|
Autophony
Autophony is the unusually loud hearing of a person's own voice. Possible causes are: * The "occlusion effect", caused by an object, such as an unvented hearing aid or a plug of ear wax, blocking the ear canal and reflecting sound vibration back towards the eardrum. * Serous * Open or , allowing vocal or breathing sounds to be conducted into the middle ear * |
Superior Canal Dehiscence
Superior semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome is a set of hearing and balance symptoms, related to a rare medical condition of the inner ear, known as ''superior canal dehiscence''. The symptoms are caused by a thinning or complete absence of the part of the temporal bone overlying the superior semicircular canal of the vestibular system. There is evidence that this rare defect, or susceptibility, is congenital. There are also numerous cases of symptoms arising after physical trauma to the head. It was first described in 1998 by Lloyd B. Minor of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore. Symptoms Superior canal dehiscence (SCD) can affect both hearing and balance to different extents in different people. Symptoms of SCDS include: * Autophony – person's own speech or other self-generated noises (e.g. heartbeat, eye movements, creaking joints, chewing) are heard unusually loudly in the affected ear * Dizziness/ vertigo/ chronic disequilibrium caused by the dysfunction of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Canal Dehiscence Syndrome
Superior semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome is a set of hearing and balance symptoms, related to a rare medical condition of the inner ear, known as ''superior canal dehiscence''. The symptoms are caused by a thinning or complete absence of the part of the temporal bone overlying the superior semicircular canal of the vestibular system. There is evidence that this rare defect, or susceptibility, is congenital. There are also numerous cases of symptoms arising after physical trauma to the head. It was first described in 1998 by Lloyd B. Minor of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore. Symptoms Superior canal dehiscence (SCD) can affect both hearing and balance to different extents in different people. Symptoms of SCDS include: * Autophony – person's own speech or other self-generated noises (e.g. heartbeat, eye movements, creaking joints, chewing) are heard unusually loudly in the affected ear * Dizziness/ vertigo/ chronic disequilibrium caused by the dysfunction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occlusion Effect
The occlusion effect occurs when an object fills the outer portion of a person's ear canal, causing that person to perceive echo-like "hollow" or "booming" sounds generated from their own voice. The bone-conducted sound travels to the cochlea through different pathways. The outer ear pathway corresponds to the sound pressure generated in the ear canal cavity due to the vibration of the ear canal wall, which constitutes the source of the occlusion effect. At low frequencies, the outer ear pathway is negligible when the ear canal is open but dominates when it is occluded. The occlusion effect is thus objectively characterized by an acoustic pressure increase in the occluded ear canal at low frequencies and which can be measured with a probe-tube microphone. Considering that the vibrating ear canal wall acts as an ideal source of volume velocity (also known as volumetric flow rate), the occlusion device increases the “opposition” of the ear canal cavity to the volume velocity imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
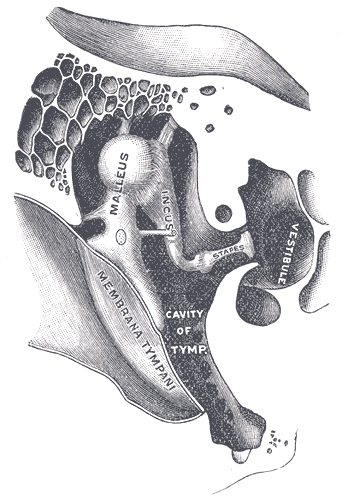
Ear Canal
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter. Structure The human ear canal is divided into two parts. The elastic cartilage part forms the outer third of the canal; its anterior and lower wall are cartilaginous, whereas its superior and back wall are fibrous. The cartilage is the continuation of the cartilage framework of pinna. The cartilaginous portion of the ear canal contains small hairs and specialized sweat glands, called apocrine glands, which produce cerumen ( ear wax). The bony part forms the inner two thirds. The bony part is much shorter in children and is only a ring (''annulus tympanicus'') in the newborn. The layer of epithelium encompassing the bony portion of the ear canal is much thinner and therefore, more sensitive in comparison to the cartilaginous portion. Size and sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otitis Media
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating and a fever may also be present. The other main type is otitis media with effusion (OME), typically not associated with symptoms, although occasionally a feeling of fullness is described; it is defined as the presence of non-infectious fluid in the middle ear which may persist for weeks or months often after an episode of acute otitis media. Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is middle ear inflammation that results in a perforated tympanic membrane with discharge from the ear for more than six weeks. It may be a complication of acute otitis media. Pain is rarely present. All three types of otitis media may be associated with hearing loss. If children with hearing loss due to OME do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patulous Eustachian Tube
Patulous Eustachian tube (PET) is the name of a physical disorder where the Eustachian tube, which is normally closed, instead stays intermittently open. When this occurs, the person experiences autophony, the hearing of self-generated sounds. These sounds, such as one's own breathing, voice, and heartbeat, vibrate directly onto the ear drum and can create a "bucket on the head" effect. PET is a form of eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD), which is said to be present in about 1 percent of the general population. Signs and symptoms With patulous Eustachian tube, variations in upper airway pressure associated with respiration are transmitted to the middle ear through the Eustachian tube. This causes an unpleasant fullness feeling in the middle ear and alters the auditory perception. Complaints seem to include muffled hearing and autophony. In addition, patulous Eustachian tube generally feels dry with no clogged feeling or sinus pressure. Patients hear their own voice or its ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symptoms And Signs Of Mental Disorders
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pain or pains in the body. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or abnormal physiological state that may be detected during a physical examination, examining the patient history, or diagnostic procedure. These signs are visible or otherwise detectable such as a rash or bruise. Medical signs, along with symptoms, assist in formulating diagnostic hypothesis. Examples of signs include elevated blood pressure, nail clubbing of the fingernails or toenails, staggering gait, and arcus senilis and arcus juvenilis of the eyes. Indication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid. In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the ... through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting Vibration, vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduction (physiology), transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |