|
Aaron Ben Jacob Of Karlin
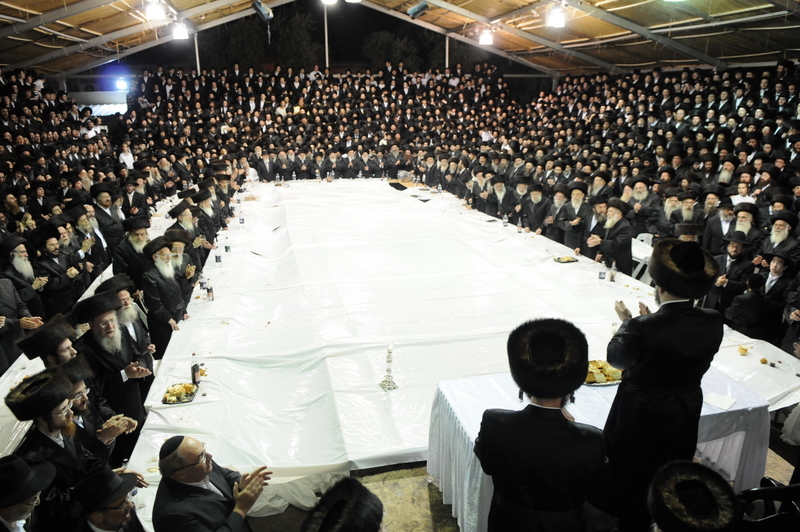
Aaron ben Jacob Perlov of Karlin (1736 – 1772), known among the Ḥasidim as Rabbi Aaron the Great, or simply as the "Preacher" or "Censor", was one of the early rabbis of the sect who helped the rapid spread of Ḥasidism in Eastern Europe, and was distinguished for the fiery eloquence of his exhortations. He died one year before his master, Rabbi Dov Ber of Mezeritch, and was succeeded by his disciple, Rabbi Shlomo of Karlin. Rabbi Shlomo was in turn succeeded by Rabbi Aharon's son, Asher. Perlov composed and wrote the famous Sabbath hymn ''Yah Ekhsof'' (יה_אכסוף) which is still a part of the liturgy of the Ḥasidim. His ethical will and some collectanea are printed in the work of his grandson, Aaron ben Asher of Karlin. See also * Karlin (Pinsk) * Karlin-Stolin (Hasidic dynasty) Karlin-Stolin is a Hasidic dynasty, originating with Rebbe Aaron ben Jacob of Karlin in present-day Belarus. One of the first centres of Hasidim to be set up in Lithuania, many Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karlin-Stolin (Hasidic Dynasty)
Karlin-Stolin is a Hasidic dynasty, originating with Rebbe Aaron ben Jacob of Karlin in present-day Belarus. One of the first centres of Hasidim to be set up in Lithuania, many Lithuanian Hasidic groups are its offshoots. Today, the Karlin-Stolin dynasty is thriving once again, after being decimated by the Holocaust. Karlin-Stolin Hasidim can be found all over the world: Israel, the United States, Russia, England, Mexico, and Ukraine. The Karliner Hasidim are especially known for their custom to cry out in a strong and loud voice to God when praying. They are also known for their hospitality. Karlin-Stolin Hasidim established themselves in Eretz Yisrael in the mid-19th century, settling in Tiberias, Hebron, and Safed. In 1869, they redeemed the site of a former synagogue in Tiberias which had been built in 1786 by Rabbi Menachem Mendel of Vitebsk, but was destroyed in the Galilee earthquake of 1837. Construction of the new synagogue started in 1870, and was made possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasidic Judaism
Hasidism, sometimes spelled Chassidism, and also known as Hasidic Judaism (Ashkenazi Hebrew: חסידות ''Ḥăsīdus'', ; originally, "piety"), is a Judaism, Jewish religious group that arose as a spiritual revival movement in the territory of contemporary Western Ukraine during the 18th century, and spread rapidly throughout Eastern Europe. Today, most affiliates reside in Israel and the United States. Israel Ben Eliezer, the "Baal Shem Tov", is regarded as its founding father, and his disciples developed and disseminated it. Present-day Hasidism is a sub-group within Haredi Judaism and is noted for its religious conservatism and social seclusion. Its members adhere closely both to Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox Jewish practice – with the movement's own unique emphases – and the traditions of Eastern European Jews. Many of the latter, including various special styles of dress and the use of the Yiddish language, are nowadays associated almost exclusively with Hasidism. Hasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbi
A rabbi () is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi – known as ''semikha'' – following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of the rabbi developed in the Pharisees, Pharisaic (167 BCE–73 CE) and Talmudic (70–640 CE) eras, when learned teachers assembled to codify Judaism's written and oral laws. The title "rabbi" was first used in the first century CE. In more recent centuries, the duties of a rabbi became increasingly influenced by the duties of the Clergy, Protestant Christian minister, hence the title "pulpit rabbis", and in 19th-century Germany and the United States rabbinic activities including sermons, pastoral counseling, and representing the community to the outside, all increased in importance. Within the various Jewish denominations, there are different requirements for rabbinic ordination, and differences in opinion regarding who is recognized as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dov Ber Of Mezeritch
Dov Ber ben Avraham of Mezeritch ( yi, דֹּב בֶּער מִמֶּזְרִיטְשְׁ; died December 1772 OS), also known as the '' Maggid of Mezeritch'', was a disciple of Rabbi Israel ben Eliezer (the Baal Shem Tov), the founder of Hasidic Judaism, and was chosen as his successor to lead the early movement. Dov Ber is regarded as the first systematic exponent of the mystical philosophy underlying the teachings of the Baal Shem Tov, and through his teaching and leadership, the main architect of the movement.see Kaufmann Kohler & Louis Ginzberg"Baer (Dov) of Meseritz" ''Jewish Encyclopedia'', retrieved May 20, 2006 He established his base in Mezhirichi (in Volhynia), which moved the centre of Hasidism from Medzhybizh (in Podolia), where he focused his attention on raising a close circle of disciples to spread the movement. After his death the third generation of leadership took their different interpretations and disseminated across appointed regions of Eastern Europe, rapid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yah Ekhsof
Yah may refer to: * Jah, shortened form of Yahweh, the Hebrew name for God * YAH, The IATA code for La Grande-4 Airport in northern Quebec, Canada * Yazgulyam language The Yazgulyam language (also Yazgulami, Yazgulyami, Iazgulem, Yazgulam, Yazgulyamskiy, Jazguljamskij, Qzgulqmski tg, yazgulomi) is a member of the Southeastern subgroup of the Iranian languages, spoken by around 9,000 people along the Yazgulya ..., by ISO 639 code * "Yah" (song), by Kendrick Lamar from his album ''Damn'' * a young person from a particular class or subcultural group in the UK, also known as a ' rah' See also * IAH (other) * YA (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethical Will
An ethical will (Hebrew: ) is a document that passes ethical values from one generation to the next. Rabbis and Jewish laypeople have continued to write ethical wills during the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. (Riemer) In recent years, the practice has been more widely used by the general public. In ''BusinessWeek'' magazine and in an American Bar Association electronic newsletter it is described as an aid to estate planning; (Murphy; Friedman) in health care and hospice (Baines; Freed) and as a spiritual healing tool. (Weil; Freed). Origins The ethical will is an ancient document from the Jewish tradition. The original template for its use came from Genesis . A dying Jacob gathered his sons to offer them his blessing and to request that they bury him not in Egypt, but instead in Canaan in the cave at Machpelah with his ancestors. Other biblical examples of ethical wills include Deuteronomy where Moses instructs the Israelites to be a holy people and teach their children ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aharon Of Karlin (II)
Aaron Ben Asher of Karlin (June 6, 1802 – June 23, 1872), known as Rabbi Aaron II of Karlin, was a famous rabbi of the Ḥasidim in northwestern Russia. Thousands of followers used to visit him annually, about the time of the Jewish New Year, as is the custom among that sect, and he was highly esteemed by his adherents. He "reigned" in Karlin, near Pinsk, in the government of Minsk (currently in Belarus), in succession to his father and his grandfather, Aaron ben Jacob. A few years before his death, he quarreled with a family of Karlin and moved from there to Stolin, a town several miles distant. Considering the amount of business that the yearly influx of strangers brought to the city where he resided, his removal was regarded as a misfortune for Karlin. He died, aged seventy years and seventeen days, in Malinov (also spelled Mlinov and Mlynov), near Dubno, in Volhynia, while on a journey to the wedding of his granddaughter, and was succeeded by his son, Asher of Stolin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karlin (Pinsk)
Karlin or Karalin ( be, Каралін; russian: Карлин; yi, קארלין) is a village outside Pinsk, Belarus. It was founded as an independent town in 1690 and was named after the village's founder, Jan Karol Dolski. By 1695, Dolski had built a church (now a concert hall) and a fortified manor on the spot. He also allowed Jews to settle in the area, where it became the seat of a Hasidic dynasty. Overview The Wiśniowiecki family took control of the village and extended the castle. In 1706, however, the village was captured by the Swedish forces and burnt. Following the destruction of Pinsk, many locals moved to the partially restored village, which with time became a notable suburb. In 1786, a new church of the Bernardines was built there (currently an Orthodox church devoted to St. Barbara). In the second partition of Poland in 1793, Karlin was part of the region ceded to Russia. In 1799, the Russian authorities incorporated Karlin into Pinsk. Notable people from Karli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1736 Births
Events January–March * January 12 – George Hamilton, 1st Earl of Orkney, becomes the first Field Marshal of Great Britain. * January 23 – The Civil Code of 1734 is passed in Sweden. * January 26 – Stanislaus I of Poland abdicates his throne. * February 12 – Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor marries Maria Theresa of Austria, ruler of the Habsburg Empire. * March 8 – Nader Shah, founder of the Afsharid dynasty, is crowned Shah of Iran on a date selected by court astrologers. * March 31 – Bellevue Hospital is founded in New York. April–June * April 14 – The Porteous Riots erupt in Edinburgh (Scotland), after the execution of smuggler Andrew Wilson, when town guard Captain John Porteous orders his men to fire at the crowd. Porteous is arrested later. * April 14 – German adventurer Theodor Stephan Freiherr von Neuhoff is crowned King Theodore of Corsica, 25 days after his arrival on Corsica on March 20. His reign ends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1772 Deaths
Year 177 ( CLXXVII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Commodus and Plautius (or, less frequently, year 930 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 177 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Lucius Aurelius Commodus Caesar (age 15) and Marcus Peducaeus Plautius Quintillus become Roman Consuls. * Commodus is given the title ''Augustus'', and is made co-emperor, with the same status as his father, Marcus Aurelius. * A systematic persecution of Christians begins in Rome; the followers take refuge in the catacombs. * The churches in southern Gaul are destroyed after a crowd accuses the local Christians of practicing cannibalism. * Forty-seven Christians are martyred in Lyon (Saint Blandina and Pothinus, bish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century Polish–Lithuanian Rabbis
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebbes Of Karlin–Stolin
A Rebbe ( yi, רבי, translit=rebe) or Admor ( he, אדמו״ר) is the spiritual leader in the Hasidic movement, and the personalities of its dynasties.Heilman, Samuel"The Rebbe and the Resurgence of Orthodox Judaism."''Religion and Spirituality (Audio)''. UCTV, 20 Oct 2011. web. 31 Jul 2013. The titles of Rebbe and Admor, which used to be a general honor title even before the beginning of the movement, became, over time, almost exclusively identified with its Tzaddikim. Terminology and origin Usage Today, ''rebbe'' is used in the following ways: # Rabbi, a teacher of Torah – Yeshiva students or ''cheder'' (elementary school) students, when talking to their teacher, would address him with the honorific ''Rebbe'', as the Yiddish-German equivalent to the Hebrew word ''rabbi'' ( ' ). # Personal mentor and teacher—A person's main Rosh Yeshiva, Yeshiva teacher, or mentor, who teaches him or her Talmud and Torah and gives religious guidance, is referred to as ''rebbe'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |