|
Abdallah Al-Ghalib II
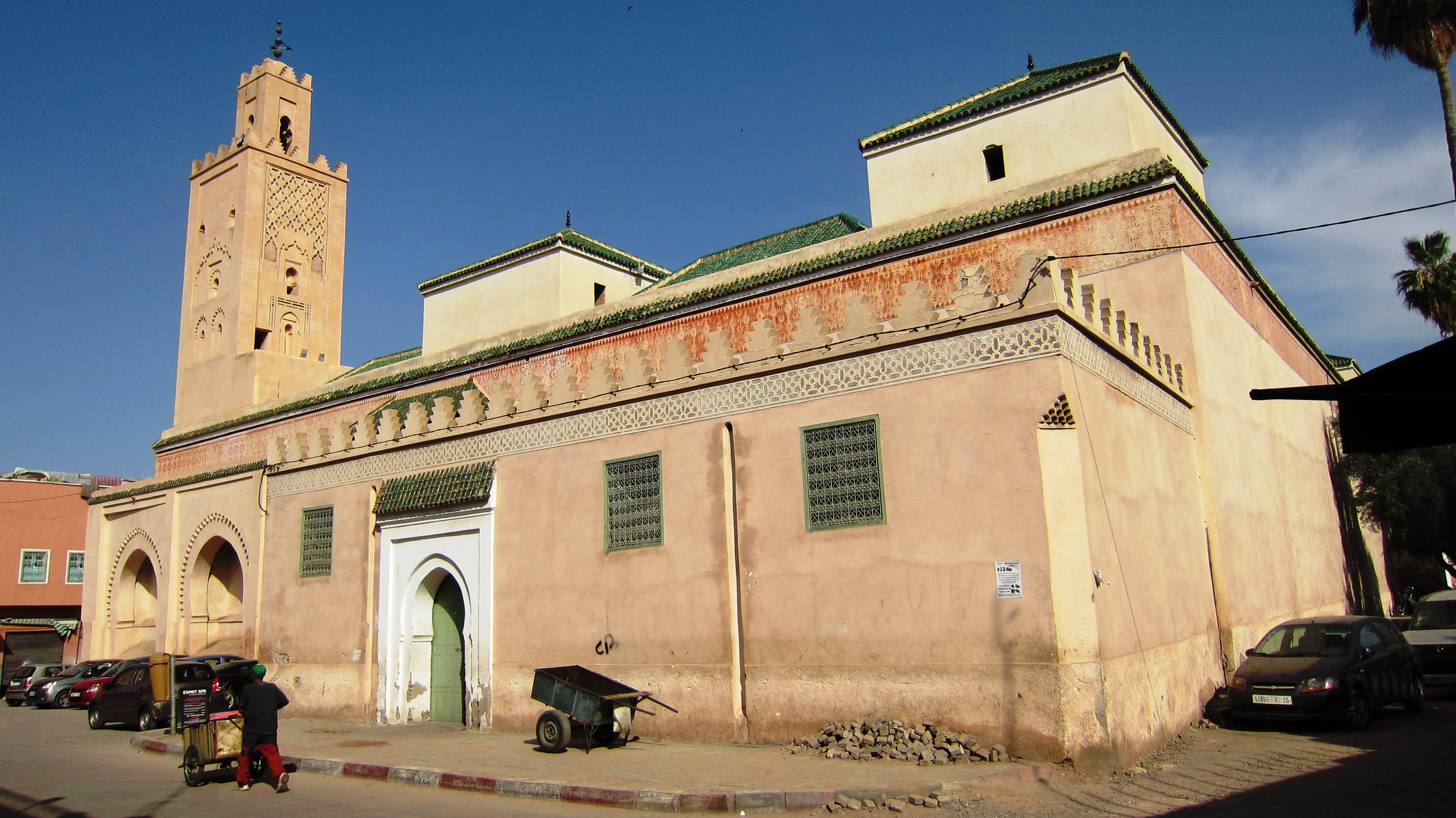
Abdallah al-Ghalib II was a member of the Saadian dynasty who ruled parts of Morocco during the succession conflicts within the dynasty between 1603 and 1627. He was the son of Muhammad al-Sheikh al-Ma'mun, who was in turn the son of the powerful sultan Ahmad al-Mansur. Life During this period, the Saadian realm was divided between two main parts: one ruled from the main capital in Marrakesh, and the other from Fes in the north. Control of both regions changed hands multiple times. Abdallah ruled from Marrakesh between 1606 and 1609. In 1609 he successfully ordered the assassination of his uncle Abu Faris Abdallah al-Wathiq, who was established in Fes at the time. After 1609 he then ruled in Fes (as his father had previously done) until his death in 1623, while Zaydan al-Nasir ruled in Marrakesh. During his period of leadership in Fes, in 1609, he commissioned the construction of a second ablutions pavilion in the courtyard (''sahn'') of the famous Qarawiyyin Mosque T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saadi Dynasty
The Saadi Sultanate (also rendered in English as Sa'di, Sa'did, Sa'dian, or Saadian; ar, ž¦┘äž│ž╣ž»┘Ŗ┘ł┘å, translit=as-sa╩┐diyy┼½n) was a state which ruled present-day Morocco and parts of West Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was led by the Saadi dynasty, an Arabs, Arab Moroccan Sharifism, Sharifian dynasty. The dynasty's rise to power started in 1510 when Abu Abdallah al-Qaim, Muhammad al-Qa'im was declared leader of the tribes of the Sous valley in their resistance against the Portugal, Portuguese who occupied Agadir and other coastal cities. Al-Qai'm's son, Ahmad al-Araj, secured control of Marrakesh by 1525 and, after a period of rivalry, his brother Mohammed ash-Sheikh, Muhammad al-Shaykh captured Agadir from the Portuguese and eventually captured Fez, Morocco, Fez from the Wattasid dynasty, Wattasids, securing control over nearly all of Morocco. After Muhammad al-Shaykh's assassination by the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in 1557 his son Abdallah al-Ghalib enjoyed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saadi Sultanate
The Saadi Sultanate (also rendered in English as Sa'di, Sa'did, Sa'dian, or Saadian; ar, ž¦┘äž│ž╣ž»┘Ŗ┘ł┘å, translit=as-sa╩┐diyy┼½n) was a state which ruled present-day Morocco and parts of West Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was led by the Saadi dynasty, an Arabs, Arab Moroccan Sharifism, Sharifian dynasty. The dynasty's rise to power started in 1510 when Abu Abdallah al-Qaim, Muhammad al-Qa'im was declared leader of the tribes of the Sous valley in their resistance against the Portugal, Portuguese who occupied Agadir and other coastal cities. Al-Qai'm's son, Ahmad al-Araj, secured control of Marrakesh by 1525 and, after a period of rivalry, his brother Mohammed ash-Sheikh, Muhammad al-Shaykh captured Agadir from the Portuguese and eventually captured Fez, Morocco, Fez from the Wattasid dynasty, Wattasids, securing control over nearly all of Morocco. After Muhammad al-Shaykh's assassination by the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in 1557 his son Abdallah al-Ghalib enjoyed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultans Of Morocco
Sultan (; ar, ž│┘äžĘž¦┘å ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who claimed almost full sovereignty (i.e., not having dependence on any higher ruler) without claiming the overall caliphate, or to refer to a powerful governor of a province within the caliphate. The adjectival form of the word is "sultanic", and the state and territories ruled by a sultan, as well as his office, are referred to as a sultanate ( '. The term is distinct from king ( '), despite both referring to a sovereign ruler. The use of "sultan" is restricted to Muslim countries, where the title carries religious significance, contrasting the more secular ''king'', which is used in both Muslim and non-Muslim countries. Brunei and Oman are the only independent countries which retain the tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1623 Deaths
Sixteen or 16 may refer to: *16 (number), the natural number following 15 and preceding 17 *one of the years 16 BC, AD 16, 1916, 2016 Films * '' Pathinaaru'' or ''Sixteen'', a 2010 Tamil film * ''Sixteen'' (1943 film), a 1943 Argentine film directed by Carlos Hugo Christensen * ''Sixteen'' (2013 Indian film), a 2013 Hindi film * ''Sixteen'' (2013 British film), a 2013 British film by director Rob Brown Music *The Sixteen, an English choir *16 (band), a sludge metal band * Sixteen (Polish band), a Polish band Albums * ''16'' (Robin album), a 2014 album by Robin * 16 (Madhouse album), a 1987 album by Madhouse * ''Sixteen'' (album), a 1983 album by Stacy Lattisaw *''Sixteen'' , a 2005 album by Shook Ones * ''16'', a 2020 album by Wejdene Songs * "16" (Sneaky Sound System song), 2009 * "Sixteen" (Thomas Rhett song), 2017 * "Sixteen" (Ellie Goulding song), 2019 *"16", by Craig David from ''Following My Intuition'', 2016 *"16", by Green Day from ''39/Smooth'', 1990 *"16", by H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Al-Qarawiyyin
The University of al-Qarawiyyin ( ar, ž¼ž¦┘ģž╣ž® ž¦┘ä┘éž▒┘ł┘Ŗ┘Ŗ┘å; ber, ŌĄ£Ō┤░ŌĄÖŌ┤ĘŌ┤░ŌĄĪŌĄēŌĄ£ ŌĄÅ ŌĄŹŌĄćŌ┤░ŌĄĢŌ┤░ŌĄĪŌĄēŌĄóŌĄēŌĄÅ; french: Universit├® Al Quaraouiyine), also written Al-Karaouine or Al Quaraouiyine, is a university located in Fez, Morocco. It was founded as a mosque by Fatima al-Fihri in 857ŌĆō859 and subsequently became one of the leading spiritual and educational centers of the Islamic Golden Age. It was incorporated into Morocco's modern state university system in 1963 and officially renamed "University of Al Quaraouiyine" two years later. The mosque building itself is also a significant complex of historical Moroccan and Islamic architecture that features elements from many different periods of Moroccan history. Scholars consider al-Qarawiyyin to have been effectively run as a madrasa until after World War II.Lulat, Y. G.-M.: ''A History Of African Higher Education From Antiquity To The Present: A Critical Synthesis Studies in Higher Education'', Greenwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahn
A ''sahn'' ( ar, žĄ┘ÄžŁ┘Æ┘å, '), is a courtyard in Islamic architecture, especially the formal courtyard of a mosque. Most traditional mosques have a large central ''sahn'', which is surrounded by a ''Riwaq (arcade), riwaq'' or arcade (architecture), arcade on all sides. In traditional Islamic design, residences and neighborhoods can have private ''sahn'' courtyards. The ''sahn'' is a common element in religious buildings and residences throughout the Muslim world, used in urban and rural settings. The cloister is its equivalent in European medieval architecture and its religious buildings. Etymology The word Sahn (žĄ┘ÄžŁ┘Æ┘å) means a courtyard in Arabic. History Originally, the ''sahn'' was used for dwellings, as a secure and private setting within a residence compound's walls. Ruins of houses in Sumerian Ur with have been found, from the Third Dynasty of Ur (2100ŌĆō2000 BCE). Most mosque courtyards (sahn) contained a public fountain where Muslims performed Wudu a ritual pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wudu
WußĖŹ┼½╩Š ( ar, ž¦┘ä┘łžČ┘łžĪ ' ) is the Islamic procedure for cleansing parts of the body, a type of ritual purification, or ablution. The 4 Fardh (Mandatory) acts of ''Wudu'' consists of washing the face, arms, then wiping the head and the feet with water. Wudu is an important part of ritual purity in Islam. It is governed by ''fiqh'' (Islamic jurisprudence), which specifies rules concerning hygiene and defines the rituals that constitute it. It is typically performed before prayers ('' salah or salat''). Activities that invalidate ''wudu'' include urination, defecation, flatulence, deep sleep, light bleeding, menstruation, postpartum and sexual intercourse. ''Wudu'' is often translated as 'partial ablution', as opposed to '' ghusl'' as 'full ablution' where the whole body is washed. It also contrasts with ''tayammum'' ('dry ablution'), which uses sand or dust in place of water, principally due to water scarcity or other harmful effects on the person. Purification of the bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmad Al-Mansur
Ahmad al-Mansur ( ar, žŻž©┘ł ž¦┘äž╣ž©ž¦ž│ žŻžŁ┘ģž» ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘åžĄ┘łž▒, Ahmad Abu al-Abbas al-Mansur, also al-Mansur al-Dahabbi (the Golden), ar, žŻžŁ┘ģž» ž¦┘ä┘ģ┘åžĄ┘łž▒ ž¦┘äž░┘ćž©┘Ŗ; and Ahmed al-Mansour; 1549 in Fes ŌĆō 25 August 1603, Fes) was the Saadi Sultan of Morocco from 1578 to his death in 1603, the sixth and most famous of all rulers of the Saadis. Ahmad al-Mansur was an important figure in both Europe and Africa in the sixteenth century. His powerful army and strategic location made him an important power player in the late Renaissance period. He has been described as "a man of profound Islamic learning, a lover of books, calligraphy and mathematics, as well as a connoisseur of mystical texts and a lover of scholarly discussions." Early life Ahmad was the fifth son of Mohammed ash-Sheikh who was the first Saadi sultan of Morocco. His mother was Lalla Masuda. After the murder of their father, Mohammed in 1557 and the following struggle for power, the two brothers Ahmad a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultan
Sultan (; ar, ž│┘äžĘž¦┘å ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who claimed almost full sovereignty (i.e., not having dependence on any higher ruler) without claiming the overall caliphate, or to refer to a powerful governor of a province within the caliphate. The adjectival form of the word is "sultanic", and the state and territories ruled by a sultan, as well as his office, are referred to as a sultanate ( '. The term is distinct from king ( '), despite both referring to a sovereign ruler. The use of "sultan" is restricted to Muslim countries, where the title carries religious significance, contrasting the more secular ''king'', which is used in both Muslim and non-Muslim countries. Brunei and Oman are the only independent countries which retain the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saadian Dynasty
The Saadi Sultanate (also rendered in English as Sa'di, Sa'did, Sa'dian, or Saadian; ar, ž¦┘äž│ž╣ž»┘Ŗ┘ł┘å, translit=as-sa╩┐diyy┼½n) was a state which ruled present-day Morocco and parts of West Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was led by the Saadi dynasty, an Arabs, Arab Moroccan Sharifism, Sharifian dynasty. The dynasty's rise to power started in 1510 when Abu Abdallah al-Qaim, Muhammad al-Qa'im was declared leader of the tribes of the Sous valley in their resistance against the Portugal, Portuguese who occupied Agadir and other coastal cities. Al-Qai'm's son, Ahmad al-Araj, secured control of Marrakesh by 1525 and, after a period of rivalry, his brother Mohammed ash-Sheikh, Muhammad al-Shaykh captured Agadir from the Portuguese and eventually captured Fez, Morocco, Fez from the Wattasid dynasty, Wattasids, securing control over nearly all of Morocco. After Muhammad al-Shaykh's assassination by the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in 1557 his son Abdallah al-Ghalib enjoyed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saadi Dynasty
The Saadi Sultanate (also rendered in English as Sa'di, Sa'did, Sa'dian, or Saadian; ar, ž¦┘äž│ž╣ž»┘Ŗ┘ł┘å, translit=as-sa╩┐diyy┼½n) was a state which ruled present-day Morocco and parts of West Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was led by the Saadi dynasty, an Arabs, Arab Moroccan Sharifism, Sharifian dynasty. The dynasty's rise to power started in 1510 when Abu Abdallah al-Qaim, Muhammad al-Qa'im was declared leader of the tribes of the Sous valley in their resistance against the Portugal, Portuguese who occupied Agadir and other coastal cities. Al-Qai'm's son, Ahmad al-Araj, secured control of Marrakesh by 1525 and, after a period of rivalry, his brother Mohammed ash-Sheikh, Muhammad al-Shaykh captured Agadir from the Portuguese and eventually captured Fez, Morocco, Fez from the Wattasid dynasty, Wattasids, securing control over nearly all of Morocco. After Muhammad al-Shaykh's assassination by the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in 1557 his son Abdallah al-Ghalib enjoyed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
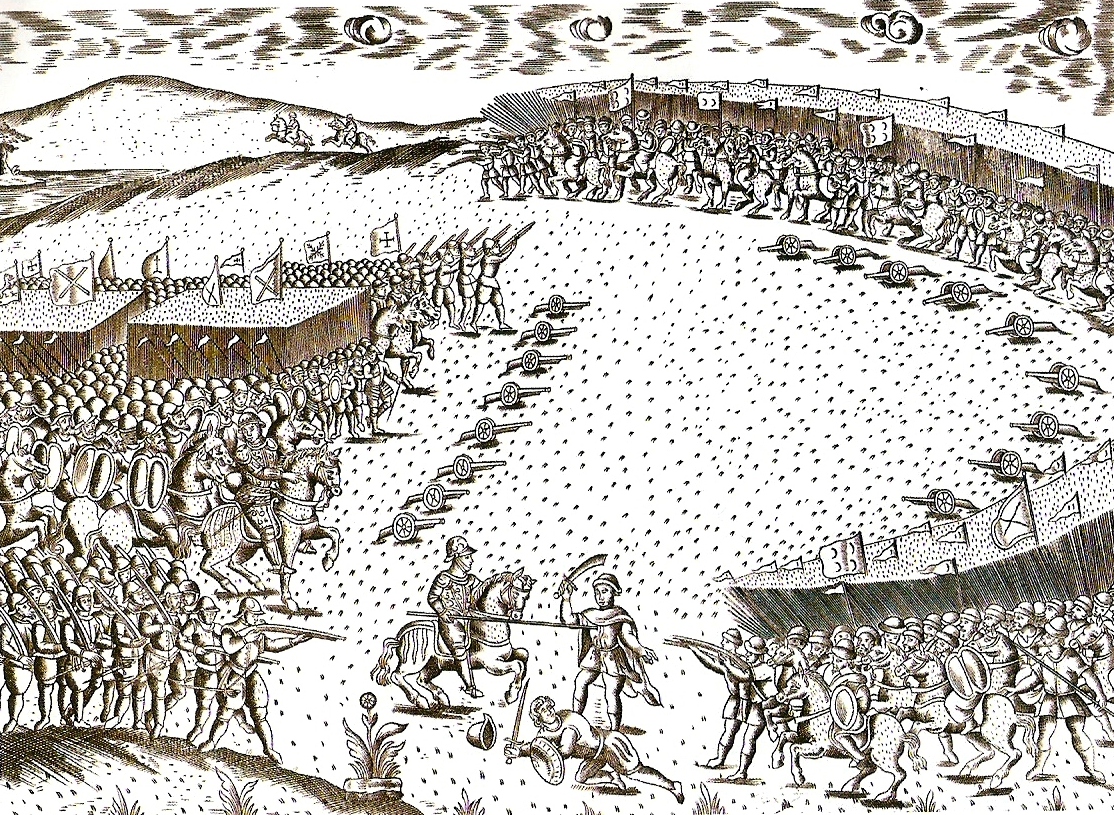
Zidan Abu Maali
Zidan Abu Maali ( ar, ž▓┘Ŗž»ž¦┘å žŻž©┘ł ┘ģž╣ž¦┘ä┘Ŗ) (? ŌĆō September 1627; or Muley Zidan) was the embattled Saadi Sultan of Morocco from 1603 to 1627. He was the son and heir of Ahmad al-Mansur by his wife Lalla Aisha bint Abu Bakkar, a lady of the Chebanate tribe. He ruled only over the southern half of the country after his brother Mohammed esh Sheikh el Mamun took the northern half and a rebel from Tafilalt, Ahmed ibn Abi Mahalli, marched on Marrakesh claiming to be the Mahdi. This led Muley Zidan to be encircled in Safi amid other failed military campaigns against the rebellious north. These events were exacerbated by a context of chaos that ensued amid a plague pandemic which left a third of the country dead. His reign saw the end of the Anglo-Spanish war (with the 1604 Treaty of London)ŌĆöwhich broke the Anglo-Dutch axis that Morocco was relying upon as a means of protection from Spain, and so caused the Spanish navy to resume devastating raids on the Moroccan coastŌĆ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(qarawiyyin_crop).jpg)


.jpg)