|
ALCO Century 636
The ALCo Century 636 was the most powerful single-engine diesel-electric locomotive constructed by the American Locomotive Company (ALCo). It used their 251 prime mover. The locomotive had a C-C wheel arrangement and . The locomotive rode on a pair of trucks of all-new design, known as the Hi-Ad, standing for 'high adhesion'. Visually, it is similar to the Century 630, but can be distinguished by the intercooler box. The C630 has two grilles here, one above the other. The C636 only has the upper grille. Production Between 1967 and 1968, 34 C636 locomotives were built by Alco in Schenectady, New York. Despite many new and innovative features, the C636 could not hold its own in the marketplace. Three demonstrator locomotives were built costing Alco about $5.5 million. Problems with Alco demonstrator number 636-2, the only demonstrator locomotive operating, were a factor in dissuading potential customers. During an evaluation on the Santa Fe Railway, the same traction motor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MLW M-636
The M-636 was a six-axle, 3,600 hp diesel locomotive marketed as part of the Montreal Locomotive Works six-axle "M-Line" series of locomotives. It was essentially the Canadian-built version of the ALCO Century 636 The ALCo Century 636 was the most powerful single-engine diesel-electric locomotive constructed by the American Locomotive Company (ALCo). It used their 251 prime mover. The locomotive had a C-C wheel arrangement and . The locomotive rode o ..., and it saw many sales to Canadian, Mexican and Australian customers. Today, there are a handful M-636s left in revenue service. Original owners See also * List of MLW diesel locomotives References {{MLW diesels M-636 BHP Billiton diesel locomotives C-C locomotives Diesel locomotives of Western Australia Railway locomotives introduced in 1969 Standard gauge locomotives of Australia Standard gauge locomotives of the United States Standard gauge locomotives of Canada Diesel-electric locomotives of Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
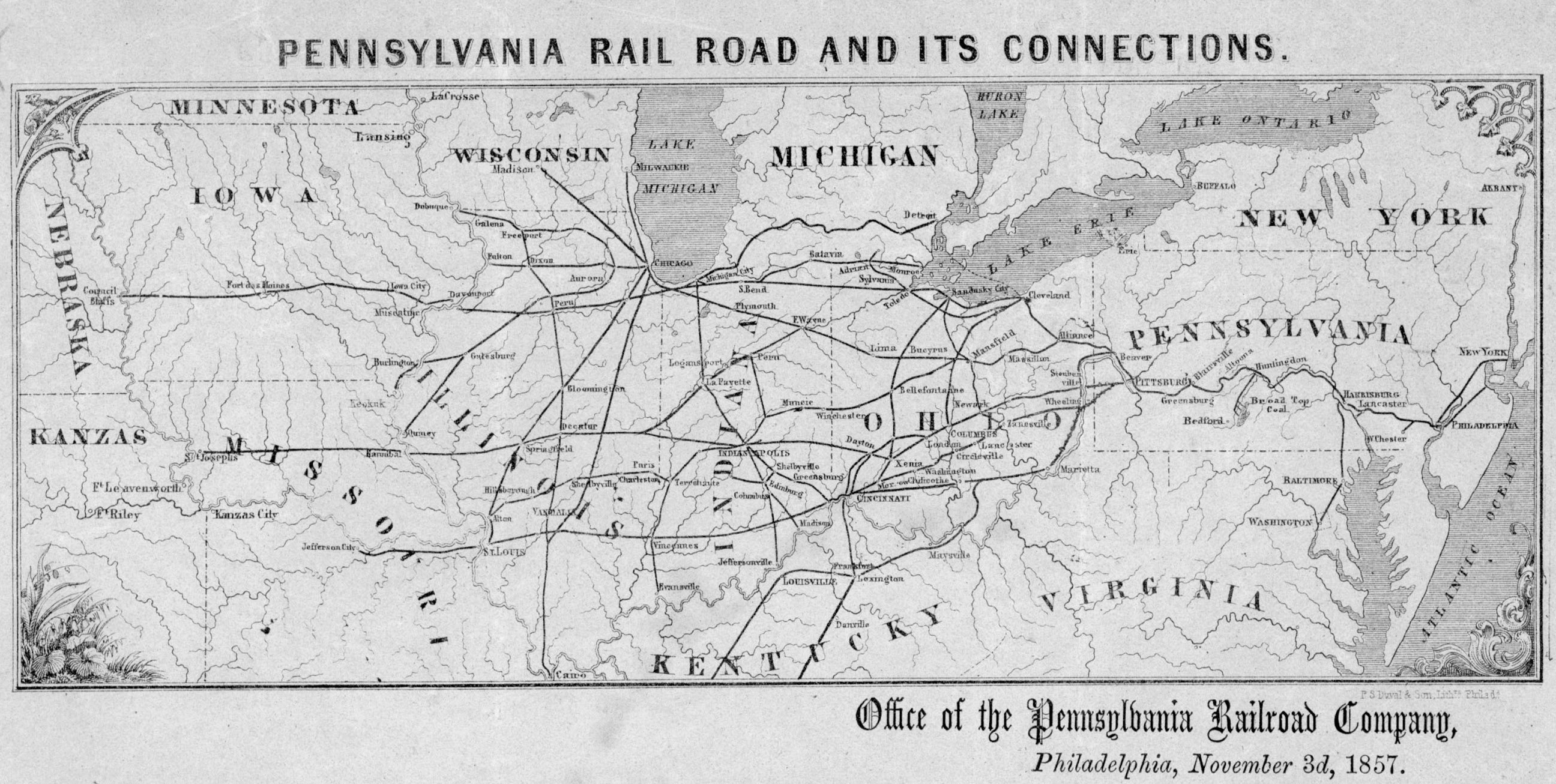
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named for the commonwealth in which it was established. By 1882, Pennsylvania Railroad had become the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Its budget was second only to the U.S. government. Over the years, it acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
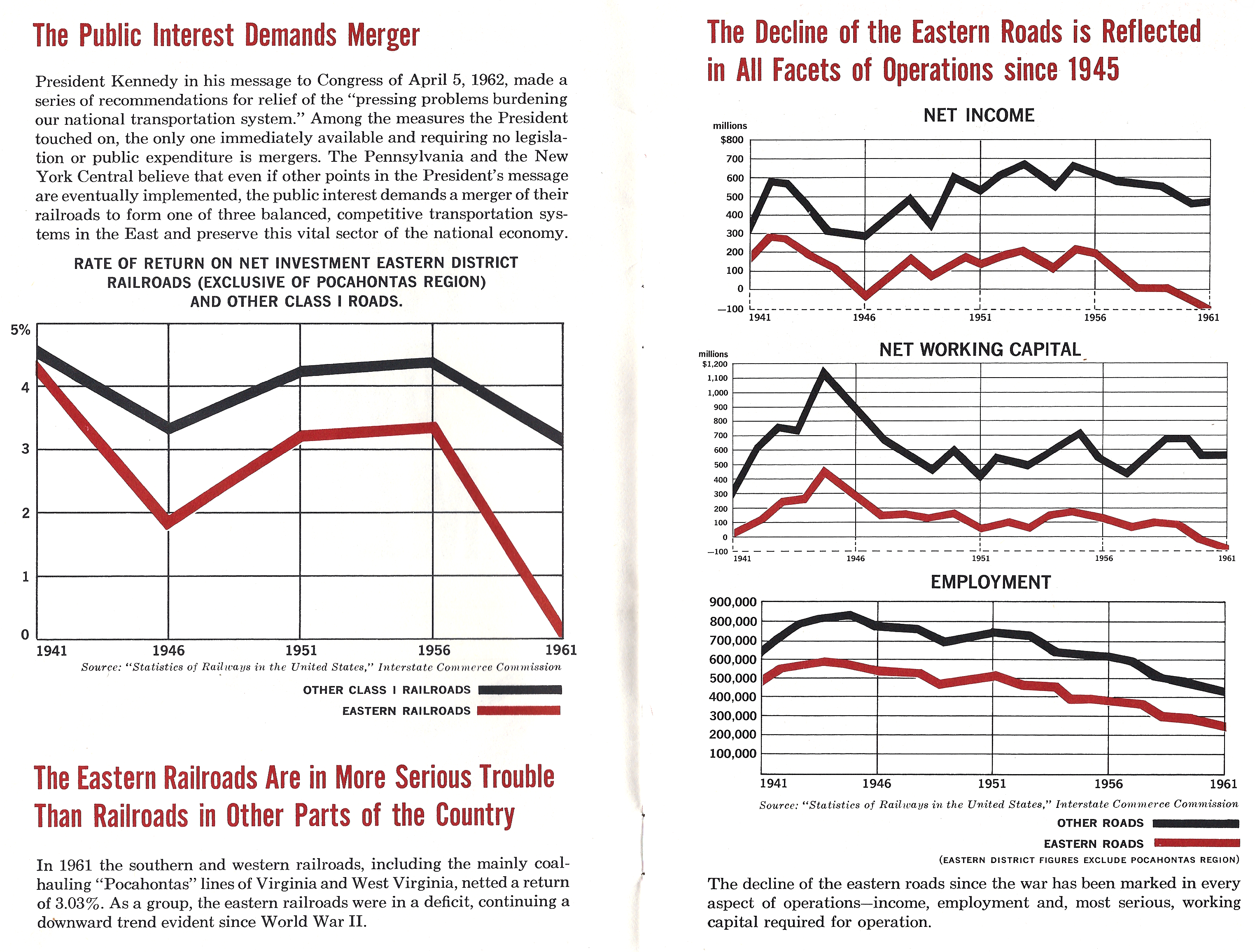
Penn Central
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American Railroad classes, class I railroad that operated from 1968 to 1976. Penn Central combined three traditional corporate rivals (the Pennsylvania Railroad, Pennsylvania, New York Central Railroad, New York Central and the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad, New York, New Haven and Hartford railroads), all united by heavy service into the New York metropolitan area and (to a lesser extent) New England and Chicago. The new company failed barely two years after formation, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history at the time. The Penn Central's railroad assets were nationalized into Conrail along with the other bankrupt northeastern roads; its real estate and insurance holdings successfully Reorganization, reorganized into American Premier Underwriters. History Pre-merger The Penn Central railroad system developed in response to challenges facing Northeast United States, northeaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illinois Central Gulf
The Illinois Central Railroad , sometimes called the Main Line of Mid-America, was a railroad in the Central United States, with its primary routes connecting Chicago, Illinois, with New Orleans, Louisiana, and Mobile, Alabama. A line also connected Chicago with Sioux City, Iowa (1870). There was a significant branch to Omaha, Nebraska (1899), west of Fort Dodge, Iowa, and another branch reaching Sioux Falls, South Dakota (1877), starting from Cherokee, Iowa. The Sioux Falls branch has been abandoned in its entirety. The Canadian National Railway acquired control of the IC in 1998, and merged its operations in 1999. Illinois Central continues to exist as a paper railroad. History The IC was one of the oldest Class I railroads in the United States. The company was incorporated by the Illinois General Assembly on January 16, 1836. Within a few months Rep. Zadok Casey (D-Illinois) introduced a bill in the U.S. House of Representatives authorizing a land grant to the company to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illinois Central Railroad
The Illinois Central Railroad , sometimes called the Main Line of Mid-America, was a railroad in the Central United States, with its primary routes connecting Chicago, Illinois, with New Orleans, Louisiana, and Mobile, Alabama. A line also connected Chicago with Sioux City, Iowa (1870). There was a significant branch to Omaha, Nebraska (1899), west of Fort Dodge, Iowa, and another branch reaching Sioux Falls, South Dakota (1877), starting from Cherokee, Iowa. The Sioux Falls branch has been abandoned in its entirety. The Canadian National Railway acquired control of the IC in 1998, and merged its operations in 1999. Illinois Central continues to exist as a paper railroad. History The IC was one of the oldest Class I railroads in the United States. The company was incorporated by the Illinois General Assembly on January 16, 1836. Within a few months Rep. Zadok Casey (D-Illinois) introduced a bill in the U.S. House of Representatives authorizing a land grant to the company to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Québec Cartier Mining Company
Québec Cartier Mining Company was one of the leading producers of iron ore products in North America, now part of ArcelorMittal. The company was founded in the late 1950s by multiple Canadian and American investors, based in Quebec, Canada. The first open pit mine was located in Lac-Jeanine, Quebec. The Hart-Jaune Dam over the nearby Hart Jaune River supplied power. The company then built the town of Gagnon, in 1963 to accommodate workers and families. Eighteen years later, the company extended its operations seventy miles north to Fire Lake. In 1973, they started operating in Mont Wright, Quebec, where they created the town of Fermont. At their Mont Wright plant, the company operates an open pit mine and a crusher/concentrator facility capable of producing eighteen million metric tonnes of iron ore concentrates annually. The company also operates a pellet plant with an annual production capacity of some nine million metric tonnes of iron ore pellets at Port-Cartier. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bassendean, Western Australia
__NOTOC__ Bassendean (once referred to as West Guildford) is a north-eastern suburb of Perth, Western Australia. Its local government area is the Town of Bassendean. It is also the name of the sand dune system on the Swan Coastal Plain known as the ''Bassendean Dune System''. History In 1829, the land along the Swan River was allotted to British settlers as they arrived in the newly created Swan River Colony. James Henty and his brothers were granted 2,000 acres upon which they grazed their livestock and built a mud-brick homestead. They called their property ''Stoke Farm''. In 1832, the Henty brothers sold the farm to the Colonial Secretary, Peter Broun who re-named the homestead ''Bassendean''. Over the years the Bassendean property became incorporated into the suburb of West Guildford and in 1922, West Guildford was renamed Bassendean. Flooding in 1929 caused severe damage, especially to the primary school oval. In December 1934, Bassendean Road Board held a referendum, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Engineering
Commonwealth Engineering (often shortened to Com-Eng, later Comeng [ ]) was an Australian engineering company that designed and built railway locomotives, rolling stock and trams. History Smith and Waddington, the predecessor to Commonwealth Engineering, was founded in 1921, in the Sydney suburb of Camperdown, New South Wales, Camperdown, as a body builder for custom motor cars. It went bankrupt in the Great Depression in Australia, Depression, and was reformed as Waddingtons Body Works and the main factory was moved to Granville, New South Wales, Granville, after a fire in the main workshop. The Government of Australia took control of the company during World War II as the company was in serious financial difficulties but had many government orders in its books. The government purchased a controlling stake in the company in 1946 and changed the name to Commonwealth Engineering. In 1949 a factory was established in Rocklea, Queensland. This was followed in 1952 a plant in Basse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Newman Railway
The Mount Newman railway, owned and operated by BHP, is a private rail network in the Pilbara region of Western Australia built to carry iron ore. It is one of two railway lines BHP operates in the Pilbara, the other being the Goldsworthy railway.Rail In addition to the BHP network, there are three more independent iron ore rail lines in the Pilbara: operate the Hamersley & Robe River railwa ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilbara Iron
Pilbara Iron is a wholly owned subsidiary of the multinational Rio Tinto Group, that manages assets for Hamersley Iron Pty Ltd, a wholly owned subsidiary of Rio Tinto, and Robe River Iron Associates, an unincorporated joint venture between Rio (53% and operator since 2000) and three Japanese steel companies Mitsui Iron Ore Development P/L (33%), Nippon Steel Australia P/L (10.5%) and Sumitomo Metal Australia P/L (3.5%). All of these companies are involved in the mining of iron ore, predominantly from the Pilbara region of Western Australia. In 2004, Rio Tinto announced that Robe and Hamersley would start merging operations under the new Pilbara Iron entity. The concept had been tested by the formation of Pilbara Rail in 2001, which generated more than $16 million in savings. Pilbara Rail was folded into Pilbara Iron in 2005. Each company continues to market products separately and retains ownership and profits from the underlying mines, as well as strategic development of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilbara
The Pilbara () is a large, dry, thinly populated region in the north of Western Australia. It is known for its Aboriginal peoples; its ancient landscapes; the red earth; and its vast mineral deposits, in particular iron ore. It is also a global biodiversity hotspot for subterranean fauna. Definitions of the Pilbara region At least two important but differing definitions of "the Pilbara" region exist. Administratively it is one of the nine regions of Western Australia defined by the ''Regional Development Commissions Act 1993''; the term also refers to the Pilbara shrublands bioregion (which differs in extent) under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA). General The Pilbara region, as defined by the Regional Development Commissions Act 1993 and administered for economic development purposes by the Pilbara Development Commission, has an estimated population of 61,688 , and covers an area of . It contains some of Earth's oldest rock formations, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |