|
Abruzzo–Erickson Syndrome
Abruzzo–Erickson syndrome is an extremely rare disorder characterized by deafness, protruding ears, coloboma, a cleft palate or palatal rugosity, radial synostosis, and short stature. It was first characterized by Abruzzo and Erickson in 1977 as a CHARGE like syndrome as variably expressed among a family of two brothers, their mother, and their maternal uncle. Members of this family exhibited many of the CHARGE symptoms, but notably did not have choanal atresia and the brothers experienced typical genital development. Due to the recent discovery of this disorder, its etiology is not fully known but it is understood that it arises from mutations on the TBX22 gene on the X-chromosome. The disorder is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. There is currently no known cure but its symptoms can be treated. Signs and Symptoms Abruzzo-Erikson syndrome is characterized by cleft palate, coloboma, hypospadias, deafness, short stature, and radial synostosis. There are also additional s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-linked Recessive
X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes the phenotype to be always expressed in males (who are necessarily homozygous for the gene mutation because they have one X and one Y chromosome) and in females who are homozygous for the gene mutation, see zygosity. Females with one copy of the mutated gene are carriers. X-linked inheritance means that the gene causing the trait or the disorder is located on the X chromosome. Females have two X chromosomes while males have one X and one Y chromosome. Carrier females who have only one copy of the mutation do not usually express the phenotype, although differences in X-chromosome inactivation (known as skewed X-inactivation) can lead to varying degrees of clinical expression in carrier females, since some cells will express one X allele and some will express the other. The current estimate of sequenced X-linked genes is 499, and the total, including vaguely defined trait ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
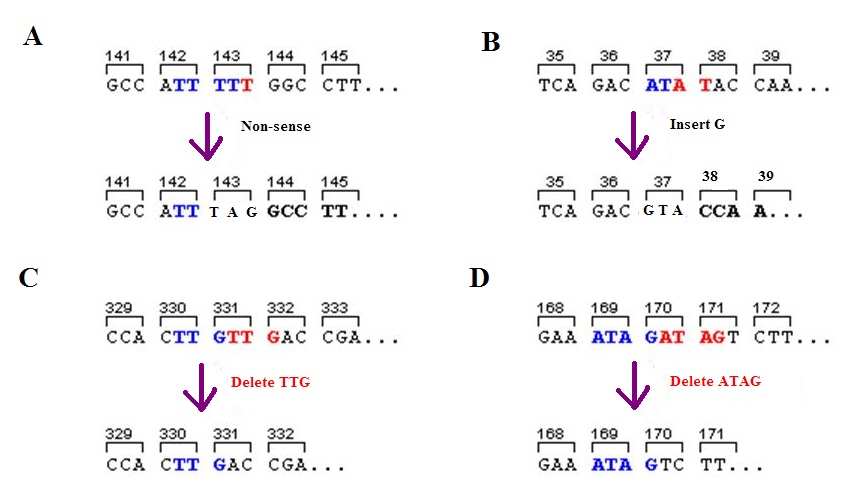
Nonsense Mutation
In genetics, a nonsense mutation is a point mutation in a sequence of DNA that results in a premature stop codon, or a ''nonsense codon'' in the transcribed mRNA, and in leading to a truncated, incomplete, and usually nonfunctional protein product. The functional effect of a nonsense mutation depends on the location of the stop codon within the coding DNA. For example, the effect of a nonsense mutation depends on the proximity of the nonsense mutation to the original stop codon, and the degree to which functional subdomains of the protein are affected. As nonsense mutations leads to premature termination of polypeptide chains; they are also called chain termination mutations. Missense mutations differ from nonsense mutations since they are point mutations that exhibit a single nucleotide change to cause substitution of a different amino acid. A nonsense mutation also differs from a nonstop mutation, which is a point mutation that removes a stop codon. About 10% of patients facin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Disorders With OMIM But No Gene
Genetic may refer to: *Genetics, in biology, the science of genes, heredity, and the variation of organisms **Genetic, used as an adjective, refers to genes ***Genetic disorder, any disorder caused by a genetic mutation, whether inherited or de novo ***Genetic mutation, a change in a gene ****Heredity, genes and their mutations being passed from parents to offspring **Genetic recombination, refers to the recombining of alleles resulting in a new molecule of DNA *Genetic relationship (linguistics), in linguistics, a relationship between two languages with a common ancestor language *Genetic algorithm In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to gene ..., in computer science, a kind of search technique modeled on evolutionary biology See also * Genetic memory (other) {{disam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndromes Affecting Stature
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a syndrome is paired with a definite cause this becomes a disease. In some instances, a syndrome is so closely linked with a pathogenesis or cause that the words ''syndrome'', ''disease'', and ''disorder'' end up being used interchangeably for them. This substitution of terminology often confuses the reality and meaning of medical diagnoses. This is especially true of inherited syndromes. About one third of all phenotypes that are listed in OMIM are described as dysmorphic, which usually refers to the facial gestalt. For example, Down syndrome, Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome, and Andersen–Tawil syndrome are disorders with known pathogeneses, so each is more than just a set of signs and symptoms, despite the ''syndrome'' nomenclature. In other instances, a synd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Craniofacial Surgery
Craniofacial surgery is a surgical subspecialty that deals with congenital and acquired deformities of the head, skull, face, neck, jaws and associated structures. Although craniofacial treatment often involves manipulation of bone, craniofacial surgery is not tissue-specific; craniofacial surgeons deal with bone, skin, nerve, muscle, teeth, and other related anatomy. Defects typically treated by craniofacial surgeons include craniosynostosis (isolated and syndromic), rare craniofacial clefts, acute and chronic sequelae of facial fractures, cleft lip and palate, micrognathia, Treacher Collins Syndrome, Apert's Syndrome, Crouzon's Syndrome, Craniofacial microsomia, microtia and other congenital ear anomalies, and many others.Training in craniofacial surgery requires completion of a Craniofacial surgery fellowship. Such fellowships are available to individuals who have completed residency in oral and maxillofacial surgery, plastic and reconstructive surgery, or ENT surgery . Those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
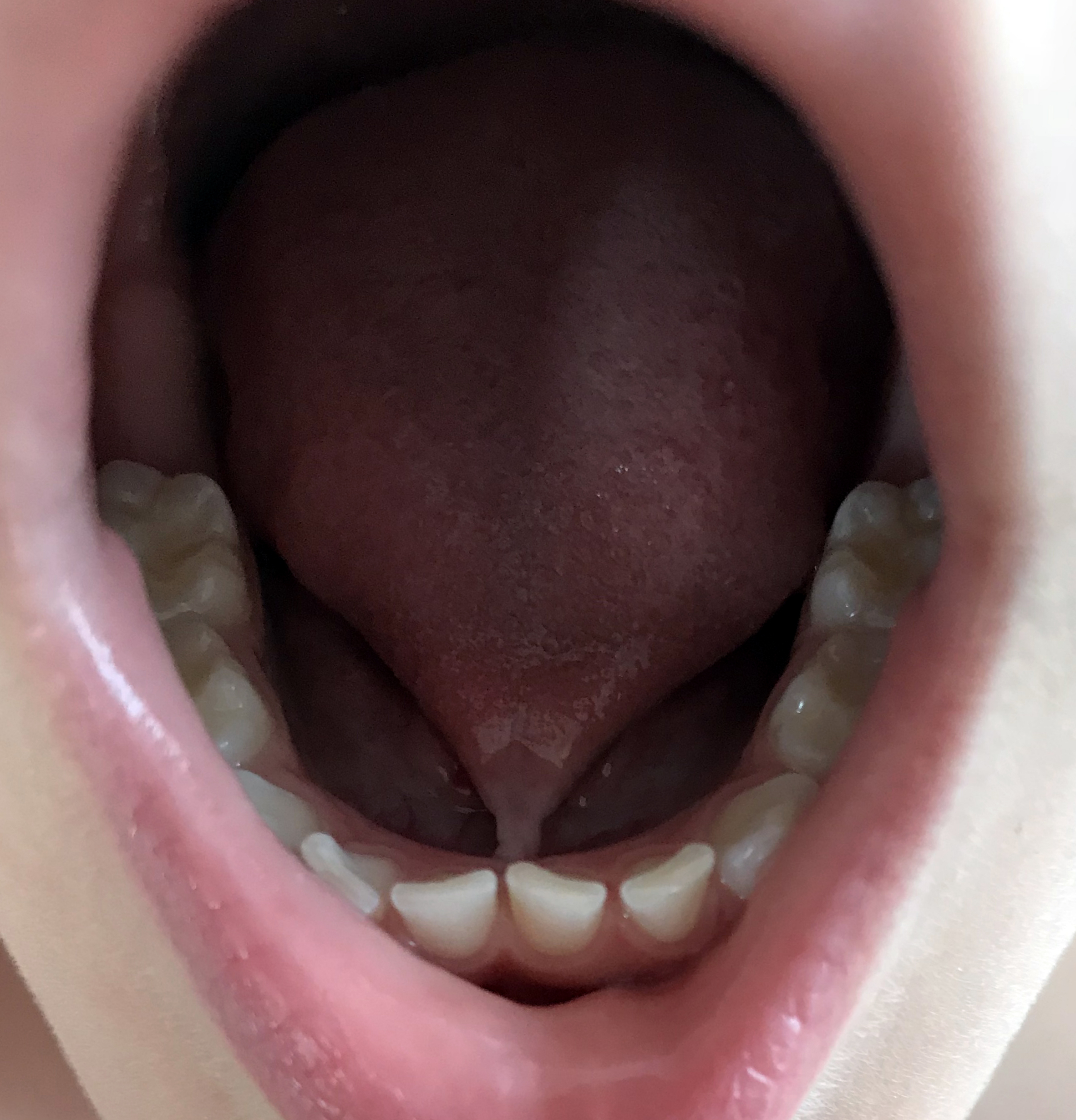
Ankyloglossia
Ankyloglossia, also known as tongue-tie, is a congenital oral anomaly that may decrease the mobility of the tongue tip and is caused by an unusually short, thick lingual frenulum, a membrane connecting the underside of the tongue to the floor of the mouth. Ankyloglossia varies in degree of severity from mild cases characterized by mucous membrane bands to complete ankyloglossia whereby the tongue is tethered to the floor of the mouth. Presentation Ankyloglossia can affect eating, especially breastfeeding, speech and oral hygiene Travis, Lee Edward (1971). Handbook of speech language pathology and audiology. New York, New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts Education Division Meredith Corporation. as well as have mechanical/social effects. Ankyloglossia can also prevent the tongue from contacting the anterior palate. This can then promote an infantile swallow and hamper the progression to an adult-like swallow which can result in an open bite deformity. It can also result in mandibu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missense Mutation
In genetics, a missense mutation is a point mutation in which a single nucleotide change results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid. It is a type of nonsynonymous substitution. Substitution of protein from DNA mutations Missense mutation refers to a change in one amino acid in a protein, arising from a point mutation in a single nucleotide. Missense mutation is a type of nonsynonymous substitution in a DNA sequence. Two other types of nonsynonymous substitution are the nonsense mutations, in which a codon is changed to a premature stop codon that results in truncation of the resulting protein, and the nonstop mutations, in which a stop codon erasement results in a longer, nonfunctional protein. Missense mutations can render the resulting protein nonfunctional, and such mutations are responsible for human diseases such as Epidermolysis bullosa, sickle-cell disease, SOD1 mediated ALS, and a substantial number of cancers. In the most common variant of sickle-cell d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splice Site Mutation
A splice site mutation is a genetic mutation that inserts, deletes or changes a number of nucleotides in the specific site at which splicing takes place during the processing of precursor messenger RNA into mature messenger RNA. Splice site consensus sequences that drive exon recognition are located at the very termini of introns. The deletion of the splicing site results in one or more introns remaining in mature mRNA and may lead to the production of abnormal proteins. When a splice site mutation occurs, the mRNA transcript possesses information from these introns that normally should not be included. Introns are supposed to be removed, while the exons are expressed. The mutation must occur at the specific site at which intron splicing occurs: within non-coding sites in a gene, directly next to the location of the exon. The mutation can be an insertion, deletion, frameshift, etc. The splicing process itself is controlled by the given sequences, known as splice-donor and splic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frameshift Mutation
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels ( insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon ("UAA", "UGA" or "UAG") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deafness
Deafness has varying definitions in cultural and medical contexts. In medical contexts, the meaning of deafness is hearing loss that precludes a person from understanding spoken language, an audiological condition. In this context it is written with a lower case ''d''. It later came to be used in a cultural context to refer to those who primarily communicate through sign language regardless of hearing ability, often capitalized as ''Deaf'' and referred to as "big D Deaf" in speech and sign. The two definitions overlap but are not identical, as hearing loss includes cases that are not severe enough to impact spoken language comprehension, while cultural Deafness includes hearing people who use sign language, such as children of deaf adults. Medical context In a medical context, deafness is defined as a degree of hearing difference such that a person is unable to understand speech, even in the presence of amplification. In profound deafness, even the highest intensity sound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |