|
Aymaratherium
''Aymaratherium'' is an extinct genus of nothrotheriid ground sloths that lived during the Late Miocene and Early Pliocene of Bolivia. Fossils of ''Aymaratherium'' have been found in the Pomata Ayte locality of the Umala Formation. Etymology The genus name, ''Aymaratherium'', is derived from the Aymara, a native ethnic group and language from the Andes, and ''therion'', meaning "beast". The specific name honors Jean Joinville Vacher, for his friendship and constant support for palaeontological investigations over the years. Discovery ''Aymaratherium'' was first described in 2016 on the basis of a nearly complete right dentary (specimen MNHN-Bol-V 008954), which was made of the holotype. In addition, three complete humeri (MNHN-Bol-V 003789, 012874 and 012875), a right astragalus (MNHN-Bol-V 012983), and a complete right calcaneus (MNHN-Bol-V 003307) have also been assigned to the genus. The locality of the holotype was recovered from the Pomata-Ayte locality, in the Umala Forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nothrotheriidae
Nothrotheriidae is a family of extinct ground sloths that lived from approximately 17.5 mya—10,000 years ago, existing for approximately . Previously placed within the tribe Nothrotheriini or subfamily Nothrotheriinae within Megatheriidae, they are now usually placed in their own family, Nothrotheriidae. Nothrotheriids appeared in the Burdigalian, some 19.8 million years ago, in South America. The group includes the comparatively slightly built ''Nothrotheriops'', which reached a length of about . While nothrotheriids were small compared to some of their megatheriid relatives, their claws provided an effective defense against predators, like those of larger anteaters today. Evolution During the late Miocene and Pliocene, the sloth genus ''Thalassocnus'' of the west coast of South America became adapted to a shallow-water marine lifestyle. However, the family placement of ''Thalassocnus'' has been disputed; while long considered a nothrotheriid, one recent analysis moves it to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nothrotheriinae
Nothrotheriidae is a family of extinct ground sloths that lived from approximately 17.5 mya—10,000 years ago, existing for approximately . Previously placed within the tribe Nothrotheriini or subfamily Nothrotheriinae within Megatheriidae, they are now usually placed in their own family, Nothrotheriidae. Nothrotheriids appeared in the Burdigalian, some 19.8 million years ago, in South America. The group includes the comparatively slightly built ''Nothrotheriops'', which reached a length of about . While nothrotheriids were small compared to some of their megatheriid relatives, their claws provided an effective defense against predators, like those of larger anteaters today. Evolution During the late Miocene and Pliocene, the sloth genus ''Thalassocnus'' of the west coast of South America became adapted to a shallow-water marine lifestyle. However, the family placement of ''Thalassocnus'' has been disputed; while long considered a nothrotheriid, one recent analysis moves it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aymara People
Aymara may refer to: Languages and people * Aymaran languages, the second most widespread Andean language ** Aymara language, the main language within that family ** Central Aymara, the other surviving branch of the Aymara(n) family, which today includes only the endangered Jaqaru/Kawki language * Aymara people, the native ethnic group identified with the speakers of Altiplano Aymara Culture * ''Corazón Aymara'' (English: ''Aymara Heart''), 1925 Bolivian silent feature film directed by Pedro Sambarino * Grupo Aymara, Bolivian folk troupe of traditional music of pre-Hispanic and contemporary music of the Andes * Socialist Aymara Group (Spanish: ''Grupo Aymara Socialista''), left-wing indigenous political group in Bolivia Places * Aymaraes Province, the largest of seven provinces of the Apurímac Region in Peru * Aymara Lupaca Reserved Zone, a protected area in southeastern Peru Nature * ''Aymaramyia'', genus of crane bird found in Peru * ''Aymaratherium'', genus of extinct sloth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
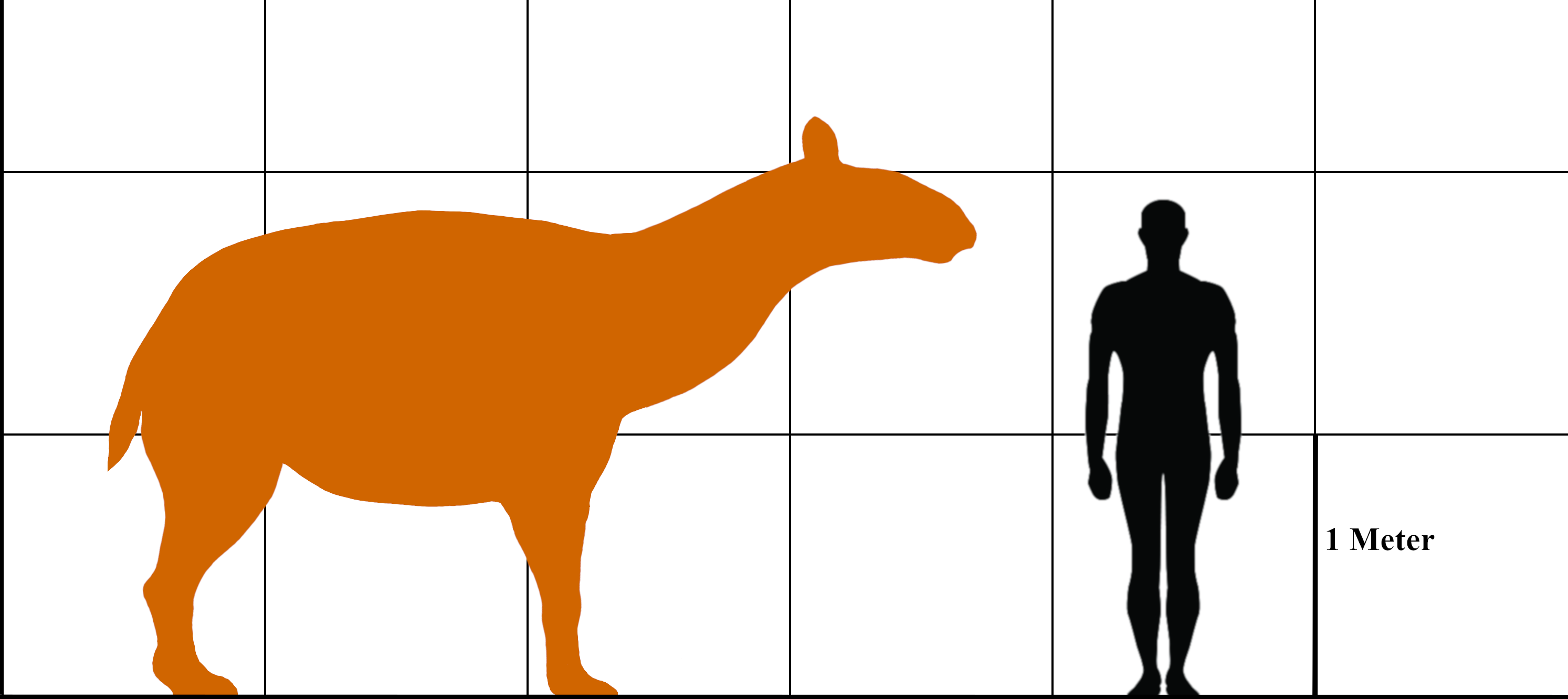
Macrauchenia
''Macrauchenia'' ("long llama", based on the now-invalid llama genus, ''Auchenia'', from Greek "big neck") was a large, long-necked and long-limbed, three-toed native South American mammal in the order Litopterna. The genus gives its name to its family, the Macraucheniidae or "robust litopterns". Like other litopterns, it is most closely related to the odd-toed ungulates ( Perissodactyla), from which litopterns diverged approximately 66 million years ago. The oldest fossils in the genus date to the late Miocene, around seven million years ago, and ''M. patachonica'' disappears from the fossil record during the late Pleistocene, around 20,000-10,000 years ago. ''M. patachonica'' is one of the last and best known member of the family and is known primarily from the Luján Formation in Argentina, but is known from localities across southern South America. Another genus of macraucheniid ''Xenorhinotherium'' was present in northeast Brazil and Venezuela during the Late Pleistocene. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hapalops
''Hapalops'' is an extinct genus of ground sloth from the Early to Late Miocene of Brazil (Solimões Formation), Bolivia ( Honda Group), Colombia ( Honda Group),Croft, 2007, p.300 and Argentina (Santa Cruz Formation) in South America.''Hapalops'' at Fossilworks.org History ''Hapalops'' was first described by notable Argentine paleontologist and zoologist in 1887, with his description of ''H. rectangularis'' as the type species. It was erected based on the posterior part of a left dentary that had been collected from the |
Megatherioidea
Sloths are a group of Neotropical xenarthran mammals constituting the suborder Folivora, including the extant arboreal tree sloths and extinct terrestrial ground sloths. Noted for their slowness of movement, tree sloths spend most of their lives hanging upside down in the trees of the tropical rainforests of South America and Central America. Sloths are considered to be most closely related to anteaters, together making up the xenarthran order Pilosa. There are six extant sloth species in two genera – '' Bradypus'' (three–toed sloths) and '' Choloepus'' (two–toed sloths). Despite this traditional naming, all sloths have three toes on each rear limb-- although two-toed sloths have only two digits on each forelimb. The two groups of sloths are from different, distantly related families, and are thought to have evolved their morphology via parallel evolution from terrestrial ancestors. Besides the extant species, many species of ground sloths ranging up to the size of elep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Parsimony (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, maximum parsimony is an optimality criterion under which the phylogenetic tree that minimizes the total number of character-state changes (or miminizes the cost of differentially weighted character-state changes) is preferred. Under the maximum-parsimony criterion, the optimal tree will minimize the amount of homoplasy (i.e., convergent evolution, parallel evolution, and evolutionary reversals). In other words, under this criterion, the shortest possible tree that explains the data is considered best. Some of the basic ideas behind maximum parsimony were presented by James S. Farris in 1970 and Walter M. Fitch in 1971. Maximum parsimony is an intuitive and simple criterion, and it is popular for this reason. However, although it is easy to ''score'' a phylogenetic tree (by counting the number of character-state changes), there is no algorithm to quickly ''generate'' the most-parsimonious tree. Instead, the most-parsimonious tree must be sought in "tree space" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalonyx
''Megalonyx'' (Greek, "large claw") is an extinct genus of ground sloths of the family Megalonychidae, native to North America during the Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs. It became extinct during the Quaternary extinction event at the end of the Rancholabrean of the Pleistocene, living from ~5 million to 11,000 years ago. The type species, ''M. jeffersonii'', measured about and weighed up to . ''Megalonyx'' is descended from ''Pliometanastes,'' a genus of ground sloth that had arrived in North America during the Late Miocene, prior to the Great American Biotic Interchange. ''Megalonyx'' had the widest distribution of any North American ground sloth, having a range encompassing most of the contiguous United States, extending as far north as Alaska during warm periods. Taxonomy In 1796, Colonel John Stuart sent Thomas Jefferson, shortly before he took office as Vice President of the United States, some fossil bones: a femur fragment, ulna, radius, and foot bones including three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalassocnus
''Thalassocnus'' is an extinct genus of semiaquatic ground sloths from the Miocene and Pliocene of the Pacific South American coast. It is monotypic within the subfamily Thalassocninae. The five species—''T. antiquus'', ''T. natans'', ''T. littoralis'', ''T. carolomartini'', and ''T. yuacensis''—represent a chronospecies, a population gradually adapting to marine life in one direct lineage. They are the only known aquatic sloths, but they may have also been adapted to a terrestrial lifestyle. They have been found in the Pisco Formation of Peru, the Tafna Formation of Argentina, and the Bahía Inglesa, Coquimbo, and Horcón formations of Chile. Thalassocninae has been placed in both the families Megatheriidae and Nothrotheriidae. ''Thalassocnus'' evolved several marine adaptations over the course of 4 million years, such as dense and heavy bones to counteract buoyancy, the internal nostrils migrating farther into the head to help with breathing while completely submerged, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nothrotherium
''Nothrotherium'' is an extinct genus of medium-sized ground sloth from South America (Bolivia, Brazil and the Ware Formation, La Guajira, Colombia).Amson et al., 2016, p.12 It differs from ''Nothrotheriops'' in smaller size and differences in skull and hind leg bones, but both genera can be traced back to ''Hapalops'', the genus which both evolved from in different ecological conditions. Taxonomy ''Nothrotherium'' is derived from the Greek ''nothros'' �ωθρός meaning "lazy" or "slothful," and ''therion'' �ηρίον "beast", and the species ''N. maquinense'' is named after the Maquiné Grotto in Brazil, where it was found. Synonyms such as ''Coelodon'' occasionally cause confusion where they occur in early texts such as that of Alfred Russel Wallace's major work, ''The Geographical Distribution of Animals'' (1876). This genus formerly included the species ''Nothrotheriops shastensis'', which was later moved to ''Nothrotheriops''. Description Analysis of a coprolite associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cingulata
Cingulata, part of the superorder Xenarthra, is an order of armored New World placental mammals. Dasypodids and chlamyphorids, the armadillos, are the only surviving families in the order. Two groups of cingulates much larger than extant armadillos (maximum body mass of 45 kg (100 lb) in the case of the giant armadillo) existed until recently: pampatheriids, which reached weights of up to 200 kg (440 lb) and chlamyphorid glyptodonts, which attained masses of 2,000 kg (4,400 lb) or more. The cingulate order originated in South America during the Paleocene epoch about 66 to 56 million years ago, and due to the continent's former isolation remained confined to it during most of the Cenozoic. However, the formation of a land bridge allowed members of all three families to migrate to southern North America during the Pliocene or early Pleistocene as part of the Great American Interchange. After surviving for tens of millions of years, all of the pampat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |