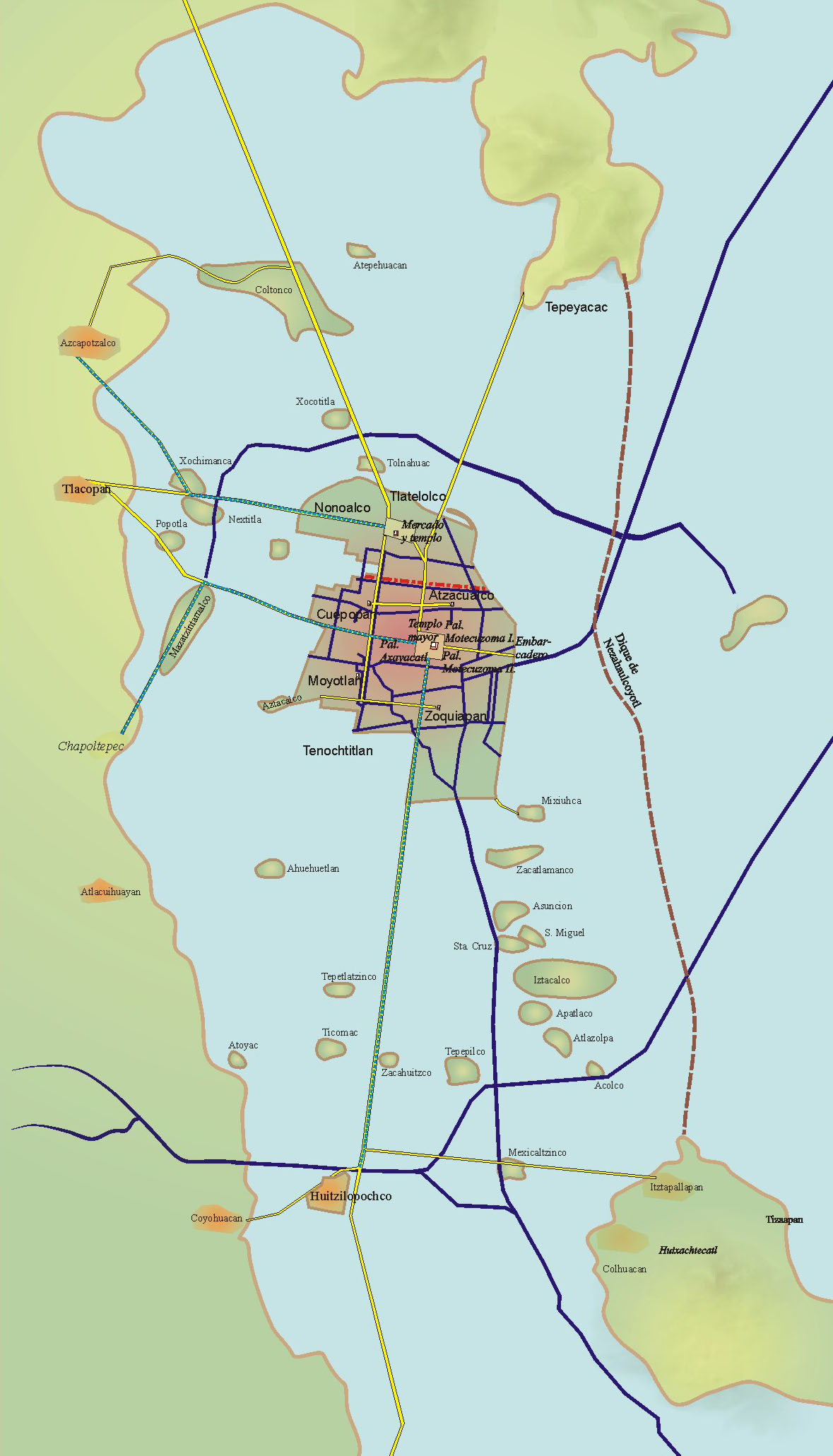
Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, México-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was captured by the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a '' cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or polities) on the island, the other being . The city is located in modern-day Mexico City. Etymolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diego Durán
Diego Durán (c. 1537 – 1588) was a Dominican friar best known for his authorship of one of the earliest Western books on the history and culture of the Aztecs, ''The History of the Indies of New Spain'', a book that was much criticised in his lifetime for helping the "heathen" maintain their culture. Also known as the Durán Codex, ''The History of the Indies of New Spain'' was completed in about 1581. Durán also wrote ''Book of the Gods and Rites'' (1574–1576), and ''Ancient Calendar'' (c. 1579). He was fluent in Nahuatl, the Aztec language, and was therefore able to consult natives and Aztec codices as well as work done by earlier friars. His empathetic nature allowed him to gain the confidence of many native people who would not share their stories with Europeans, and was able to document many previously unknown folktales and legends that make his work unique. Early life Durán was born sometime around 1537 in Seville, Spain. His family traveled to Mexico when he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toltecs
The Toltec culture () was a pre-Columbian Mesoamerican culture that ruled a state centered in Tula, Hidalgo, Mexico, during the Epiclassic and the early Post-Classic period of Mesoamerican chronology, reaching prominence from 950 to 1150 CE. The later Aztec culture saw the Toltecs as their intellectual and cultural predecessors and described Toltec culture emanating from ''Tōllān'' ( Nahuatl for Tula) as the epitome of civilization; in the Nahuatl language the word ''Tōltēkatl'' (singular) or ''Tōltēkah'' (plural) came to take on the meaning "artisan". The Aztec oral and pictographic tradition also described the history of a Toltec Empire, giving lists of rulers and their exploits. Modern scholars debate whether the Aztec narratives of Toltec history should be given credence as descriptions of actual historical events. While all scholars acknowledge that there is a large mythological part of the narrative, some maintain that, by using a critical comparative method, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coatlinchan
Coatlinchan is a town in the Mexican state of Mexico. San Miguel Coatlinchán (in Nahuatl: Coatl, in, chantli, 'snake, possessive prefix, home' 'In the home of the snakes') is a locality of the state of Mexico, in the municipality of Texcoco. Nearby was the original location of the monolith of Tláloc, located today at the entrance of the National Museum of Anthropology in Mexico City. Location and demographics San Miguel Coatlinchán is in the south of the municipality of Texcoco and about south of the municipal seat of the city of Texcoco de Mora, in the transition zone between the Valley of Mexico and the foot of the Sierra Nevada. Elevation is denominated Sierra Quetzaltepec of which descends the stream Coatlinchán through the Barranca of Santa Clara. Its geographical coordinates are 19°26'56 "N 98°52'20" W, and its altitude is above sea level. Its main route of communication is the Federal Highway 136, former Mexico-Texcoco Highway and with which it is linked by two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acolhua
The Acolhua are a Mesoamerican people who arrived in the Valley of Mexico in or around the year 1200 CE. The Acolhua were a sister culture of the Aztecs (or Mexica) as well as the Tepanec, Chalca, Xochimilca and others. The most important political entity in ancient Mesoamerica was the Triple Alliance (Nahuatl, ''excan tlatoloyan''), founded in 1428 when the rulers of Tenochtitlan, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan formed an alliance that replaced the Tepanec Empire of Azcapotzalco and eventually integrated into a single polity the most developed regions of western Mesoamerica. Because of the predominance of Tenochtitlan, it has also been called the Mexica, Aztec, or Tenochca Empire. It came to an end with the Spanish conquest of 1521. Each of the three allied kings led a group of lesser kingdoms that coincided with the three major ethnic components and political powers of previous times: the Colhuas, the Acolhua-Chichimecs, and the Tepanecs. The domain of Tenochtitlan was the southern pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huehue Acamapichtli
Huehue Acamapichtli (''Ācamāpichtli'' ːkamaːˈpit͡ʃt͡ɬi= "Handful of reeds", ) was a king ( Nahuatl: ''tlatoani'') of Culhuacán. He was a son — and successor — of King Coxcoxtli and his wife. His sister was Atotoztli I of Culhuacán — mother of ''tlatoani'' of Tenochtitlan, named also Acamapichtli.Frederick Ward Putnam, Alfred Louis Kroeber, Robert Harry Lowie''Publications in American Archaeology and Ethnology'', Opseg 17 Diego Durán, Fernando Alvarado Tezozómoc and Fernando de Alva Cortés Ixtlilxochitl Fernando is a Spanish and Portuguese given name and a surname common in Spain, Portugal, Italy, France, Switzerland, former Spanish or Portuguese colonies in Latin America, Africa, the Philippines, India, and Sri Lanka. It is equivalent to the G ... mentioned that Huehue Acamapichtli occupied the throne of Culhuacán in 1324. Sources {{end box Tlatoque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coxcoxtli
Coxcoxtli () was a king of city-state Colhuacan (altepetl), Culhuacán. He had two children — a son called Huehue Acamapichtli and a daughter Atotoztli I, who married Opochtli Iztahuatzin and bore him Acamapichtli, the first ruler of Tenochtitlan. He was thus an ancestor of Aztec emperors. Sources Bibliography * * {{Authority control Tlatoque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culhuacán (altepetl)
Culhuacan ( nci-IPA, Cōlhuàcān, koːlˈwaʔkaːn) was one of the Nahuatl-speaking pre-Columbian city-states of the Valley of Mexico. According to tradition, Culhuacan was founded by the Toltecs under Mixcoatl and was the first Toltec city. The Nahuatl speakers agreed that Culhuacán was the first city to give its rulers the title of "speaker" (''tlatoani''). History Culhuacan was perhaps the first of the chinampa towns founded on the shores of Lake Xochimilco, with chinampas dating to 1100 C.E.Richard Blanton, "Prehispanic Adaptation in the Ixtapalapa Region, Mexico" ''Science'' 1972; 175(4028):1317-26 From written records there is evidence that Culhuacan survived the fall of Tollan and maintained its prestige until the mid-14th century. According to the ''Crónica Mexicayotl'', transcribed in 1609, in 1299, Culhuacan's ''tlatoani'', Coxcoxtli, helped the Tepanecs of Azcapotzalco, the Xochimilca and other cities expel the Mexica from Chapultepec. Coxcoxtli then gave the Mexi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calpulli
In precolumbian Aztec society, a calpulli (from Classical Nahuatl '' calpōlli'', , meaning "large house") was the designation of an organizational unit below the level of the altepetl "city-state". In Spanish sources, they are termed ''parcialidades'' or ''barrios.''Carrasco, Pedro. "Calpulli." In Davíd Carrasco (ed). ''The Oxford Encyclopedia of Mesoamerican Cultures''. Vol 1. New York: Oxford University Press, 2001. A Nahua city-state was divided into a number of calpullis, whose inhabitants were collectively responsible for different organizational and religious tasks in relation to the larger altepetl. Calpullis controlled land which was available for calpulli members to cultivate and also operated the Tēlpochcalli schools for young men of commoner descent. In Aztec culture, as in most other civilizations, the family unit was very important. There were several levels of organization in Aztec family life beginning with the base family unit. The base family unit consisted of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenoch
Tenoch (or Tenuch, ) was a ruler of the Mexicas (Aztecas) during the fourteenth century during the Aztec travels from Aztlán to Tenochtitlan. Tenoch's father was Iztac Mixcoatl, who had a total of seven sons with two wives. The Tenochtitlan people were originally referred to as Tenochca, then the Mexica. He was a respected chief who was elected to power by the council of elders and died sometime between 1350 and 1375, depending on the source. There is disagreement whether Tenoch is a mythological person or a real Mexica leader who was later mythologized. Tenoch was one of nine Mexica leaders who were told how Mexica could gain support from the forces of nature. After traveling southward for a span of 200 years, the Mexica found the sign. In honor of their leader, they named the small, reedy island in Lake Texcoco, Tenochtitlan. Tenochtitlan soon became the capital of the Aztec Empire. The Nahuatl symbols of his name are found in the Mexican flag The national flag of Mexico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Chimalpopoca
''Codex Chimalpopoca'' or ''Códice Chimalpopoca'' is a postconquest cartographic Aztec codex which is officially listed as being in the collection of the Instituto Nacional de Antropología e Historia located in Mexico City under "Collección Antiguo no. 159". It is best known for its stories of the hero-god Quetzalcoatl.Bierhorst, John. In Davíd Carrasco (ed). "Chimalpopoca, Codex." In ''The Oxford Encyclopedia of Mesoamerican Cultures''. : Oxford University Press, 2001. The current whereabouts of the codex are unknown. It appears to have been lost in the mid-twentieth century. Study of the codex is therefore necessarily provided only through copies and photographs. The codex consists of three parts, two of which are more important, one that regards the pre-Hispanic history of Central Mexico, the ''Anales de Cuauhtitlan'' and the other that regards the study of Aztec cosmology, the ''Leyenda de los Soles''. Physical characteristics According to Walter Lehmann, who studied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |