|
Abraham Rice
Abraham Joseph Rice (born Abraham Reiss) (c. 18001862) was the first ordained rabbi to serve in a rabbinical position in the United States. Rice was born in 1800 or 1802 at Gochsheim, near Schweinfurt, Lower Franconia. An injury in infancy left him with a limp.Levine He studied at the Würzburg ''yeshivah,'' and was ordained by Rabbi Abraham Bing. He later continued his studies at the ''yeshivah'' of Rabbi Wolf Hamburger in Fürth, and then headed a small ''yeshivah'' in the village of Zell, near Würzburg.Singer In the 1830s he married Rosalie Leucht, and in 1840 they immigrated to the United States. After a brief attempt at reviving the Jewish community in Newport, Rhode Island, he accepted an appointment as the first rabbi of Congregation Nidche Israel in Baltimore. Rice usually delivered his sermons in German, later occasionally in English, and insisted on retaining all the traditional ''piyyutim'' in the prayers. His constant battle against assimilation and lax observa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic (Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew School
Hebrew school is Jewish education focusing on topics of Jewish history, learning the Hebrew language, and finally learning their Torah Portion, in preparation for the ceremony in Judaism of entering adulthood, known as a Bar or Bat Mitzvah. Hebrew School is usually taught in dedicated classrooms at a Synagogue, under the instruction of a Hebrew teacher (who is fluent in Hebrew), and often receives support from the Cantor for learning the ancient chanting of their Torah portion, and from the Rabbi during their ceremony since they must read from a Torah scroll, which has no Hebrew vowels, and very close together texts and minimal line spacing; making it very challenging for almost anyone to read from. The first usage is more common in the United States, while the second is used elsewhere outside Israel, for example, in reference to the in Barranquilla, Colombia, or the Associated Hebrew Schools in Toronto. Background and history According to an article in the '' Jewish Quar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beth Din
A beit din ( he, בית דין, Bet Din, house of judgment, , Ashkenazic: ''beis din'', plural: batei din) is a Rabbinic Judaism, rabbinical court of Judaism. In ancient times, it was the building block of the legal system in the Biblical Land of Israel. Today, it is invested with legal powers in a number of religious matters (''din Torah'', "matter of litigation", plural ''dinei Torah'') both in Israel and in Jewish communities in the Jewish diaspora, Diaspora, where its judgments hold varying degrees of authority (depending upon the jurisdiction and subject matter) in matters specifically related to Jewish religious life. History Rabbinic literature, Rabbinical commentators point out that the first suggestion in the Torah that the ruler divest his legal powers and delegate his power of judgment to lower courts was made by Jethro (Bible), Jethro to Moses (Book of Exodus, Exodus ). This situation was formalised later when God gave the explicit command to "establish judges and off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Occident And American Jewish Advocate
''The Occident and American Jewish Advocate'' or simply ''The Occident'' (1843-1869), was the first general Jewish periodical published in the United States. (The only earlier periodical, Solomon Henry Jackson's '' The Jew'', was published as an anti-missionary journal). Compiled by Rabbi Isaac Leeser Isaac Leeser (December 12, 1806 – February 1, 1868) was an American Orthodox Jewish religious leader, teacher, scholar and publisher. He helped found the Jewish press of America, produced the first Jewish translation of the Bible into English, ... from inception through 1868, in 1869 the publication was edited by Mayer Sulzberger. (Sulzberger, a successful attorney was a disciple of Leeser's in his youth. Leeser hoped Sulzberger would enter the rabbinate, but Sulzberger chose a career in law instead, but pledged to Leeser that he would edit the Occident for a year, which he fulfilled after Leeser's death.) A monthly publication, ''the Occident'' did print weekly from April 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Leeser
Isaac Leeser (December 12, 1806 – February 1, 1868) was an American Orthodox Jewish religious leader, teacher, scholar and publisher. He helped found the Jewish press of America, produced the first Jewish translation of the Bible into English, and helped organize various social and educational organizations. He is considered one of the most important nineteenth century American Jewish personalities. He was "fiercely opposed" to Reform Judaism and was regarded as one of the most important "orthodox" rabbis of his era. Leeser is regarded as a forerunner by both Modern Orthodox Judaism and Conservative Judaism. Early life Isaac Leeser was born to Sarah Leeser and her husband Leffman Leeser in Neuenkirchen/Rheine, Westphalia, but his parents died when he was young. His grandmother encouraged his religious studies under the guidance of the chief rabbi of Münster. Young Leeser was educated at the primary school in nearby Dülmen and then at a gymnasium in Münster. This gave him a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halacha
''Halakha'' (; he, הֲלָכָה, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical commandments (''mitzvot''), subsequent Talmudic and rabbinic laws, and the customs and traditions which were compiled in the many books such as the ''Shulchan Aruch''. ''Halakha'' is often translated as "Jewish law", although a more literal translation of it might be "the way to behave" or "the way of walking". The word is derived from the root which means "to behave" (also "to go" or "to walk"). ''Halakha'' not only guides religious practices and beliefs, it also guides numerous aspects of day-to-day life. Historically, in the Jewish diaspora, ''halakha'' served many Jewish communities as an enforceable avenue of law – both civil and religious, since no differentiation of them exists in classical Judaism. Since the Jewish Enlightenment (''Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The term ''Talmud'' normally refers to the collection of writings named specifically the Babylonian Talmud (), although there is also an earlier collection known as the Jerusalem Talmud (). It may also traditionally be called (), a Hebrew abbreviation of , or the "six orders" of the Mishnah. The Talmud has two components: the Mishnah (, 200 CE), a written compendium of the Oral Torah; and the Gemara (, 500 CE), an elucidation of the Mishnah and related Tannaitic writings that often ventures onto other subjects and expounds broadly on the Hebrew Bible. The term "Talmud" may ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reform Judaism
Reform Judaism, also known as Liberal Judaism or Progressive Judaism, is a major Jewish denomination that emphasizes the evolving nature of Judaism, the superiority of its ethical aspects to its ceremonial ones, and belief in a continuous search for truth and knowledge, which is closely intertwined with human reason and not limited to the theophany at Mount Sinai. A highly liberal strand of Judaism, it is characterized by lessened stress on ritual and personal observance, regarding ''halakha'' (Jewish law) as non-binding and the individual Jew as autonomous, and great openness to external influences and progressive values. The origins of Reform Judaism lie in 19th-century Germany, where Rabbi Abraham Geiger and his associates formulated its early principles. Since the 1970s, the movement has adopted a policy of inclusiveness and acceptance, inviting as many as possible to partake in its communities rather than adhering to strict theoretical clarity. It is strongly identifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Har Sinai Congregation
Har Sinai Congregation ("Mount Sinai Congregation") is a Reform Jewish synagogue located in Owings Mills, Maryland. Originally established in 1842 in Baltimore, it is the oldest congregation in the United States that has used a Reform prayer rite since its inception. Many of the original congregants of Har Sinai Congregation came from what was then the Orthodox Jewish Congregation Nidchei Yisroel (later known as the Baltimore Hebrew Congregation), after Rabbi Abraham Rice protested against the performance of Masonic rites at the funeral service of one of its members. The synagogue was originally known as the Har Sinai Verein (Society). Rabbi David Philipson, in his 1907 work ''The Reform Movement in Judaism'', credited Har Sinai as "the first congregation organized as a reformed congregation" when it was established in 1842. The synagogue adopted the prayer book formulated by the Hamburg Temple, the first reform synagogue in Germany, and services were led by the members. Abram H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
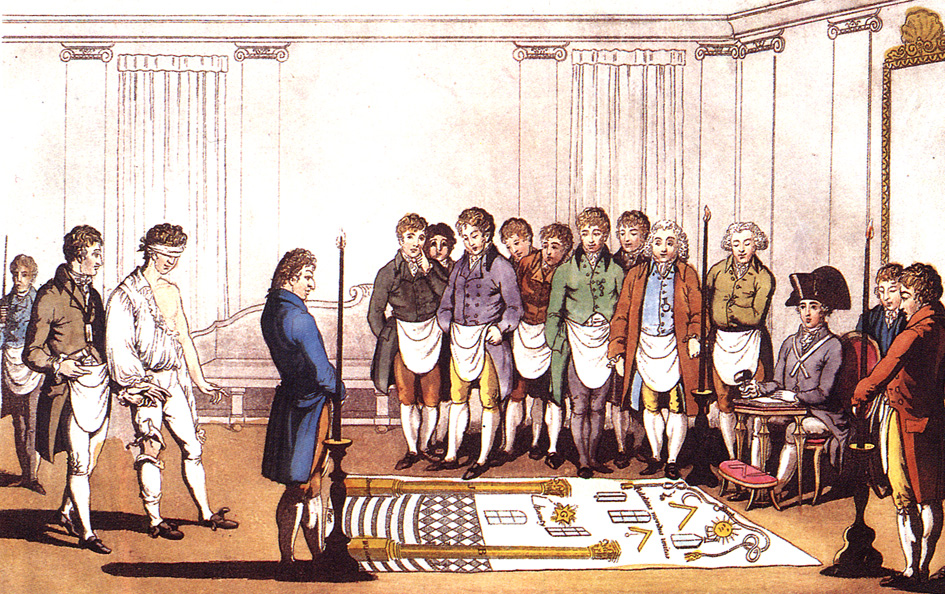
Masonic Ritual And Symbolism
Masonic ritual is the scripted words and actions that are spoken or performed during the degree work in a Masonic lodge. Masonic symbolism is that which is used to illustrate the principles which Freemasonry espouses. Masonic ritual has appeared in a number of contexts within literature including in " The Man Who Would Be King", by Rudyard Kipling, and '' War and Peace'', by Leo Tolstoy. Purpose Freemasonry is described in its own ritual as a "Beautiful and profound system of morality, veiled in allegories and illustrated by symbols". The symbolism of Freemasonry is found throughout the Masonic lodge, and contains many of the working tools of a medieval or renaissance stonemason. The whole system is transmitted to initiates through the medium of Masonic ritual, which consists of lectures and allegorical plays. Common to all of Freemasonry is the three grade system of ''Craft'' or ''Blue Lodge'' freemasonry, whose allegory is centred on the building of the Temple of Solomon, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torah Reading
Torah reading (; ') is a Jewish religious tradition that involves the public reading of a set of passages from a Torah scroll. The term often refers to the entire ceremony of removing the scroll (or scrolls) from the Torah ark, chanting the appropriate excerpt with special cantillation (trope), and returning the scroll(s) to the ark. It is also commonly called "laining" (''lein'' is also spelt ''lain'', ''leyn'', ''layn''; from the Yiddish , which means "to read"). Regular public reading of the Torah was introduced by Ezra the Scribe after the return of the Judean exiles from the Babylonian captivity ( BCE), as described in the Book of Nehemiah. In the modern era, Orthodox Jews practice Torah reading according to a set procedure almost unchanged since the Talmudic era. Since the 19th century CE, Reform and Conservative Judaism have made adaptations to the practice of Torah reading, but the basic pattern of Torah reading has usually remained the same: As a part of the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |