|
Azadinium Spinosum
''Azadinium spinosum'' is a species of dinoflagellates that produces azaspiracid toxins (toxins associated with shellfish poisoning), particularly AZA 1, AZA 2 and an isomer of AZA 2. Description It measures 12–16 µm in length and 7–11 µm wide, is a peridinin-containing photosynthetic dinoflagellate with a thin theca. Its large nucleus is spherical and present posteriorly, whereas its single chloroplast A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in ... is parietal, lobed, and extends into the epi- and hyposome. References Further reading * * * * External links * Dinophyceae {{dinoflagellate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shellfish Poisoning
Shellfish poisoning includes four syndromes that share some common features and are primarily associated with bivalve molluscs (such as mussels, clams, oysters and scallops.) As filter feeders, these shellfish may accumulate toxins produced by microscopic algae, such as cyanobacteria, diatoms and dinoflagellates. Syndromes The syndromes are: * Amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) * Diarrheal shellfish poisoning (DSP) * Neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP) * Paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) See also * Cyanotoxin * Gonyaulax ''Gonyaulax'' is a genus of dinoflagellates with the type species ''Gonyaulax spinifera'' (Claparède et Lachmann) Diesing. ''Gonyaulax'' belongs to red dinoflagellates and commonly causes red tides. It secretes a poisonous toxin known as "saxit ... References External links Human Illness Associated with Harmful Algae {{Authority control Seafood Toxic effect of noxious substances eaten as food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Episome
An episome is a special type of plasmid, which remains as a part of the eukaryotic genome without integration. Episomes manage this by replicating together with the rest of the genome and subsequently associating with metaphase chromosomes during mitosis. Episomes do not degrade, unlike standard plasmids, and can be designed so that they are not epigenetically silenced inside the eukaryotic cell nucleus. Episomes can be observed in nature in certain types of long-term infection by adeno-associated virus or Epstein-Barr virus. In 2004, it was proposed that non-viral episomes might be used in genetic therapy for long-term change in gene expression. As of 1999, there were many known sequences of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) that allow a standard plasmid to become episomally retained. One example is the S/MAR sequence. The length of episomal retention is fairly variable between different genetic constructs and there are many known features in the sequence of an episome which will aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like ''Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they circulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theca
In biology, a theca (plural thecae) is a sheath or a covering. Botany In botany, the theca is related to plant's flower anatomy. The theca of an angiosperm consists of a pair of microsporangia that are adjacent to each other and share a common area of dehiscence called the stomium. Larry Hufford, "The origin and early evolution of angiosperm stamens" i''The Anther: form, function, and phylogeny'' William G. D'Arcy and Richard C. Keating (editors), Cambridge University Press, 1996, 351pp, p.60, (from Google Books) Any part of a microsporophyll that bears microsporangia is called an anther. Most anthers are formed on the apex of a filament. An anther and its filament together form a typical (or filantherous) stamen, part of the male floral organ. The typical anther is bilocular, i.e. it consists of two thecae. Each theca contains two microsporangia, also known as pollen sacs. The microsporangia produce the microspores, which for seed plants are known as pollen grains. If t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthetic
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name ''photosynthesis'', from the Greek ''phōs'' (), "light", and ''synthesis'' (), "putting together". Most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies most of the energy necessary for life on Earth. Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centers that contain green chlorophyll (and other colored) pigments/chromophores. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peridinin
Peridinin is a light-harvesting apocarotenoid, a pigment associated with chlorophyll and found in the peridinin-chlorophyll-protein (PCP) light-harvesting complex in dinoflagellates, best studied in ''Amphidinium carterae''. Biological significance Peridinin is an apocarotenoid pigment that some organisms use in photosynthesis. Many photosynthetic dinoflagellates use peridinin, which absorbs blue-green light in the 470-550nm range, outside the range accessible to chlorophyll molecules. The peridinin-chlorophyll-protein complex is a specialized molecular complex consisting of a boat-shaped protein molecule with a large central cavity that contains peridinin, chlorophyll, and lipid molecules, usually in a 4:1 ratio of peridinin to chlorophyll. Spectral characteristics * Absorption maximum: 483 nm * Emission maximum: 676 nm * Extinction coefficient (ε): 1.96 x 106 M−1cm−1 * A483/A280 ≥ 4.6 Applications Peridinin chlorophyll (PerCP) is commonly used in immunoassa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equalling (SI standard prefix "micro-" = ); that is, one millionth of a metre (or one thousandth of a millimetre, , or about ). The nearest smaller common SI unit is the nanometre, equivalent to one thousandth of a micrometre, one millionth of a millimetre or one billionth of a metre (). The micrometre is a common unit of measurement for wavelengths of infrared radiation as well as sizes of biological cells and bacteria, and for grading wool by the diameter of the fibres. The width of a single human hair ranges from approximately 20 to . The longest human chromosome, chromosome 1, is approximately in length. Examples Between 1 μm and 10 μm: * 1–10 μm – length of a typical bacterium * 3–8 μm – width of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
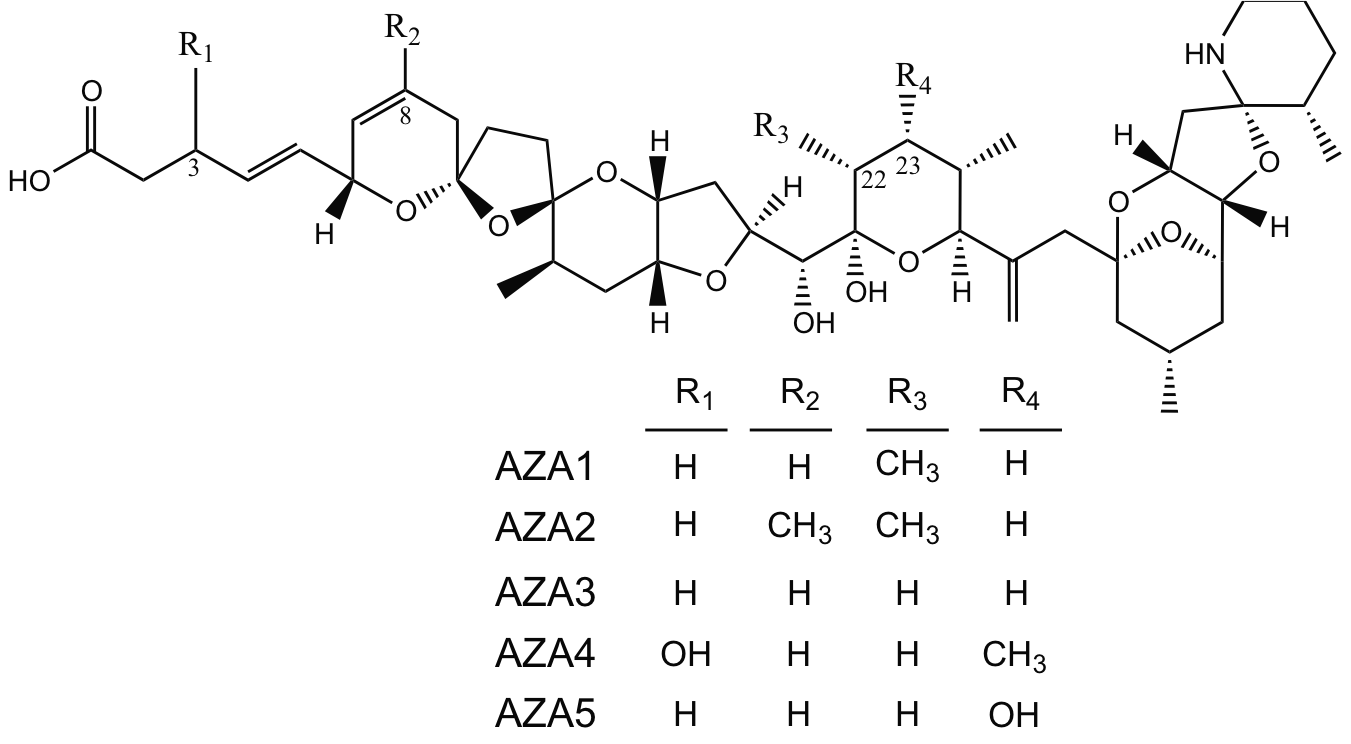
Azaspiracid
Azaspiracids (AZA) are a group of polycyclic ether marine algal toxins produced by the small dinoflagellate '' Azadinium spinosum'' that can accumulate in shellfish and thereby cause illness in humans. Azaspiracid was first identified in the 1990s following an outbreak of human illness in the Netherlands that was associated with ingestion of contaminated shellfish originating from Killary Harbour, Ireland. To date, over 20 AZA analogues have been identified in phytoplankton and shellfish. Over the last 15 years, AZAs have been reported in shellfish from many coastal regions of western Europe, Northern Africa, South America, and North America. In addition, AZAs have been found in Japanese sponges and Scandinavian crabs. Not surprisingly, the global distribution of AZAs appears to correspond to the apparent wide spread occurrence of ''Azadinium''. Empirical evidence is now available that unambiguously demonstrates the accumulation of AZAs in shellfish via direct feeding on AZA-produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
The SAR supergroup, also just SAR or Harosa, is a clade that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and Rhizaria. The name is an acronym derived from the first letters of each of these clades; it has been alternatively spelled "RAS". The term "Harosa" (at the subkingdom level) has also been used. The SAR supergroup is a node-based taxon. Note that as a formal taxon, "Sar" has only its first letter capitalized, while the earlier abbreviation, SAR, retains all uppercase letters. Both names refer to the same group of organisms, unless further taxonomic revisions deem otherwise. Members of the SAR supergroup were once included under the separate supergroups Chromalveolata (Chromista and Alveolata) and Rhizaria, until phylogenetic studies confirmed that stramenopiles and alveolates diverged with Rhizaria. This apparently excluded haptophytes and cryptomonads, leading Okamoto ''et al.'' (2009) to propose the clade Hacrobia to accommodate them. Phylogeny Based on a compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azadinium
''Azadinium'' is a genus of dinoflagellates belonging to the family Amphidomataceae. Species: *'' Azadinium asperum'' *'' Azadinium caudatum'' *'' Azadinium concinnum'' *'' Azadinium cuneatum'' *'' Azadinium dalianense'' *'' Azadinium dexteroporum'' *'' Azadinium galwayense'' *'' Azadinium luciferelloides'' *'' Azadinium obesum'' *'' Azadinium perforatum'' *'' Azadinium perfusorium'' *'' Azadinium polongum'' *'' Azadinium poporum'' *''Azadinium spinosum ''Azadinium spinosum'' is a species of dinoflagellates that produces azaspiracid toxins (toxins associated with shellfish poisoning), particularly AZA 1, AZA 2 and an isomer of AZA 2. Description It measures 12–16 µm in length and 7–11&nbs ...'' *'' Azadinium trinitatum'' *'' Azadinium zhuanum'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q21369093 Dinophyceae Dinoflagellate genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphidomataceae
Amphidomataceae is a family of dinoflagellates belonging to the class Dinophyceae, order unknown. Genera: * '' Amphidoma'' * ''Azadinium ''Azadinium'' is a genus of dinoflagellates belonging to the family Amphidomataceae. Species: *'' Azadinium asperum'' *'' Azadinium caudatum'' *'' Azadinium concinnum'' *'' Azadinium cuneatum'' *'' Azadinium dalianense'' *'' Azadinium dex ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q18606228 Dinophyceae Dinoflagellate families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |