|
ASAS-SN
The All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (ASAS-SN) is an automated program to search for new supernovae and other astronomical transients, headed by astronomers from the Ohio State University, including Christopher Kochanek and Krzysztof Stanek. It has 20 robotic telescopes in both the northern and southern hemispheres. It can survey the entire sky approximately once every day. Initially, there were four ASAS-SN telescopes at Haleakala and another four at Cerro Tololo, a Las Cumbres Observatory site. Twelve more telescopes were deployed in 2017 in Chile, South Africa and Texas, with funds from the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Ohio State University, the Mount Cuba Astronomical Foundation, China, Chile, Denmark, and Germany. All the telescopes (Nikon telephoto 400mm/F2.8 lenses) have a diameter of 14 cm and ProLine PL230 CCD cameras. The pixel resolution in the cameras is 7.8 arc seconds, so follow-up observations on other telescopes are usually required to get a mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASASSN1
C/2017 O1 (ASASSN) is a comet discovered by the All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (ASAS-SN). It was first detected on July 19, 2017, located in the southern constellation Cetus. Discovery During the ongoing ASAS-SN survey, using data from the quadruple 14-cm "Cassius" telescope on Cerro Tololo, Chile, a possible new moving transient source was detected on July 19, 2017; the team gave it the temporary designation ASASSN1. In the discovery images, C/2017 O1 had a V band magnitude of 15.3. The centroid was moving between the ASAS-SN three 90 second, dithered discovery images with no counterpart in the Minor Planet Center database. Follow-up images from the Savannah Skies Observatory recovered C/2017 O1 9.7 hours later 0.21 degrees away. These observations revealed C/2017 O1 had a halo at least 25 arcsec in radius, a compact core, and no clear tail. Further observations were made using the Las Cumbres Observatory 1m at CTIO 24.7 hours after discovery which recovered C/2017 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
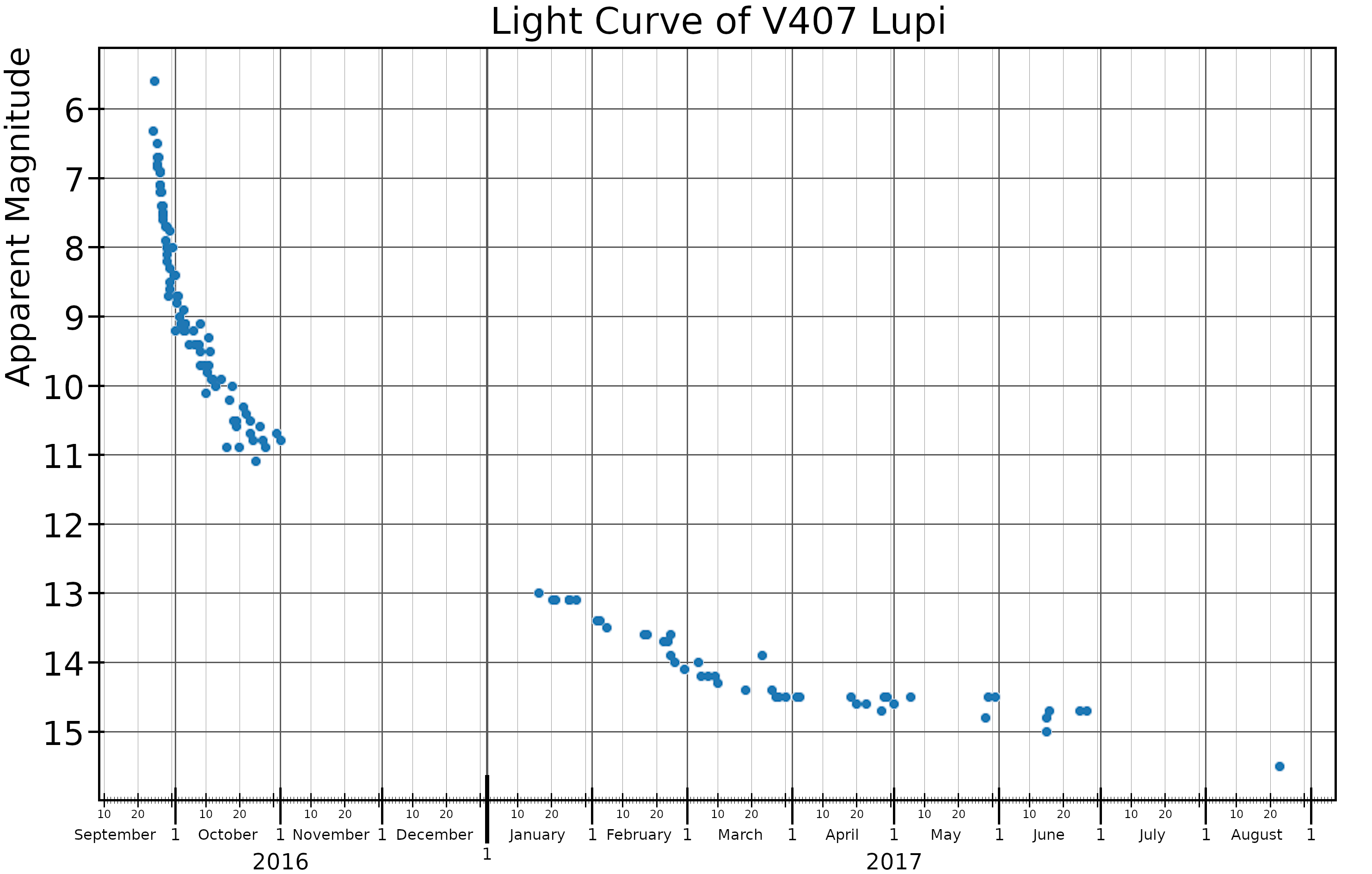
ASASSN-16kt
V407 Lupi, also known as Nova Lupi 2016, was a bright nova in the constellation Lupus discovered by All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (ASAS-SN) on 24.00 September 2016. At the time of its discovery, it had an apparent visual magnitude of 9.1. The ASAS-SN team reported that no object at the nova's location brighter than magnitude 17.5 was seen on images taken four days earlier. Wildly incorrect coordinates (in error by many degrees) were published in the announcement telegram, but corrected in a subsequent telegram. It reached a peak brightness of magnitude 5.6, faintly visible to the naked eye, on 25 September 2016. V407 Lupi declined from its peak brightness very quickly, fading by 2 magnitudes in less than three days. That is one of the most rapid declines in brightness ever seen in a nova. It is therefore classified as a "very fast" nova in the classification scheme of Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin. All novae are binary stars, with a "donor" star orbiting a wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASASSN-18fv
V906 Carinae, also known as Nova Carinae 2018, was a nova in the Milky Way galaxy which appeared in the constellation Carina, near the 5th magnitude star HD 92063. It was discovered on images taken on 20.32 March 2018 by the All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (ASAS-SN] telescope at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory. The ASAS-SN group assigned the name ASASSN-18fv to the object. The discovery image was saturated, allowing researchers to determine only that the object was brighter than apparent magnitude 10. An earlier image obtained by ASAS-SN on 26.32 March 2018 showed the nova was a magnitude ~10.4 object at that time, and the object was not detected on ASAS-SN images taken on 15.34 March 2018 and earlier. V906 Carinae was featured in the Astronomy Picture of the Day on 25 March 2018. Pre-discovery images of V906 Carinae were matched to a star of Gaia magnitude 20.1. On 21 March 2018, it had brightened to a Gaia magnitude 7.80 (visual magnitude 7.45 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krzysztof Stanek
Krzysztof Stanek is an observational astrophysicist and Professor and University Distinguished Scholar at Ohio State University. He was named a University Distinguished Scholar in 2018. His research focus is on the explosive deaths of massive stars. In 2022, Stanek was awarded a Guggenheim Fellowship. He won the Beatrice M. Tinsley Prize along with Christopher Kochanek in 2020 for their work on the All-Sky Automated Survey for Supernovae (ASAS-SN) project. He is a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. He has also been the recipient of a Harvard-Smithsonian CfA Postdoctoral Fellowship, the Polish Astronomical Society Young Astronomer Award and a Hubble Postdoctoral Fellowship The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) is the science operations center for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), science operations and mission operations center for the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), and science operations center for the .... Selected articles * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASASSN-15lh
ASASSN-15lh ( supernova designation SN 2015L) is an extremely luminous astronomical transient event discovered by the All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (ASAS-SN), with the appearance of a superluminous supernova event. It was first detected on June 14, 2015, located within a faint galaxy in the southern constellation Indus, and was the most luminous supernova-like object ever observed. At its peak, ASASSN-15lh was 570 billion times brighter than the Sun, and 20 times brighter than the combined light emitted by the Milky Way Galaxy. The emitted energy was exceeded by PS1-10adi. The nature of ASASSN-15lh is disputed. The most popular explanations are that it is the most luminous type I supernova (hypernova) ever observed, or a tidal disruption event around a supermassive black hole. Other hypotheses include: gravitational lensing; a quark nova inside a Wolf–Rayet star; or a rapid magnetar spindown. Discovery A possible supernova was first noticed during an observation i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Kochanek
Christopher Kochanek is an American astronomer. He works in the fields of cosmology, gravitational lensing, and supernovae. Kochanek currently is an Ohio Eminent Scholar at Ohio State University as well as an Elected Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. In 2020, he was the recipient of the Beatrice M. Tinsley Prize with Krzysztof Stanek for their leadership of the All-Sky Automated Survey for Supernovae ASAS-SN), in addition to the Dannie Heineman Prize for Astrophysics The Dannie Heineman Prize for Astrophysics is jointly awarded each year by the American Astronomical Society and American Institute of Physics for outstanding work in astrophysics. It is funded by the Heineman Foundation in honour of Dannie Heinem .... References Year of birth missing (living people) Living people Fellows of the American Association for the Advancement of Science Ohio State University faculty American astronomers California Institute of Technology alumni< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASASSN-19bt
ASASSN-19bt is a tidal disruption event, a star destroyed by a black hole, discovered by the All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (ASAS-SN) project, with early-time, detailed observations by the TESS satellite. It was first detected on January 21, 2019, and reached peak brightness on March 4. The black hole is in the 16th magnitude galaxy 2MASX J07001137-6602251 in the constellation Volans at a redshift of 0.0262, around 375 million light years away. Observations in UV light made with NASA's Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, previously called the Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Explorer, is a NASA three-telescope space observatory for studying gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) and monitoring the afterglow in X-ray, and UV/Visible light at the location o ... showed a drop in the temperature of the tidal disruption from around 71,500 to 35,500 degrees Fahrenheit (40,000 to 20,000 degrees Celsius) over a few days. This is the first time such an early temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
128 Nemesis
Nemesis (minor planet designation: 128 Nemesis) is a large 180 km main-belt asteroid, of carbonaceous composition. It rotates rather slowly, taking about 78 hours to complete one rotation. Nemesis is the largest member of the Nemesian asteroid family bearing its name. It was discovered by J. C. Watson on 25 November 1872, and named after Nemesis, the goddess of retribution in Greek mythology. left, Nemesis' orbit This object is orbiting the Sun with a period of and an eccentricity (ovalness) of 0.13. The orbital plane is inclined by 6.2° to the plane of the ecliptic. It is categorized as a C-type asteroid, indicating a primitive carbonaceous composition. Based on IRAS data Nemesis is about 188 km in diameter and is around the 33rd largest main-belt asteroid, while WISE measurements yield a size of ~163 km. The 77.81‑hour rotation period is the second longest for an asteroid more than 150 km in diameter. Between 2005 and 2021, 128 Nemesis has been observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2019 OK
2019 OK is a near-Earth asteroid noted for its sudden, surprise discovery on the day before its close flyby in 2019. The object's size is estimated at across, the closest asteroid of such size discovered in 2019. It is uncommon for asteroids of this size to pass within of Earth. Discovery The first valid detection occurred on 24 July 2019, when it was from Earth and had an apparent magnitude of 14.7. The full moon on 16 July 2019 slowed down the discovery rate during mid-July. The asteroid was detected by Cristóvão Jacques, Eduardo Pimentel and João Ribeiro at the private SONEAR Observatory in Oliveira, Minas Gerais when it was very close to opposition (opposite the Sun in the sky) with a solar elongation of 170 degrees. About 10 hours later it was independently detected by ASAS-SN project in images from two of its telescopes, which allowed a preliminary determination of its orbit. It was subsequently listed on the Minor Planet Center's Near-Earth Object Confirmation Page ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon And Betty Moore Foundation
The Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation is an American foundation established by Intel co-founder Gordon E. Moore and his wife Betty I. Moore in September 2000 to support scientific discovery, environmental conservation, patient care improvements and preservation of the character of the Bay Area. As outlined in the Statement of Founder's Intent, the foundation's aim is to tackle large, important issues at a scale where it can achieve significant and measurable impacts. According to the OECD, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation provided USD 60 million for development in 2020 by means of grants. Funded projects Astronomy * All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (ASAS-SN) * Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) * Hydrogen Epoch of Reionization Array (HERA) * South Pole Telescope (SPT) * Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) * W. M. Keck Observatory * BICEP and Keck Array Biology * Center for Ocean Solutions * Community Cyberinfrastructure for Advanced Marine Microbial Ecology Research and Analy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASASSN-16ma
V5856 Sagittarii, also known as Nova Sagittarii 2016 Number 4, was the 4th and brightest nova that occurred in the constellation Sagittarius during 2016. It was discovered by the All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (which assigned to it the name ASASSN-16ma) on 25.02 October 2016, at which time it had an apparent visual magnitude of 13.7. It was independently discovered by Yukio Sakurai of Mito, Ibaraki, Japan on 26.38 October 2016, by which time it had reached magnitude 10.4. It reached its peak brightness of magnitude 5.4, making it visible to the naked eye, on 8 November 2016. The nova occurred within a region of the sky monitored by the OGLE microlensing Gravitational microlensing is an astronomical phenomenon due to the gravitational lens effect. It can be used to detect objects that range from the mass of a planet to the mass of a star, regardless of the light they emit. Typically, astronomers ... experiment, and that group reported that no star brighter t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Flare
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star. Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as star (as, for example, in ''the A* search algorithm'' or ''C*-algebra''). In English, an asterisk is usually five- or six-pointed in sans-serif typefaces, six-pointed in serif typefaces, and six- or eight-pointed when handwritten. Its most common use is to call out a footnote. It is also often used to censor offensive words. In computer science, the asterisk is commonly used as a wildcard character, or to denote pointers, repetition, or multiplication. History The asterisk has already been used as a symbol in ice age cave paintings. There is also a two thousand-year-old character used by Aristarchus of Samothrace called the , , which he used when proofreading Homeric poetry to mark lines that were duplicated. Origen is know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |