|
A Study Of History
''A Study of History'' is a 12-volume universal history by the British historian Arnold J. Toynbee, published from 1934 to 1961. It received enormous popular attention but according to historian Richard J. Evans, "enjoyed only a brief vogue before disappearing into the obscurity in which it has languished." Toynbee's goal was to trace the development and decay of 19 or 21 world civilizations in the historical record, applying his model to each of these civilizations, detailing the stages through which they all pass: genesis, growth, time of troubles, universal state, and disintegration. The 19 (or 21) major civilizations, as Toynbee sees them, are: Egyptian, Andean, Sumerian, Babylonic, Hittite, Minoan, Indic, Hindu, Syriac, Hellenic, Western, Orthodox Christian (having two branches: the main or Byzantine body and the Russian branch), Far Eastern (having two branches: the main or Chinese-Korean body and the Japanese branch), Islamic (having two branches which later merged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold J
Arnold may refer to: People * Arnold (given name), a masculine given name * Arnold (surname), a German and English surname Places Australia * Arnold, Victoria, a small town in the Australian state of Victoria Canada * Arnold, Nova Scotia United Kingdom * Arnold, East Riding of Yorkshire * Arnold, Nottinghamshire United States * Arnold, California, in Calaveras County * Arnold, Carroll County, Illinois * Arnold, Morgan County, Illinois * Arnold, Iowa * Arnold, Kansas * Arnold, Maryland * Arnold, Mendocino County, California * Arnold, Michigan * Arnold, Minnesota * Arnold, Missouri * Arnold, Nebraska * Arnold, Ohio * Arnold, Pennsylvania * Arnold, Texas * Arnold, Brooke County, West Virginia * Arnold, Lewis County, West Virginia * Arnold, Wisconsin * Arnold Arboretum of Harvard University, Massachusetts * Arnold Township, Custer County, Nebraska Other uses * Arnold (automobile), a short-lived English car * Arnold of Manchester, a former English coachbuilder * Arnold (band), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in common, including language relatedness, cultural practices, and traditional beliefs. In centuries past, they had a strong shared tradition of sailing and using stars to navigate at night. The largest country in Polynesia is New Zealand. The term was first used in 1756 by the French writer Charles de Brosses, who originally applied it to all the islands of the Pacific. In 1831, Jules Dumont d'Urville proposed a narrower definition during a lecture at the Geographical Society of Paris. By tradition, the islands located in the southern Pacific have also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also refer more narrowly to the Scandinavian Peninsula (which excludes Denmark but includes part of Finland), or more broadly to include all of Finland, Iceland, and the Faroe Islands. The geography of the region is varied, from the Norwegian fjords in the west and Scandinavian mountains covering parts of Norway and Sweden, to the low and flat areas of Denmark in the south, as well as archipelagos and lakes in the east. Most of the population in the region live in the more temperate southern regions, with the northern parts having long, cold, winters. The region became notable during the Viking Age, when Scandinavian peoples participated in large scale raiding, conquest, colonization and trading mostl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yucatec Maya Language
Yucatec Maya (; referred to by its speakers simply as Maya or as , is one of the 32 Mayan languages of the Mayan language family. Yucatec Maya is spoken in the Yucatán Peninsula and northern Belize. There is also a significant diasporic community of Yucatec Maya speakers in San Francisco, though most Mayan Americans are speakers of other Mayan languages from Guatemala and Chiapas. Etymology According to the Hocabá dictionary, compiled by American anthropologist Victoria Bricker, there is a variant name , literally "flat speech"). A popular, yet false, alternative etymology of Mayab is "ma ya'ab" or "not many," "the few" which derives from New Age spiritualist interpretations of the Maya. The use of "Mayab" as the name of the language seems to be unique to the town of Hocabá, as indicated by the Hocabá dictionary and is not employed elsewhere in the region or in Mexico, by either Spanish or Maya speakers. As used in Hocabá, "Mayab" is not the recognized name of the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
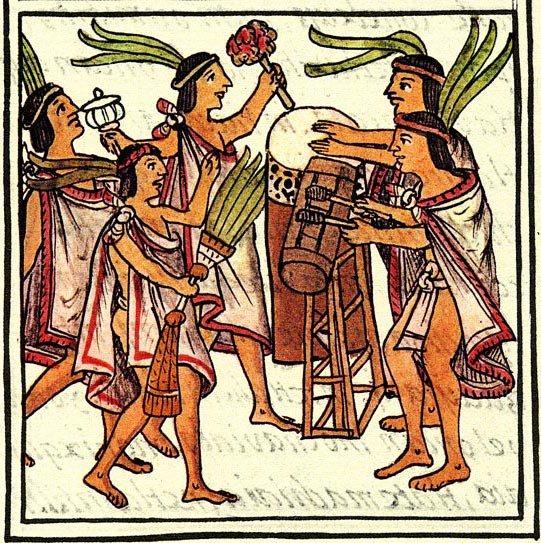
Mexica
The Mexica (Nahuatl: , ;''Nahuatl Dictionary.'' (1990). Wired Humanities Project. University of Oregon. Retrieved August 29, 2012, frolink/ref> singular ) were a Nahuatl-speaking indigenous people of the Valley of Mexico who were the rulers of the Aztec Empire. The Mexica established Tenochtitlan, a settlement on an island in Lake Texcoco, in 1325. A dissident group in Tenochtitlan separated and founded the settlement of Tlatelolco with its own dynastic lineage. In 1521, they were conquered by an alliance of Spanish conquistadors and indigenous people including the Tlaxcaltecs led by Hernán Cortés. Names The ''Mexica'' are eponymous of the place name Mexico (''Mēxihco'' ), originally referring to the interconnected settlements in the valley that is now Mexico City. The group was also known as the Culhua-Mexica in recognition of its kinship alliance with the neighboring Culhua, descendants of the revered Toltecs, who occupied the Toltec capital of Tula from the 10th to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, architecture, mathematics, calendar, and astronomical system. The Maya civilization developed in the Maya Region, an area that today comprises southeastern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize, and the western portions of Honduras and El Salvador. It includes the northern lowlands of the Yucatán Peninsula and the highlands of the Sierra Madre, the Mexican state of Chiapas, southern Guatemala, El Salvador, and the southern lowlands of the Pacific littoral plain. Today, their descendants, known collectively as the Maya, number well over 6 million individuals, speak more than twenty-eight surviving Mayan languages, and reside in nearly the same area as their ancestors. The Archaic period, before 2000 BC, saw the first developments in agricul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Iran
The culture of Iran () or culture of PersiaYarshater, Ehsa, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) is among the most influential in the world. Iran, also known as Persia, is widely considered to be one of the cradles of civilization. Due to its dominant geopolitical position in the world, it has heavily influenced peoples and cultures situated as far away as Southern Europe and Eastern Europe to the west; Central Asia to the north; the Arabian Peninsula to the south; and South Asia, East Asia, and Southeast Asia to the east. Iranian history has had a significant impact on the world through art, architecture, poetry, science and technology, medicine, philosophy, and engineering. An eclectic cultural elasticity has been said to be one of the key defining characteristics of the Iranian identity and a clue to its historical longevity. Richard N. Frye, a prominent Iranologist, stresses the high-level historical impact of Iranian culture in his 2005 book ''Greater Iran: A 20th- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Culture
Arab culture is the culture of the Arabs, from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Arabian Sea in the east, and from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the Horn of Africa and the Indian Ocean in the southeast. The various religions the Arabs have adopted throughout their history and the various empires and kingdoms that have ruled and took lead of the Arabian civilization have contributed to the ethnogenesis and formation of modern Arab culture.Language, literature, gastronomy, art, architecture, music, spirituality, philosophy and mysticism are all part of the cultural heritage of the Arabs. The Arab world is sometimes divided into separate regions depending on different cultures, dialects and traditions including: • The Levant: Lebanon, Syria, Palestine and Jordan. • Egypt • Mesopotamia (Iraq). • The Arabian Peninsula: Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Oman, Yemen and the United Arab Emirates. • Sudan • The Maghreb: Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Culture
Islamic culture and Muslim culture refer to cultural practices which are common to historically Islamic people. The early forms of Muslim culture, from the Rashidun Caliphate to the early Umayyad period and the early Abbasid period, were predominantly Arab, Byzantine, Persian and Levantine. With the rapid expansion of the Islamic empires, Muslim culture has influenced and assimilated much from the Persian, Egyptian, North Caucasian, Turkic, Mongol, Indian, Bangladeshi, Pakistani, Malay, Somali, Berber, Indonesian, and Moro cultures. Islamic culture generally includes all of the practices which have developed around the religion of Islam. There are variations in the application of Islamic beliefs in different cultures and traditions. Language and literature Arabic Arabic literature ( ar, الأدب العربي / ALA-LC: ''al-Adab al-'Arabī'') is the writing, both prose and poetry, produced by writers in the Arabic language. The Arabic word used for literature is ''" A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic of Korea) comprising its southern half. Korea consists of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and several minor islands near the peninsula. The peninsula is bordered by China to the northwest and Russia to the northeast. It is separated from Japan to the east by the Korea Strait and the Sea of Japan (East Sea). During the first half of the 1st millennium, Korea was divided between three states, Goguryeo, Baekje, and Silla, together known as the Three Kingdoms of Korea. In the second half of the 1st millennium, Silla defeated and conquered Baekje and Goguryeo, leading to the "Unified Silla" period. Meanwhile, Balhae formed in the north, superseding former Goguryeo. Unified Silla eventually collapsed into three separate states due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |