|
Autovía A-35
The Autovía A-35 (formerly known as the Almansa-Xàtiva highway) is a highway in the province of Valencia, Spain. It connects Xàtiva and the N-340 The N-340 is a major highway in Spain. It is over 1,000 km long starting south of Barcelona and running predominantly along the coast to Chiclana de la Frontera and the N-IV to Cádiz. In many places the road has now been by-passed by the .../ CV-40 to Almansa and the N-330 otherwise known as the Autovía de Levante. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Autovia A-35 A-35 A-35 A-35 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almansa
Almansa () is a Spanish town and municipality in the province of Albacete, part of the autonomous community of Castile-La Mancha. The name "Almansa" stems from the Arabic (al-manṣaf), "half way of the road". The municipality borders with Alicante, Valencia and Murcia. Almansa is famous for its '' Moros y cristianos'' festival from celebrated from 1 to 6 May. Almansa is built at the foot of a white limestone crag, which is surmounted by a Moorish castle, and rises abruptly in the midst of a fertile and irrigated plain. About south of the town centre stands an obelisk commemorating the Battle of Almansa fought there on 25 April 1707 during the War of Spanish Succession, in which a French, Spanish and Irish army under the command of duke of Berwick, a natural son of James II, routed the allied British, Portuguese and ''Spanish'' troops. Annual reenactments of that battle have been formally listed in the Spanish cultural register. The Sierra del Mugrón is located within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xàtiva
Xàtiva (, es, Játiva ) is a town in eastern Spain, in the province of Valencia, on the right (western) bank of the river Albaida and at the junction of the Valencia–Murcia and Valencia Albacete railways. It is located 25 km west of the Mediterranean Sea. During the Al-Andalus Islamic era, Arabs brought the technology to manufacture paper to Xàtiva. In the 12th century, Xàtiva was known for its schools, education, and learning circles. Islamic scholar Abu Ishaq al-Shatibi's last name refers to Xàtiva where he lived and died. After the Reconquista by Northern Christian kingdoms and the following Christian repopulation, the city became the cradle of one of the most powerful and controversial families of the Renaissance, the House of Borgia, which produced Popes like Callixtus III (Alfonso de Borgia) and Alexander VI (Rodrigo de Borgia). History Xàtiva (''Saetabis'' in Latin) was famous in Roman times for its linen fabrics, mentioned by the Latin poets Ovid and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
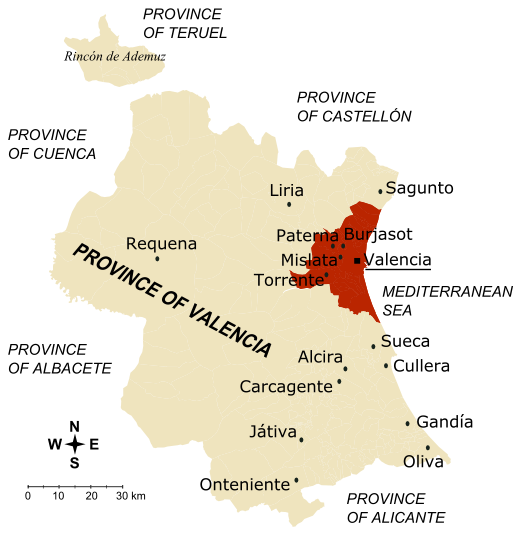
Valencia (province)
Valencia ( ca-valencia, València) is a province of Spain, in the central part of the autonomous Valencian Community. Of the province's over 2.5 million people (2018), one-third live in the capital, Valencia, which is also the capital of the autonomous community and the 3rd biggest city in Spain, with a metropolitan area of 2,522,383 people it is also one of the most populated cities of Southern Europe.http://appsso.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/nui/show.do?dataset=met_pjanaggr3&lang=en There are 265 municipalities in the province. History Although the Spanish Constitution of 1812 loosely created the province of València, a stable administrative entity does not arise until the territorial division of Spain in 1833, remaining today without major changes. The Provincial Council of Valencia dates from that period. After the Valencian Statute of Autonomy of 1982, the province became part of the Valencian Community. Valencian and Spanish are the official languages. Geography It is borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-340 (Road)
The N-340 is a major highway in Spain. It is over 1,000 km long starting south of Barcelona and running predominantly along the coast to Chiclana de la Frontera and the N-IV to Cádiz. In many places the road has now been by-passed by the Autovía A-7 and Autopista AP-7. It follows the former Roman road ''Via Augusta'', that was one of the main roads of Hispania. The N-340 route passes the Arc de Berà, a Roman arch. The road starts at the Passeig de Josep Carner in Barcelona. It follows the Avinguda del Paral·lel, Plaça d'Espanya, Carrer de Sants and Carretera de Collblanc before becoming the Carretera de Cadiz a Barcelona and heading through a series of suburbs and industrial areas. The road crosses the Llobregat valley with a junction with the Autovía A-2 and Autovía B-24, it heads through the Garraf Massif to Vilafranca del Penedès. It then heads along the coast to Tarragona, changing to the A7 until Cambrils, then crossing the River Ebro (delta) and on to Pen� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autovía A-36
The N-340 is a major highway in Spain. It is over 1,000 km long starting south of Barcelona and running predominantly along the coast to Chiclana de la Frontera and the N-IV to Cádiz. In many places the road has now been by-passed by the Autovía A-7 and Autopista AP-7. It follows the former Roman road ''Via Augusta'', that was one of the main roads of Hispania. The N-340 route passes the Arc de Berà, a Roman arch. The road starts at the Passeig de Josep Carner in Barcelona. It follows the Avinguda del Paral·lel, Plaça d'Espanya, Carrer de Sants and Carretera de Collblanc before becoming the Carretera de Cadiz a Barcelona and heading through a series of suburbs and industrial areas. The road crosses the Llobregat valley with a junction with the Autovía A-2 and Autovía B-24, it heads through the Garraf Massif to Vilafranca del Penedès. It then heads along the coast to Tarragona, changing to the A7 until Cambrils, then crossing the River Ebro (delta) and on to Pen� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-330 (Road)
The N-330 is a highway in Aragon, Spain. It forms part of European Route E7. It connects with France at the Tunnel of Somport (12 km) with Huesca. It then becomes the Autovía A-23 to Zaragoza. It heads south to Daroca, where it becomes the N-234. The road emerges again south of Teruel following the Rio Turia. The N-420 branches west in the Rincón de Valencia rising to over 1,000m. It then runs south to Utiel and the Autovía A-3 in the province of Valencia. At Requena the road heads south again into the Sierra Martés with a junction with the N-322 and then crosses the Puerto de Cruz de Confrentes and then down to the Rio Xúquer. Thereafter it passes the Reserva Nacional de Muela de Cortes and a series of olive groves to Almansa and the Autovía A-31 The Autovía A-31, also known as the Autovía de Alicante, is a highway in Spain. The road connects Madrid to Alicante. It starts at a junction with the Autovía A-3 at Alarcón and heads south east to Albac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In The Valencian Community
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations. Transport enables human trade, which is essential for the development of civilizations. Transport infrastructure consists of both fixed installations, including roads, railways, airways, waterways, canals, and pipelines, and terminals such as airports, railway stations, bus stations, warehouses, trucking terminals, refueling depots (including fueling docks and fuel stations), and seaports. Terminals may be used both for interchange of passengers and cargo and for maintenance. Means of transport are any of the different kinds of transport facilities used to carry people or cargo. They may include vehicles, riding animals, and pack animals. Vehicles may inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In Castilla–La Mancha
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations. Transport enables human trade, which is essential for the development of civilizations. Transport infrastructure consists of both fixed installations, including roads, railways, airways, waterways, canals, and pipelines, and terminals such as airports, railway stations, bus stations, warehouses, trucking terminals, refueling depots (including fueling docks and fuel stations), and seaports. Terminals may be used both for interchange of passengers and cargo and for maintenance. Means of transport are any of the different kinds of transport facilities used to carry people or cargo. They may include vehicles, riding animals, and pack animals. Vehicles may inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |