|
Aztalan Plate 34
Aztalan State Park is a Wisconsin state park in the Town of Aztalan, Jefferson County. Established in 1952, it was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1964 and added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1966. The park covers along the Crawfish River. Aztalan is the site of an ancient Mississippian culture settlement that flourished during the 10th to 13th centuries. The indigenous people constructed massive earthwork mounds for religious and political purposes. They were part of a widespread culture with important settlements throughout the Mississippi River valley and its tributaries. Their trading network extended from the Great Lakes to the Gulf Coast, and into the Southeast of the present-day United States. Pre-history (900–1300) Aztalan was first settled around 900 CE by a Native American culture known as the Middle Mississippian tradition. The chief center of a Middle Mississippian settlement is at Cahokia, in present-day Illinois, a city that at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jefferson County, Wisconsin
Jefferson County is a county in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. As of the 2020 census, the population was 84,900. Its county seat is Jefferson. Jefferson County comprises the Watertown- Fort Atkinson, WI Micropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included in the Milwaukee-Racine- Waukesha, WI Combined Statistical Area. History Jefferson County was created in 1836 as part of Wisconsin Territory and was organized in 1839. Jefferson County was founded by "Yankee" settlers from New England. It was named after Jefferson County, New York, where some of the original settlers came from. The town of Watertown, Wisconsin, was named after Watertown, New York, in Jefferson County, New York. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has an area of , of which is land and (4.5%) is water. Major highways Railroads *Canadian Pacific *Union Pacific *Wisconsin and Southern Railroad Buses *List of intercity bus stops in Wisconsin Airports * Watertown Municipal Airport ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
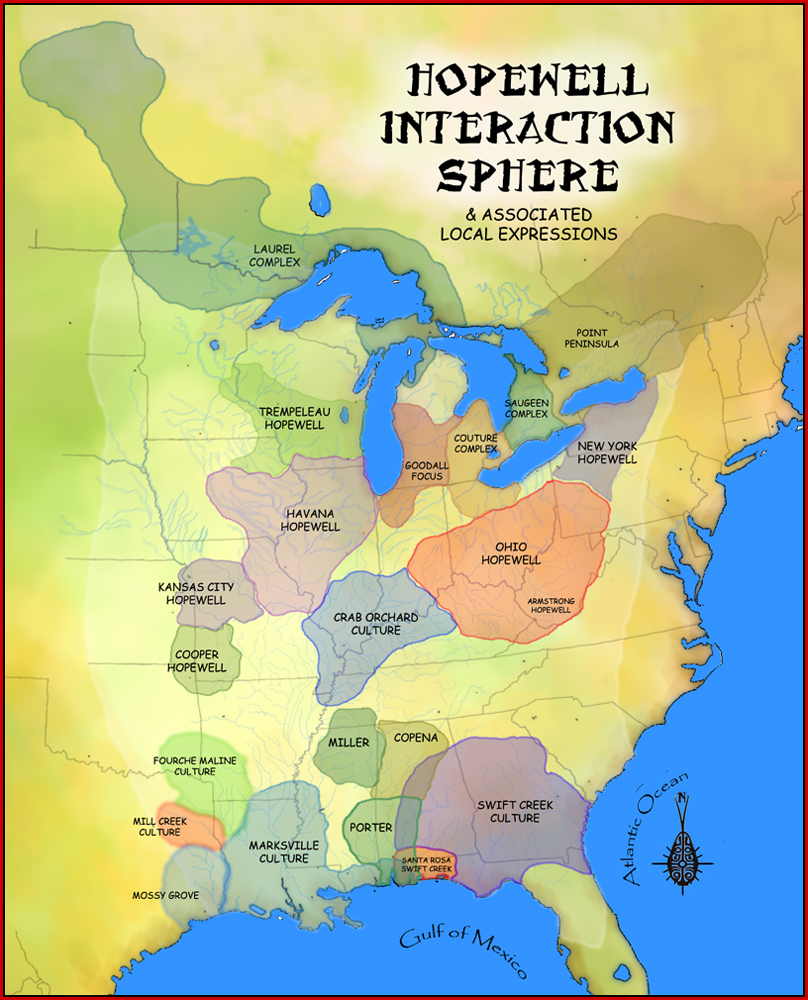
Woodland Culture
In the classification of archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 CE to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic hunter-gatherers and the agriculturalist Mississippian cultures. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic region, the Eastern United States, along to the Gulf of Mexico. This period is variously considered a developmental stage, a time period, a suite of technological adaptations or "traits", and a "family tree" of cultures related to earlier Archaic cultures. It can be characterized as a chronological and cultural manifestation without any massive changes in a shor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamarack
''Larix laricina'', commonly known as the tamarack, hackmatack, eastern larch, black larch, red larch, or American larch, is a species of larch native to Canada, from eastern Yukon and Inuvik, Northwest Territories east to Newfoundland, and also south into the upper northeastern United States from Minnesota to Cranesville Swamp, West Virginia; there is also an isolated population in central Alaska. The word ''akemantak'' is an Algonquian name for the species and means "wood used for snowshoes". Description ''Larix laricina'' is a small to medium-size boreal coniferous and deciduous tree reaching tall, with a trunk up to diameter. Tamaracks and larches (''Larix'' species) are deciduous conifers. The bark is tight and flaky, pink, but under flaking bark it can appear reddish. The leaves are needle-like, short, light blue-green, turning bright yellow before they fall in the autumn, leaving the pale pinkish-brown shoots bare until the next spring. The needles are produced spi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thatch
Thatching is the craft of building a roof with dry vegetation such as straw, water reed, sedge (''Cladium mariscus''), rushes, heather, or palm branches, layering the vegetation so as to shed water away from the inner roof. Since the bulk of the vegetation stays dry and is densely packed—trapping air—thatching also functions as insulation. It is a very old roofing method and has been used in both tropical and temperate climates. Thatch is still employed by builders in developing countries, usually with low-cost local vegetation. By contrast, in some developed countries it is the choice of some affluent people who desire a rustic look for their home, would like a more ecologically friendly roof, or who have purchased an originally thatched abode. History Thatching methods have traditionally been passed down from generation to generation, and numerous descriptions of the materials and methods used in Europe over the past three centuries survive in archives and early public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bark (botany)
Bark is the outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines, and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consists of the inner bark and the outer bark. The inner bark, which in older stems is living tissue, includes the innermost layer of the periderm. The outer bark on older stems includes the dead tissue on the surface of the stems, along with parts of the outermost periderm and all the tissues on the outer side of the periderm. The outer bark on trees which lies external to the living periderm is also called the rhytidome. Products derived from bark include bark shingle siding and wall coverings, spices and other flavorings, tanbark for tannin, resin, latex, medicines, poisons, various hallucinogenic chemicals and cork. Bark has been used to make cloth, canoes, and ropes and used as a surface for paintings and map making. A number of plants a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4). Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay particles, but become hard, brittle and non–plastic upon drying or firing. Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clay is the oldest known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been dated to around 14,000 BC, and clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poaceae
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and pasture. The latter are commonly referred to collectively as grass. With around 780 genera and around 12,000 species, the Poaceae is the fifth-largest plant family, following the Asteraceae, Orchidaceae, Fabaceae and Rubiaceae. The Poaceae are the most economically important plant family, providing staple foods from domesticated cereal crops such as maize, wheat, rice, barley, and millet as well as feed for meat-producing animals. They provide, through direct human consumption, just over one-half (51%) of all dietary energy; rice provides 20%, wheat supplies 20%, maize (corn) 5.5%, and other grains 6%. Some members of the Poaceae are used as building materials (bamboo, thatch, and straw); others can provide a source of biofuel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wattle And Daub
Wattle and daub is a composite building method used for making walls and buildings, in which a woven lattice of wooden strips called wattle is daubed with a sticky material usually made of some combination of wet soil, clay, sand, animal dung and straw. Wattle and daub has been used for at least 6,000 years and is still an important construction method in many parts of the world. Many historic buildings include wattle and daub construction. History The wattle and daub technique was used already in the Neolithic period. It was common for houses of Linear pottery and Rössen cultures of middle Europe, but is also found in Western Asia (Çatalhöyük, Shillourokambos) as well as in North America (Mississippian culture) and South America (Brazil). In Africa it is common in the architecture of traditional houses such as those of the Ashanti people. Its usage dates back at least 6,000 years. There are suggestions that construction techniques such as lath and plaster and even cob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Ice Age
The Little Ice Age (LIA) was a period of regional cooling, particularly pronounced in the North Atlantic region. It was not a true ice age of global extent. The term was introduced into scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939. Matthes described glaciers in the Sierra Nevada of California that he believed could not have survived the hypsithermal; his usage of "Little Ice Age" has been superseded by "Neoglaciation". The period has been conventionally defined as extending from the 16th to the 19th centuries, (noted in Grove 2004:4). but some experts prefer an alternative timespan from about 1300 to about 1850. The NASA Earth Observatory notes three particularly cold intervals. One began about 1650, another about 1770, and the last in 1850, all of which were separated by intervals of slight warming. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Third Assessment Report considered that the timing and the areas affected by the Little Ice Age suggested largely independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It was officially named the North Central Region by the Census Bureau until 1984. It is between the Northeastern United States and the Western United States, with Canada to the north and the Southern United States to the south. The Census Bureau's definition consists of 12 states in the north central United States: Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, South Dakota, and Wisconsin. The region generally lies on the broad Interior Plain between the states occupying the Appalachian Mountains, Appalachian Mountain range and the states occupying the Rocky Mountains, Rocky Mountain range. Major rivers in the region include, from east to west, the Ohio River, the Upper Mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mill Creek Chert
Mill Creek chert is a type of chert found in Southern Illinois and heavily exploited by members of the Mississippian culture (800 to 1600 CE). Artifacts made from this material are found in archaeological sites throughout the American Midwest and Southeast. It is named for a village and stream near the quarries, Mill Creek, Illinois and Mill Creek, a tributary of the Cache River. The chert was used extensively for the production of utilitarian tools such as hoes and spades, and for polished ceremonial objects such as bifaces, spatulate celts and maces. History ''Chert'' is a siliceous (silica) stone, a variety of quartz similar to flint but more brittle. It naturally occurs as large, flat, elliptically shaped nodules in creek beds, and sometimes as hill-top residuum. The nodules were formed as part of the Ullin limestone formation during the Mississippian geologic period (roughly 359 to 318 million years ago). Mill Creek Chert is a tough, coarse-grained chert, usually brown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southwest and south by the Mexico, Mexican States of Mexico, states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatan, and Quintana Roo; and on the southeast by Cuba. The Southern United States, Southern U.S. states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, which border the Gulf on the north, are often referred to as the "Third Coast" of the United States (in addition to its Atlantic and Pacific Ocean, Pacific coasts). The Gulf of Mexico took shape approximately 300 million years ago as a result of plate tectonics.Huerta, A.D., and D.L. Harry (2012) ''Wilson cycles, tectonic inheritance, and rifting of the North American Gulf of Mexico continental margin.'' Geosphere. 8(1):GES00725.1, first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

