|
ALICE (accelerator)
Accelerators and Lasers In Combined Experiments (ALICE), or Energy Recovery Linac Prototype (ERLP) is a 35MeV energy recovery linac test facility at Daresbury Laboratory in Cheshire, England. The project was originally conceived as a test bed for the 4th Generation Light Source (4GLS), and consists of: * A 350keV photoinjector laser. * An 8.35MeV superconducting RF booster linac. * A 35MeV superconducting RF main linac in which energy is recovered from used electron bunches and given to new bunches. * An infrared free electron laser (FEL), using a permanent magnet undulator on permanent loan from Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (TJNAF). * An ERL transport system that transports electron bunches through the FEL and back to the linac with the correct RF phase to decelerate them and thereby to recover energy from them. The ALICE accelerator is an Energy Recovery Linac (ERL) that incorporates all the features of the 4th generation light source albeit at smaller scale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Large Ion Collider Experiment
ALICE (A Large Ion Collider Experiment) is one of eight detector experiments at the Large Hadron Collider at CERN. The other seven are: ATLAS, CMS, TOTEM, LHCb, LHCf, MoEDAL and FASER. Introduction ALICE is optimized to study heavy-ion ( Pb-Pb nuclei) collisions at a centre of mass energy up to 5.02 TeV per nucleon pair. The resulting temperature and energy density allow exploration of quark–gluon plasma, a fifth state of matter wherein quarks and gluons are freed. Similar conditions are believed to have existed a fraction of the second after the Big Bang before quarks and gluons bound together to form hadrons and heavier particles. ALICE is focusing on the physics of strongly interacting matter at extreme energy densities. The properties of the quark–gluon plasma and the understanding of quark deconfinement are key issues in quantum chromodynamics (QCD). The results obtained by ALICE corroborate the understanding of color confinement and chiral symmetry restorat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
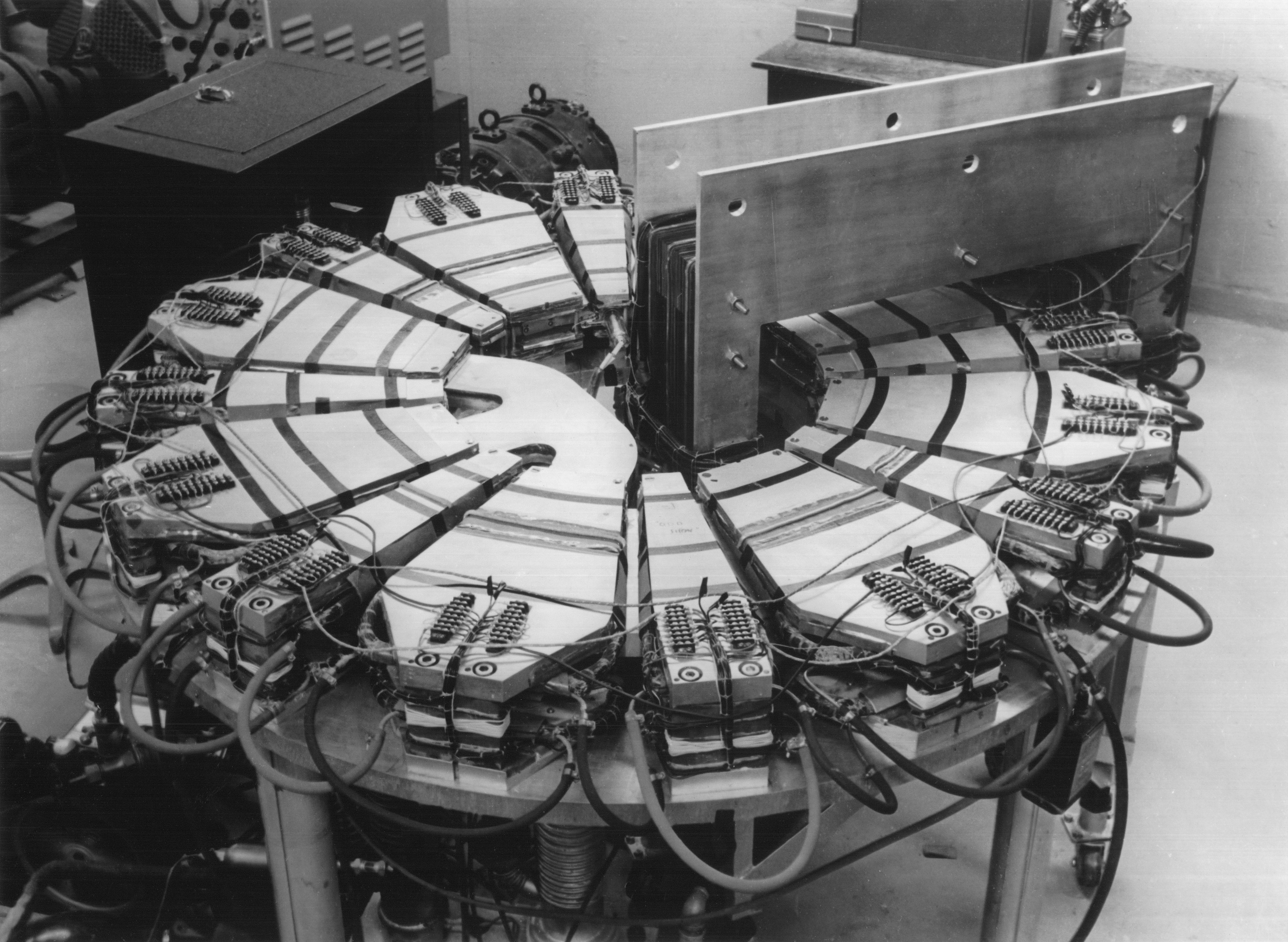
Microwave Cavity
A microwave cavity or ''radio frequency (RF) cavity'' is a special type of resonator, consisting of a closed (or largely closed) metal structure that confines electromagnetic fields in the microwave region of the spectrum. The structure is either hollow or filled with dielectric material. The microwaves bounce back and forth between the walls of the cavity. At the cavity's resonant frequencies they reinforce to form standing waves in the cavity. Therefore, the cavity functions similarly to an organ pipe or sound box in a musical instrument, oscillating preferentially at a series of frequencies, its resonant frequencies. Thus it can act as a bandpass filter, allowing microwaves of a particular frequency to pass while blocking microwaves at nearby frequencies. A microwave cavity acts similarly to a resonant circuit with extremely low loss at its frequency of operation, resulting in quality factors (Q factors) up to the order of 106, compared to 102 for circuits made with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Accelerators
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined beams. Large accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle physics. The largest accelerator currently active is the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) near Geneva, Switzerland, operated by the CERN. It is a collider accelerator, which can accelerate two beams of protons to an energy of 6.5 TeV and cause them to collide head-on, creating center-of-mass energies of 13 TeV. Other powerful accelerators are, RHIC at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York and, formerly, the Tevatron at Fermilab, Batavia, Illinois. Accelerators are also used as synchrotron light sources for the study of condensed matter physics. Smaller particle accelerators are used in a wide variety of applications, including particle therapy for oncological purposes, radioisotope production for medical diagnostics, ion imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brady Haran
Brady John Haran (born 18 June 1976) is an Australian-British independent filmmaker and video journalist who produces educational videos and documentary films for his YouTube channels, the most notable being ''Periodic Videos'' and ''Numberphile''. Haran is also the co-host of the'' Hello Internet'' podcast along with fellow educational YouTuber CGP Grey. On 22 August 2017, Haran launched his second podcast, called ''The Unmade Podcast'', and on 11 November 2018, he launched his third podcast, '' The Numberphile Podcast'', based on his mathematics-centered channel of the same name. Reporter and filmmaker Brady Haran studied journalism for a year before being hired by ''The Adelaide Advertiser''. In 2002, he moved from Australia to Nottingham, United Kingdom. In Nottingham, he worked for the BBC, began to work with film, and reported for ''East Midlands Today'', BBC News Online and BBC radio stations. In 2007, Haran worked as a filmmaker-in-residence for Nottingham Science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Chicane
A magnetic chicane also called a bunch compressor helps form dense bunches of electrons in a free-electron laser. A magnetic chicane makes electrons detour slightly from their otherwise straight bath, and in that way is similar to a chicane on a road. A magnetic chicane consists of four dipole magnets, giving electrons at the beginning of a bunch a longer path than electrons at the end of the bunch, thereby allowing the laging electrons to catch up. Free-electron laser A free-electron laser depends upon a beam of tightly bunched electrons. Short bunches of electrons are produced by a photoinjector, but they quickly grow, because electrons have negative charge and little mass, causing the bunch to expand. As the bunch is accelerated, the electrons gain mass and quickly approach the speed of light. After that, electrons at the end of the bunch cannot go any faster to catch up with electrons at the beginning of the bunch. Chirp This problem is solved by adjusting the phase of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirp
A chirp is a signal in which the frequency increases (''up-chirp'') or decreases (''down-chirp'') with time. In some sources, the term ''chirp'' is used interchangeably with sweep signal. It is commonly applied to sonar, radar, and laser systems, and to other applications, such as in spread-spectrum communications (see chirp spread spectrum). This signal type is biologically inspired and occurs as a phenomenon due to dispersion (a non-linear dependence between frequency and the propagation speed of the wave components). It is usually compensated for by using a matched filter, which can be part of the propagation channel. Depending on the specific performance measure, however, there are better techniques both for radar and communication. Since it was used in radar and space, it has been adopted also for communication standards. For automotive radar applications, it is usually called linear frequency modulated waveform (LFMW). In spread-spectrum usage, surface acoustic wave (SAW) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picocoulomb
The coulomb (symbol: C) is the unit of electric charge in the International System of Units (SI). In the present version of the SI it is equal to the electric charge delivered by a 1 ampere constant current in 1 second and to elementary charges, , (about ). Name and history By 1878, the British Association for the Advancement of Science had defined the volt, ohm, and farad, but not the coulomb. In 1881, the International Electrical Congress, now the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), approved the volt as the unit for electromotive force, the ampere as the unit for electric current, and the coulomb as the unit of electric charge. At that time, the volt was defined as the potential difference .e., what is nowadays called the "voltage (difference)"across a conductor when a current of one ampere dissipates one watt of power. The coulomb (later "absolute coulomb" or "abcoulomb" for disambiguation) was part of the EMU system of units. The "international coulomb" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picosecond
A picosecond (abbreviated as ps) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to 10−12 or (one trillionth) of a second. That is one trillionth, or one millionth of one millionth of a second, or 0.000 000 000 001 seconds. A picosecond is to one second as one second is to approximately 31,689 years. Multiple technical approaches achieve imaging within single-digit picoseconds: for example, the streak camera or intensified CCD (ICCD) cameras are able to picture the motion of light. One picosecond is equal to 1000 femtoseconds, or 1/1000 nanoseconds. Because the next SI unit is 1000 times larger, measurements of 10−11 and 10−10 second are typically expressed as tens or hundreds of picoseconds. Some notable measurements in this range include: * 1.0 picoseconds (1.0 ps) – cycle time for electromagnetic frequency 1 terahertz (THz) (1 x 1012 hertz), an inverse unit. This corresponds to a wavelength of 0.3 mm, as can be calculated by m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proof Of Principle
Proof of concept (POC or PoC), also known as proof of principle, is a realization of a certain method or idea in order to demonstrate its feasibility, or a demonstration in principle with the aim of verifying that some concept or theory has practical potential. A proof of concept is usually small and may or may not be complete. These collaborative trials aim to test feasibility of business concepts and proposals to solve business problems and accelerate business innovation goals. A proof of value (PoV) is sometimes used along proof of concept, and differs by focusing more on demonstrating the potential customers use case and value, and is usually less in-depth than a proof of concept. Usage history The term has been in use since 1967. In a 1969 hearing of the Committee on Science and Astronautics, Subcommittee on Advanced Research and Technology, ''proof of concept'' was defined as following: One definition of the term "proof of concept" was by Bruce Carsten in the context o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMMA (accelerator)
The electron machine with many applications or electron model for many applications (EMMA) is a linear non-scaling FFAG (fixed-field alternating-gradient) particle accelerator at Daresbury Laboratory in the UK that can accelerate electrons from 10 to 20 MeV. A FFAG is a type of accelerator in which the magnetic field in the bending magnets is constant during acceleration. This means the particle beam will move radially outwards as its momentum increases. Acceleration was successfully demonstrated in EMMA, paving the way for future non-scaling FFAGs to meet important applications in energy, security and medicine. A linear non-scaling FFAG is one in which a quantity known as the betatron tune is allowed to vary unchecked. In a conventional synchrotron such a variation would result in loss of the beam. However, in EMMA the beam will cross these resonances so rapidly that their effect should not be seen. EMMA will use the ALICE accelerator as a source of electrons and will be situat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FFAG Accelerator
A Fixed-Field alternating gradient Accelerator (FFA; also abbreviated FFAG) is a circular particle accelerator concept that can be characterized by its time-independent magnetic fields (''fixed-field'', like in a cyclotron) and the use of alternating gradient strong focusing (as in a synchrotron). In all circular accelerators, magnetic fields are used to bend the particle beam. Since the magnetic force required to bend the beam increases with particle energy, as the particles accelerate, either their paths will increase in size, or the magnetic field must be increased over time to hold the particles in a constant size orbit. Fixed-field machines, such as cyclotrons and FFAs, use the former approach and allow the particle path to change with acceleration. In order to keep particles confined to a beam, some type of focusing is required. Small variations in the shape of the magnetic field, while maintaining the same overall field direction, are known as weak focusing. Strong, or al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility
Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility (TJNAF), commonly called Jefferson Lab or JLab, is a US National Laboratory located in Newport News, Virginia. Its stated mission is "to provide forefront scientific facilities, opportunities and leadership essential for discovering the fundamental structure of nuclear matter; to partner in industry to apply its advanced technology; and to serve the nation and its communities through education and public outreach." Since June 1, 2006, it has been operated by Jefferson Science Associates, LLC, a limited liability company created by Southeastern Universities Research Association and PAE Applied Technologies. Until 1996 it was known as the Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility (CEBAF); commonly, this name is still used for the main accelerator. Founded in 1984, Jefferson Lab employs more than 750 people, and more than 2,000 scientists from around the world have conducted research using the facility. History The facility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_2.jpg)