|
AAI Sparrowhawk
The AAI SparrowHawk is an American two-seat pusher ultralight autogyro, available in kit form for amateur construction. Design and development AAI (American Autogyros Inc) was formed as a division of Groen Brothers Aviation (GBA) late in 2002, with the initial task of improving stability in existing autogyros. After a series of such modifications they decided to develop their own aircraft and a proof-of-concept machine first flew in February 2003. This was based around the pod of an RAF 2000 autogyro but had a different tail design. The first AAI built production prototype flew on 25 February 2004. The SparrowHawk is a pusher configuration autogyro with an uncowled single 160 hp (120 kW) Subaru EJ25 flat-four engine mounted behind a totally enclosed glass fibre cabin. This pod, which seats two side by side, has almost triangular sides and is entered via optional large, partially glazed doors. An aluminum keel projects aft of the pod and a vertical member fixed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subaru EJ25
The Subaru EJ engine is a series of four-stroke automotive engines manufactured by Subaru. They were introduced in 1989, intended to succeed the previous Subaru EA engine. The EJ series was the mainstay of Subaru's engine line, with all engines of this series being 16-valve horizontal flat-fours, with configurations available for single, or double-overhead camshaft arrangements (SOHC or DOHC). Naturally aspirated and turbocharged versions are available, ranging from . These engines are commonly used in light aircraft, kit cars and engine swaps into air-cooled Volkswagens, and are also popular as a swap into copy wasserboxer engined Volkswagen T3/Vanagon. Primary engineering on the EJ series was done by Masayuki Kodama, Takemasa Yamada and Shuji Sawafuji of Fuji Heavy Industries, Subaru's parent company. EJ15 (1.5L Boxer NA) Usage: * Impreza GC1 series ( JDM) - Replaced by Subaru EL engine in 2006 GD, GG, GE & GH series ( JDM) Impreza. * Impreza 93-06 (Latin America) Specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
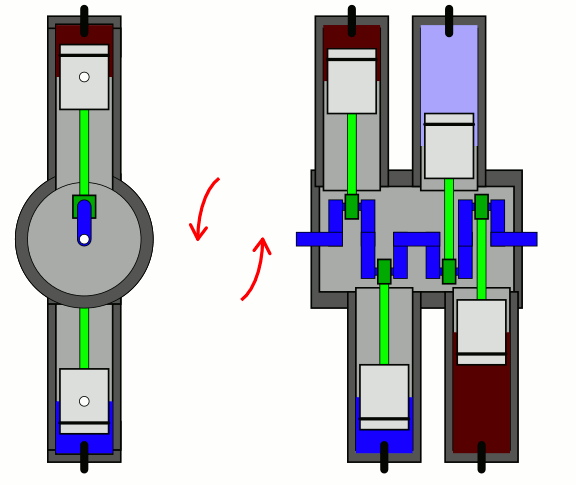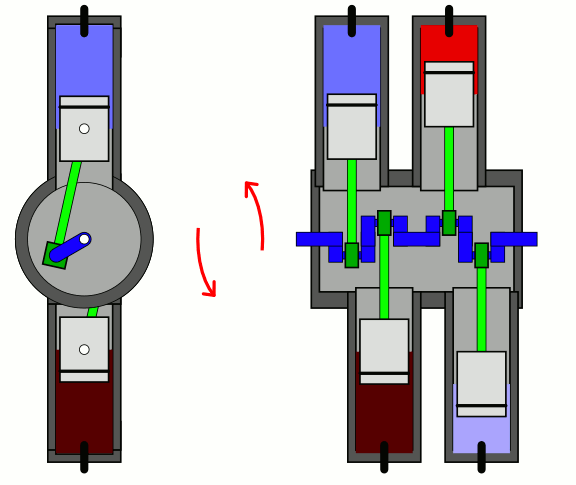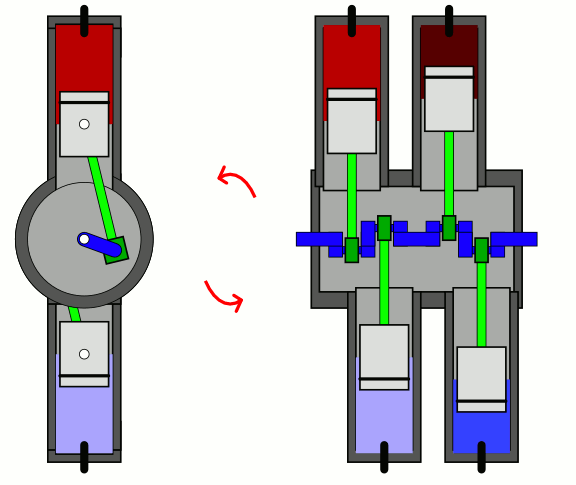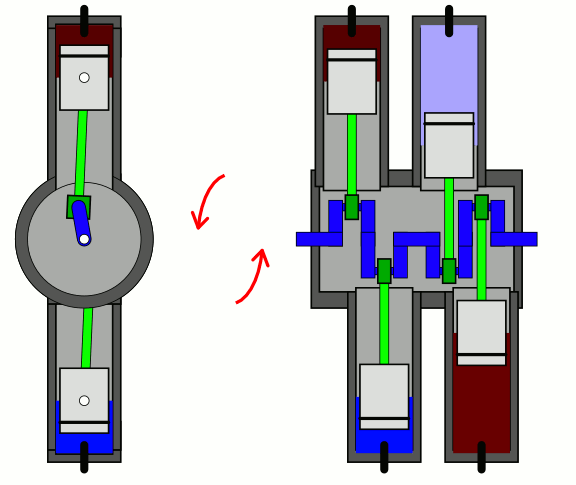
Flat Four
A flat-four engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-four engine, is a four-cylinder piston engine with two banks of cylinders lying on opposite sides of a common crankshaft. The most common type of flat-four engine is the boxer-four engine, each pair of opposed pistons moves inwards and outwards at the same time. A boxer-four engine has perfect primary and secondary balance, however, the two cylinder heads means the design is more expensive to produce than an inline-four engine. Boxer-four engines have been used in cars since 1897, especially by Volkswagen and Subaru. They have also occasionally been used in motorcycles and frequently in aircraft. Cessna and Piper use flat four engines from Lycoming and Continental in the most common civil aircraft in the world - the Cessna 172, and Piper Cherokee, while many ultralight and LSA planes use versions of the Rotax 912. Design Most flat-four engines are designed so that each pair of opposing pistons moves inwards and outw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricycle Gear
Tricycle gear is a type of aircraft undercarriage, or ''landing gear'', arranged in a tricycle fashion. The tricycle arrangement has a single nose wheel in the front, and two or more main wheels slightly aft of the center of gravity. Tricycle gear aircraft are the easiest for takeoff, landing and taxiing, and consequently the configuration is the most widely used on aircraft.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 524. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. Aviation Publishers Co. Limited, ''From the Ground Up'', page 11 (27th revised edition) History Several early aircraft had primitive tricycle gear, notably very early Antoinette planes and the Curtiss Pushers of the pre-World War I Pioneer Era of aviation. Waldo Waterman's 1929 tailless '' Whatsit'' was one of the first to have a steerable nose wheel. In 1956, Cessna introduced sprung-steel tricycle landing gear on the Cessna 172. Their marketing department described this as "Land-O-Matic" t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally aircraft, air or watercraft, water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw and p-factor and is not the primary control used to turn the airplane. A rudder operates by redirecting the fluid past the hull (watercraft), hull or fuselage, thus imparting a turning or yaw (rotation), yawing motion to the craft. In basic form, a rudder is a flat plane or sheet of material attached with hinges to the craft's stern, tail, or after end. Often rudders are shaped so as to minimize Drag (physics), hydrodynamic or aerodynamic drag. On simple watercraft, a tiller—essentially, a stick or pole acting as a lever arm—may be attached to the top of the rudder to allow it to be turned by a helmsman. In larger vessels, cables, pushrods, or hydraulics may be used to link rudders to steering wheels. In typical air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (aircraft)
In aeronautics, the chord is an imaginary straight line joining the leading edge and trailing edge of an aerofoil. The chord length is the distance between the trailing edge and the point where the chord intersects the leading edge.L. J. Clancy (1975), ''Aerodynamics'', Section 5.2, Pitman Publishing Limited, London. The point on the leading edge used to define the chord may be the surface point of minimum radius. p.18 For a turbine aerofoil the chord may be defined by the line between points where the front and rear of a 2-dimensional blade section would touch a flat surface when laid convex-side up. The wing, horizontal stabilizer, vertical stabilizer and propeller/rotor blades of an aircraft are all based on aerofoil sections, and the term ''chord'' or ''chord length'' is also used to describe their width. The chord of a wing, stabilizer and propeller is determined by measuring the distance between leading and trailing edges in the direction of the airflow. (If a wing has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicopter Rotor
A helicopter main rotor or rotor system is the combination of several rotary wings (rotor blades) with a control system, that generates the aerodynamic lift force that supports the weight of the helicopter, and the thrust that counteracts aerodynamic drag in forward flight. Each main rotor is mounted on a vertical mast over the top of the helicopter, as opposed to a helicopter tail rotor, which connects through a combination of drive shaft(s) and gearboxes along the tail boom. The blade pitch is typically controlled by the pilot using the helicopter flight controls. Helicopters are one example of rotary-wing aircraft (rotorcraft). The name is derived from the Greek words ''helix'', helik-, meaning spiral; and ''pteron'' meaning wing. Design principles Overview The helicopter rotor is powered by the engine, through the transmission, to the rotating mast. The mast is a cylindrical metal shaft that extends upward from—and is driven by—the transmission. At the top of the mast i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Fibre
Glass fiber ( or glass fibre) is a material consisting of numerous extremely fine fibers of glass. Glassmakers throughout history have experimented with glass fibers, but mass manufacture of glass fiber was only made possible with the invention of finer machine tooling. In 1893, Edward Drummond Libbey exhibited a dress at the World's Columbian Exposition incorporating glass fibers with the diameter and texture of silk fibers. Glass fibers can also occur naturally, as Pele's hair. Glass wool, which is one product called "fiberglass" today, was invented some time between 1932 to 1933 by Games Slayter of Owens-Illinois, as a material to be used as thermal building insulation. It is marketed under the trade name Fiberglas, which has become a genericized trademark. Glass fiber when used as a thermal insulating material is specially manufactured with a bonding agent to trap many small air cells, resulting in the characteristically air-filled low-density "glass wool" family of prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat-four
A flat-four engine, also known as a horizontally opposed-four engine, is a four-cylinder piston engine with two banks of cylinders lying on opposite sides of a common crankshaft. The most common type of flat-four engine is the boxer-four engine, each pair of opposed pistons moves inwards and outwards at the same time. A boxer-four engine has perfect primary and secondary balance, however, the two cylinder heads means the design is more expensive to produce than an inline-four engine. Boxer-four engines have been used in cars since 1897, especially by Volkswagen and Subaru. They have also occasionally been used in motorcycles and frequently in aircraft. Cessna and Piper use flat four engines from Lycoming and Continental in the most common civil aircraft in the world - the Cessna 172, and Piper Cherokee, while many ultralight and LSA planes use versions of the Rotax 912. Design Most flat-four engines are designed so that each pair of opposing pistons moves inwards and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF 2000
The RAF 2000 is a two-seat kit built autogyro that was designed by Bernard J. Haseloh. Kits were first manufactured by Rotary Air Force Marketing Inc. in Canada. The marketing and manufacturing rights were sold to the Mocke Family in Upington, Northern Cape, South Africa in April 2007. They formed UMRTC Eben Mocke to produce the aircraft design.Bayerl, Robby; Martin Berkemeier; et al: ''World Directory of Leisure Aviation 2011–12'', page 187. WDLA UK, Lancaster UK, 2011. ISSN 1368-485XTacke, Willi; Marino Boric; et al: ''World Directory of Light Aviation 2015–16'', page 200. Flying Pages Europe SARL, 2015. The RAF 2000 is one of only a few autogyros with type approval from the Light Aircraft Association in the United Kingdom. Development The RAF 2000 was a development of the single seat RAF 1000 and was designed primarily by Bernard J Haseloh. The aircraft kits were manufactured by Rotary Air Force Inc of Canada until April 2007 when the marketing and manufacturing r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft/page Content
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groen Brothers Aviation
Skyworks Global, formerly Groen Brothers Aviation, Inc. and then Groen Aeronautics Corporation, is an American autogyro research and development company based in Salt Lake City, Utah. The company was founded in 1986 by David Groen and his late brother Jay Groen. David Groen remains as Senior Advisor. In 2001, ''Time'' magazine listed GBA's Hawk Gyroplane as one of their featured "Inventions of the Year." History The original name of Skyworks Global was Groen Brothers Aviation. It started out by incorporating helicopter design components into autogyro design. They added helicopter-style collective pitch control which allowed their aircraft to achieve vertical takeoff and landing and to stabilize flight at high and low speeds.One Step Beyond Rotor & Wing, retrieved 3 January 2012 The company holds thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |