|
ASUDAS
The ASUDAS (Arizona State University Dental Anthropology System) is a reference system for collecting data on human tooth morphology and variation created by Christy G. Turner II, Christian R. Nichol, and G. Richard Scott. The ASUDAS gives detailed descriptions for common crown and root shape variants and their different degrees of expression. It also comprises a set of reference plaques illustrating dental variants as well as showing their expression levels in 3D. The ASUDAS was designed to ensure a standardized scoring procedure with minimum error in order to warrant comparability between data collected by different observers. The ASUDAS currently comprises a set of 42 dental variants that can be observed in the permanent adult dentition. The majority are crown and root shape variants, although the system also includes some skeletal variants of the maxilla and mandible. Most of the variants occur at different frequencies in human populations around the world. Examples of denta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Plaques Of The ASUDAS
Reference is a relationship between objects in which one object designates, or acts as a means by which to connect to or link to, another object. The first object in this relation is said to ''refer to'' the second object. It is called a ''name'' for the second object. The second object, the one to which the first object refers, is called the ''referent'' of the first object. A name is usually a phrase or expression, or some other symbolic representation. Its referent may be anything – a material object, a person, an event, an activity, or an abstract concept. References can take on many forms, including: a thought, a sensory perception that is audible (onomatopoeia), visual (text), olfactory, or tactile, emotional state, relationship with other, spacetime coordinate, symbolic or alpha-numeric, a physical object or an energy projection. In some cases, methods are used that intentionally hide the reference from some observers, as in cryptography. References feature in many sph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsatellite
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from one to six or more base pairs) are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. They have a higher mutation rate than other areas of DNA leading to high genetic diversity. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists and in genetic genealogy, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name "satellite" DNA refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying "satellite" layers of repetitive DNA. They are widely used for DNA profiling in cancer diagnosis, in kinship analysis (especially paternity testing) and in forensic identific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Mobility
Geographic mobility is the measure of how populations and goods move over time. Geographic mobility, population mobility, or more simply mobility is also a statistic that measures migration within a population. Commonly used in demography and human geography, it may also be used to describe the movement of animals between populations. These moves can be as large scale as international migrations or as small as regional commuting arrangements. Geographic mobility has a large impact on many sociological factors in a community and is a current topic of academic research.Population Mobility:Migration in a Global Economy (2013). Harvard College. It varies between different regions depending on both formal policies and established social norms, and has different effects and responses in different societies. Population mobility has implications ranging from administrative changes in government and impacts on local economic growth to housing markets and demand for regional services. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Migration
Human migration is the movement of people from one place to another with intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily, at a new location (geographic region). The movement often occurs over long distances and from one country to another (external migration), but internal migration (within a single country) is also possible; indeed, this is the dominant form of human migration globally. Migration is often associated with better human capital at both individual and household level, and with better access to migration networks, facilitating a possible second move. It has a high potential to improve human development, and some studies confirm that migration is the most direct route out of poverty.Age is also important for both work and non-work migration. People may migrate as individuals, in family units or in large groups. There are four major forms of migration: invasion, conquest, colonization and emigration/immigration. Persons moving from their home due to forced displa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
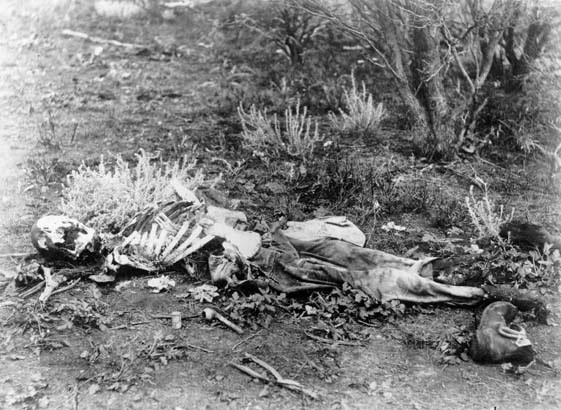
Forensic Anthropology
Forensic anthropology is the application of the anatomical science of anthropology and its various subfields, including forensic archaeology and forensic taphonomy, in a legal setting. A forensic anthropologist can assist in the identification of deceased individuals whose remains are decomposed, burned, mutilated or otherwise unrecognizable, as might happen in a plane crash. Forensic anthropologists are also instrumental in the investigation and documentation of genocide and mass graves. Along with forensic pathologists, forensic dentists, and homicide investigators, forensic anthropologists commonly testify in court as expert witnesses. Using physical markers present on a skeleton, a forensic anthropologist can potentially determine a person's age, sex, stature, and race. In addition to identifying physical characteristics of the individual, forensic anthropologists can use skeletal abnormalities to potentially determine cause of death, past trauma such as broken bones or me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area.Brown University, "Biogeography." Accessed February 24, 2014. . Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals. Mycogeography is the branch that studies distribution of fungi, such as mushrooms. Knowledge of spatial variation in the numbers and types of organisms is as vital to us today as it was to our early human ancestors, as we adapt to heterogeneous but geographically predictable environments. Biogeography is an integrative field of inquiry that unites concepts and information from ecology, evolutionary biology, taxonomy, geology, physical geography, palaeontology, and climatology.Dansereau, Pierre. 1957 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taphonomy
Taphonomy is the study of how organisms decay and become fossilized or preserved in the paleontological record. The term ''taphonomy'' (from Greek , 'burial' and , 'law') was introduced to paleontology in 1940 by Soviet scientist Ivan Efremov to describe the study of the transition of remains, parts, or products of organisms from the biosphere to the lithosphere. The term taphomorph is used to describe fossil structures that represent poorly-preserved, deteriorated remains of a mixture of taxonomic groups, rather than of a single one. Description Taphonomic phenomena are grouped into two phases: biostratinomy, events that occur between death of the organism and the burial; and diagenesis, events that occur after the burial. Since Efremov's definition, taphonomy has expanded to include the fossilization of organic and inorganic materials through both cultural and environmental influences. This is a multidisciplinary concept and is used in slightly different contexts throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major Tissue (biology), tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many other animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the Crown (tooth), crown. The other major tissues are dentin, cementum, and Pulp (tooth), dental pulp. It is a very hard, white to off-white, highly mineralised substance that acts as a barrier to protect the tooth but can become susceptible to degradation, especially by acids from food and drink. Calcium hardens the tooth enamel. In rare circumstances enamel fails to form, leaving the underlying dentin exposed on the surface. Features Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and contains the highest percentage of minerals (at 96%),Ross ''et al.'', p. 485 with water and organic material composing the rest.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nancy, Elsevier, pp. 70–94 The primary mineral is hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate. Enamel is formed o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area of , about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8.7% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. In general terms, Asia is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammary Gland
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland in humans and other mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, humans and chimpanzees), the udder in ruminants (for example, cows, goats, sheep, and deer), and the dugs of other animals (for example, dogs and cats). Lactorrhea, the occasional production of milk by the glands, can occur in any mammal, but in most mammals, lactation, the production of enough milk for nursing, occurs only in phenotypic females who have gestated in recent months or years. It is directed by hormonal guidance from sex steroids. In a few mammalian species, male lactation can occur. With humans, male lactation can occur only under specific circumstances. Mammals are divided into 3 groups: prototherians, metatherians, and eutherians. In the case of prototherians, both males and females have functional mamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
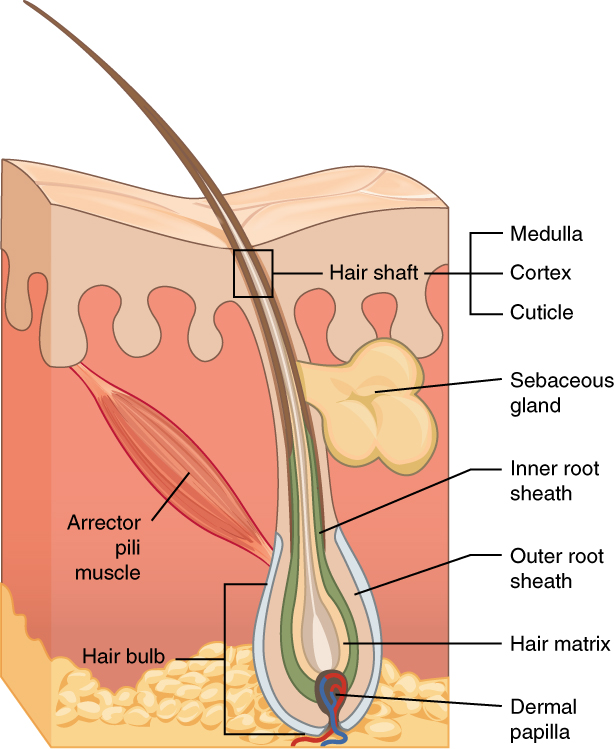
Hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair. Most common interest in hair is focused on hair growth, hair types, and hair care, but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably alpha-keratin. Attitudes towards different forms of hair, such as hairstyles and hair removal, vary widely across different cultures and historical periods, but it is often used to indicate a person's personal beliefs or social position, such as their age, sex, or religion. Overview The word "hair" usually refers to two distinct structures: #the part beneath the skin, called the hair follicle, or, when pulled from the skin, the bulb or root. This organ is located in the dermis and maintains stem cells, which not only re-grow the hair after it falls out, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleiotropy
Pleiotropy (from Greek , 'more', and , 'way') occurs when one gene influences two or more seemingly unrelated phenotypic traits. Such a gene that exhibits multiple phenotypic expression is called a pleiotropic gene. Mutation in a pleiotropic gene may have an effect on several traits simultaneously, due to the gene coding for a product used by a myriad of cells or different targets that have the same signaling function. Pleiotropy can arise from several distinct but potentially overlapping mechanisms, such as gene pleiotropy, developmental pleiotropy, and selectional pleiotropy. Gene pleiotropy occurs when a gene product interacts with multiple other proteins or catalyzes multiple reactions. Developmental pleiotropy occurs when mutations have multiple effects on the resulting phenotype. Selectional pleiotropy occurs when the resulting phenotype has many effects on fitness (depending on factors such as age and gender). An example of pleiotropy is phenylketonuria, an inherited d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |