|
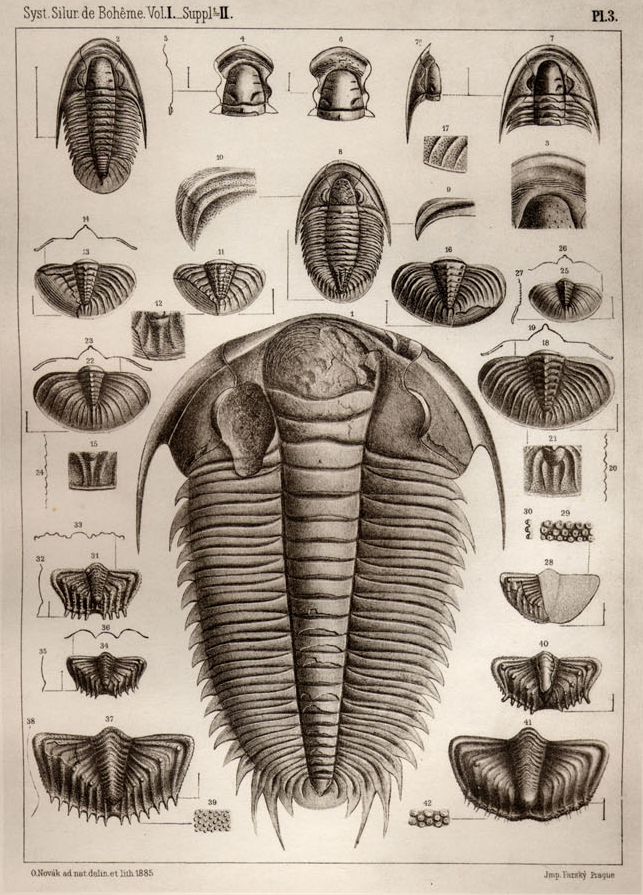
Acadoparadoxides
''Acadoparadoxides'' is an extinct genus of redlichiid trilobite belonging to the family Paradoxididae The Paradoxididae are a family of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. They occurred during the late Lower Cambrian ( Toyonian) and disappeared at the end of the Middle Cambrian. Representatives of this family have been found in th .... These fast-moving low-level epifaunal carnivores lived in the Middle Cambrian (abt 500 Ma). Selected species The following species have been described: References Redlichiida genera Paradoxidoidea Cambrian trilobites Prehistoric life of Europe Fossil taxa described in 1957 {{Redlichiida-stub Cambrian genus extinctions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradoxididae
The Paradoxididae are a family of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. They occurred during the late Lower Cambrian (Toyonian) and disappeared at the end of the Middle Cambrian. Representatives of this family have been found in the paleocontinents of Avalonia, Baltica, and Gondwana, now Canada (Nova-Scotia, New Brunswick, Newfoundland), USA (Massachusetts, South Carolina), England, Wales, Morocco, Spain, Czech Republic, Poland, Russia (Novaya Zemlya, Northern Siberia, North-East Yakutia), Mongolia, and Turkey. Species in this family can typically grow large to very large (over 30 cm), are relatively flat, have an inverted egg-shaped outline, opisthoparian sutures, a glabella that in early genera has parallel sides and expands forward in later representatives, and approaches or reaches the frontal border. All species have an almost semicircular headshield (or cephalon) with long backward-directed genal spines. The articulate middle part of the body (or thorax) con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museo Civico Di Storia Naturale Di Milano
The Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Milano (Milan Natural History Museum) is a museum in Milan, Italy. It was founded in 1838 when naturalist Giuseppe de Cristoforis donated his collections to the city. Its first director was Giorgio Jan. The Museum is located within a 19th-century building in the Indro Montanelli Garden, near the historic city gate of Porta Venezia. The structure was built between 1888 and 1893 in Neo-Romanesque style with Gothic elements. The museum is divided into five different permanent sections: Mineralogy (with a large collection of minerals from all over the world); Paleontology (with several fossils of dinosaurs and other prehistoric organisms); Natural History of Man (dedicated to the origins and evolution of humans with a particular attention to the relationship of the latter with the environment); Invertebrate Zoology (dedicated to mollusks, arthropods and entomology); and Vertebrate Zoology (dedicated to vertebrates, both exotic and Europea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redlichiid
Redlichiida is an order of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. Species assigned to the order Redlichiida are among the first trilobites to appear in the fossil record, about halfway during the Lower Cambrian. Due to the difficulty to relate sediments in different areas, there remains some discussion, but among the earliest are ''Fallotaspis'' (suborder Olenellina), and ''Lemdadella'' (suborder Redlichiina), both belonging to this order. The first representatives of the orders Corynexochida and Ptychopariida also appear very early on and may prove to be even earlier than any redlichiid species. In terms of anatomical comparison, the earliest redlichiid species are probably ancestral to all other trilobite orders and share many primitive characters. The last redlichiid trilobites died out before the end of the Middle Cambrian. Description Most redlichiids are rather flat (or have low dorso-ventral convexity) and their exoskeleton typically has an oval outline, abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Life Of Europe
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Trilobites
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Cambrian bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradoxidoidea
The Paradoxidoidea Hawle & Corda 1847,HAWLE, J. & CORDA, A. J. C. 1847. ''Prodrom einer Monographieder bohmischen Trilobiten''. 176 pp. J. G. Calve, Prague are a superfamily of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. They occurred during the late Lower Cambrian (Toyonian) and disappeared at the end of the Middle Cambrian. Description Species in this superfamily can be average (under 10 cm) to very large (over 30 cm), are relatively flat, have an inverted egg-shaped outline, a glabella that in early genera has parallel sides and expands forward in later representatives, and approaches or reaches the frontal border. All species have an almost semicircular headshield (or cephalon) with long backward directed genal spines. The facial suture in front of the eye diverges forward and outward in the Paradoxididae, while in the Centropleuridae it runs outward and even a bit backward (or retrodivergent). The articulate middle part of the body (or thorax) consists of 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redlichiida Genera
Redlichiida is an order of trilobites, a group of extinct marine arthropods. Species assigned to the order Redlichiida are among the first trilobites to appear in the fossil record, about halfway during the Lower Cambrian. Due to the difficulty to relate sediments in different areas, there remains some discussion, but among the earliest are '' Fallotaspis'' (suborder Olenellina), and ''Lemdadella'' (suborder Redlichiina), both belonging to this order. The first representatives of the orders Corynexochida and Ptychopariida also appear very early on and may prove to be even earlier than any redlichiid species. In terms of anatomical comparison, the earliest redlichiid species are probably ancestral to all other trilobite orders and share many primitive characters. The last redlichiid trilobites died out before the end of the Middle Cambrian. Description Most redlichiids are rather flat (or have low dorso-ventral convexity) and their exoskeleton typically has an oval outline, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period () and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last extant trilobites finally disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 252 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described. By the time trilobites first appeared in the fossil record, they were already highly diversified and geographically dispersed. Because trilobites had wide diversity and an easily fossilized exoskeleton, they left an extensive fossil record. The stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the scientific name of every taxon is almost al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joachim Barrande
Joachim Barrande (11 August 1799 – 5 October 1883) was a French geologist and palaeontologist. Career Barrande was born at Saugues, Haute Loire, and educated in the École Polytechnique and École Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées at Paris. Although he had received the training of an engineer, his first appointment was that of tutor to the duc de Bordeaux (afterwards known as the comte de Chambord), grandson of Charles X, and when the king abdicated in 1830, Barrande accompanied the royal exiles to England and Scotland, and afterwards to Prague. Settling in that city in 1831, he became occupied in engineering works, and his attention was then attracted to the fossils from the Lower Palaeozoic rocks of Bohemia. The publication in 1839 of ''Murchison's Silurian System'' incited Barrande to carry on systematic researches on the equivalent strata in Bohemia. For ten years (1840–1850) he made a detailed study of these rocks, engaging workmen specially to collect fossils, and in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)