|
Aberpergwm House
Aberpergwm House ( cy, Aberpergwm) is an abandoned and ruinous country house located in Glynneath, Wales. Within the grounds of the house sits the church of St. Cadoc, which is possibly of late medieval origin. Newman, J., ‘The Buildings of Wales: Glamorgan’, Penguin Books/University of Wales Press, 1995, Origins The present house is a remodelling of an older house known as Neuadd Pergwm.Lloyd, T., ‘The Lost Houses of Wales: A Survey of Country Houses in Wales Demolished Since c.1900 The house came into the ownership of the Williamses of Blaen Baglan in around 1560. It is said that Oliver Cromwell was related, and so the house was saved from pillage during the English Civil War. The Williams family were one of the few Welsh gentry families to remain faithful to the Welsh language.Davies, J., Jenkins, N., Baines, M., Lynch, P. I., ‘The Welsh Academy Encyclopaedia of Wales’, University of Wales Press Cardiff, 2008, (hardback), (paperback) Remodelling By 1850, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberpergwm Manor
Aberpergwm is the site of a colliery in the Vale of Neath near Glynneath in south Wales. Mine history The site at Aberpergwm had been worked since 1811 as a series of drift mines, but full commercial working began from the 1860s when W. Williams opened a mine on the site. The mine was consolidated with the nearby Pwllfaron drift mine from 1880 with common ground works, under one owner Morgan Stuart Williams. A new drift was opened in 1906, giving the combined colliery access to the Eighteen Feet, Four-Feet, Nine-Feet, Three-Feet and Cornish seams. In 1920 the colliery was bought by Vale of Neath Collieries Co., which itself was consolidated into Amalgamated Anthracite Collieries Ltd in 1929. After World War 2 the mines were nationalised, and under British Coal in 1950 the various drift mine workings employed 855 working the Eighteen Feet, Nine Feet and Three Feet seams. By 1969 the mines faced severe geological problems. As a result, only the White Four Feet and Cornish seams were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Gallery
In architecture, a long gallery is a long, narrow room, often with a high ceiling. In Britain, long galleries were popular in Elizabethan and Jacobean houses. They were normally placed on the highest reception floor of English country houses, usually running along a side of the house, with windows on one side and at the ends giving views, and doors to other rooms on the other. They served several purposes: they were used for entertaining guests, for taking exercise in the form of walking when the weather was inclement, for displaying art collections, especially portraits of the family and royalty, and acting as a corridor. A long gallery has the appearance of a spacious corridor, but it was designed as a room to be used in its own right, not just as a means of passing from one room to another, though many served as this too. In the 16th century, the seemingly obvious concept of the corridor had not been introduced to British domestic architecture; rooms were entered from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evacuations Of Civilians In Britain During World War II
The evacuation of civilians in Britain during the Second World War was designed to protect people, especially children, from the risks associated with aerial bombing of cities by moving them to areas thought to be less at risk. Under the name "Operation Pied Piper", the effort began on 1 September 1939 and officially relocated 1.5 million people. There were further waves of official evacuation and re-evacuation from the south and east coasts in June 1940, when a seaborne invasion was expected, and from affected cities after the Blitz began in September 1940. Official evacuations also took place from the UK to other parts of the British Empire, and many non-official evacuations within and from the UK. Other mass movements of civilians included British citizens arriving from the Channel Islands, and displaced people arriving from continental Europe. Background The Government Evacuation Scheme was developed during the summer of 1938 by the Anderson Committee and implemente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorleston
Gorleston-on-Sea (), known colloquially as Gorleston, is a town in the Borough of Great Yarmouth, in Norfolk, England, to the south of Great Yarmouth. Situated at the mouth of the River Yare it was a port town at the time of the Domesday Book. The port then became a centre of fishing for herring along with salt pans used for the production of salt to preserve the fish. In Edwardian times the fishing industry rapidly declined and the town's role changed to that of a seaside resort. History The place-name 'Gorleston' is first attested in the Domesday Book of 1086, where it appears as ''Gorlestuna''. It appears as ''Gurlestona'' in the Pipe Rolls of 1130. The first element may be related to the word 'girl', and is probably a personal name. The name could mean "girls' town or settlement", or a variant thereof, similar to Girlington in West Yorkshire. Historically the town was in the county of Suffolk. In the Middle Ages it had two manors, and a small manor called Bacons. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DV271 Old John, Servant At Aberpergwm
DV refers to a family of codecs and videotape, tape formats used for storing digital video, launched in 1995 by a consortium of camcorder, video camera manufacturers led by Sony and Panasonic. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, DV was strongly associated with the transition from analog video, analog to digital desktop video production, and also with several enduring "prosumer" camera designs such as the Sony DCR-VX1000, Sony VX-1000. DV is sometimes referred to as #Magnetic tape, MiniDV, which was the most popular tape format using a DV codec during this time. In 2003, DV was joined by a successor format called HDV, which used the same tapes but with an updated video codec; HDV cameras could typically switch between DV and HDV recording modes. In the 2010s, DV rapidly grew obsolete as cameras using memory cards and solid-state drives became the norm, recording at higher bit rate, bitrates and image resolution, resolutions that were impractical for mechanical tape formats. Additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
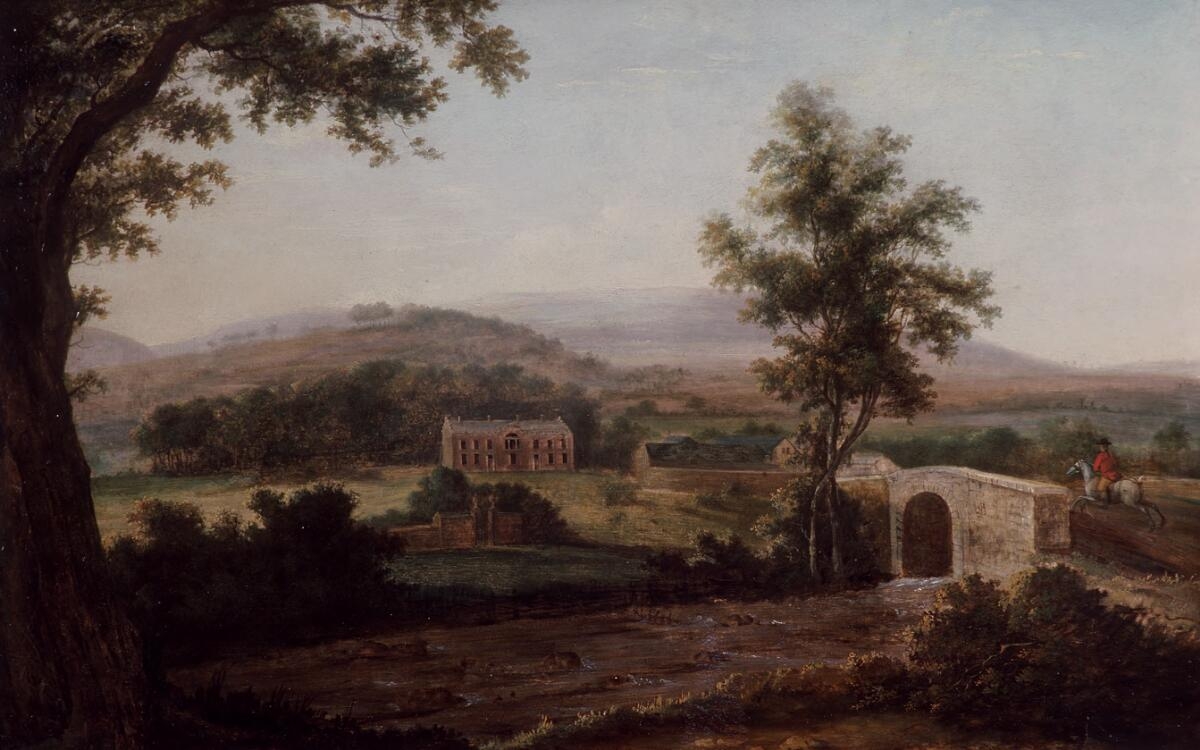
.jpg)


