|
Automatic Mutual Exclusion
Automatic mutual exclusion is a parallel computing programming paradigm in which threads are divided into atomic chunks, and the atomic execution of the chunks automatically parallelized using transactional memory. References See also * Bulk synchronous parallel The bulk synchronous parallel (BSP) abstract computer is a bridging model for designing parallel algorithms. It is similar to the parallel random access machine (PRAM) model, but unlike PRAM, BSP does not take communication and synchronization fo ... Parallel computing Programming paradigms {{compsci-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Computing
Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but has gained broader interest due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling.S.V. Adve ''et al.'' (November 2008)"Parallel Computing Research at Illinois: The UPCRC Agenda" (PDF). Parallel@Illinois, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "The main techniques for these performance benefits—increased clock frequency and smarter but increasingly complex architectures—are now hitting the so-called power wall. The computer industry has accepted that future performance increases must largely come from increasing the number of processors (or cores) on a die, rather than m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programming Paradigm
Programming paradigms are a way to classify programming languages based on their features. Languages can be classified into multiple paradigms. Some paradigms are concerned mainly with implications for the execution model of the language, such as allowing side effects, or whether the sequence of operations is defined by the execution model. Other paradigms are concerned mainly with the way that code is organized, such as grouping a code into units along with the state that is modified by the code. Yet others are concerned mainly with the style of syntax and grammar. Common programming paradigms include: * imperative in which the programmer instructs the machine how to change its state, ** procedural which groups instructions into procedures, ** object-oriented which groups instructions with the part of the state they operate on, * declarative in which the programmer merely declares properties of the desired result, but not how to compute it ** functional in which the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomicity (programming)
Atomicity may refer to: Chemistry * Atomicity (chemistry), the total number of atoms present in 1 molecule of a substance * Valence (chemistry), sometimes referred to as atomicity Computing * Atomicity (database systems), a property of database transactions which are guaranteed to either completely occur, or have no effects * Atomicity (programming), an operation appears to occur at a single instant between its invocation and its response * Atomicity, a property of an S-expression, in a symbolic language like Lisp Mathematics * Atomicity, an element of orthogonality in a component-based system * Atomicity, in order theory; see Atom (order theory) In the mathematical field of order theory, an element ''a'' of a partially ordered set with least element 0 is an atom if 0 < ''a'' and there is no ''x'' such that 0 < ''x'' < ''a''. Equivalently, one may define an atom to be an element that is < ... See also *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
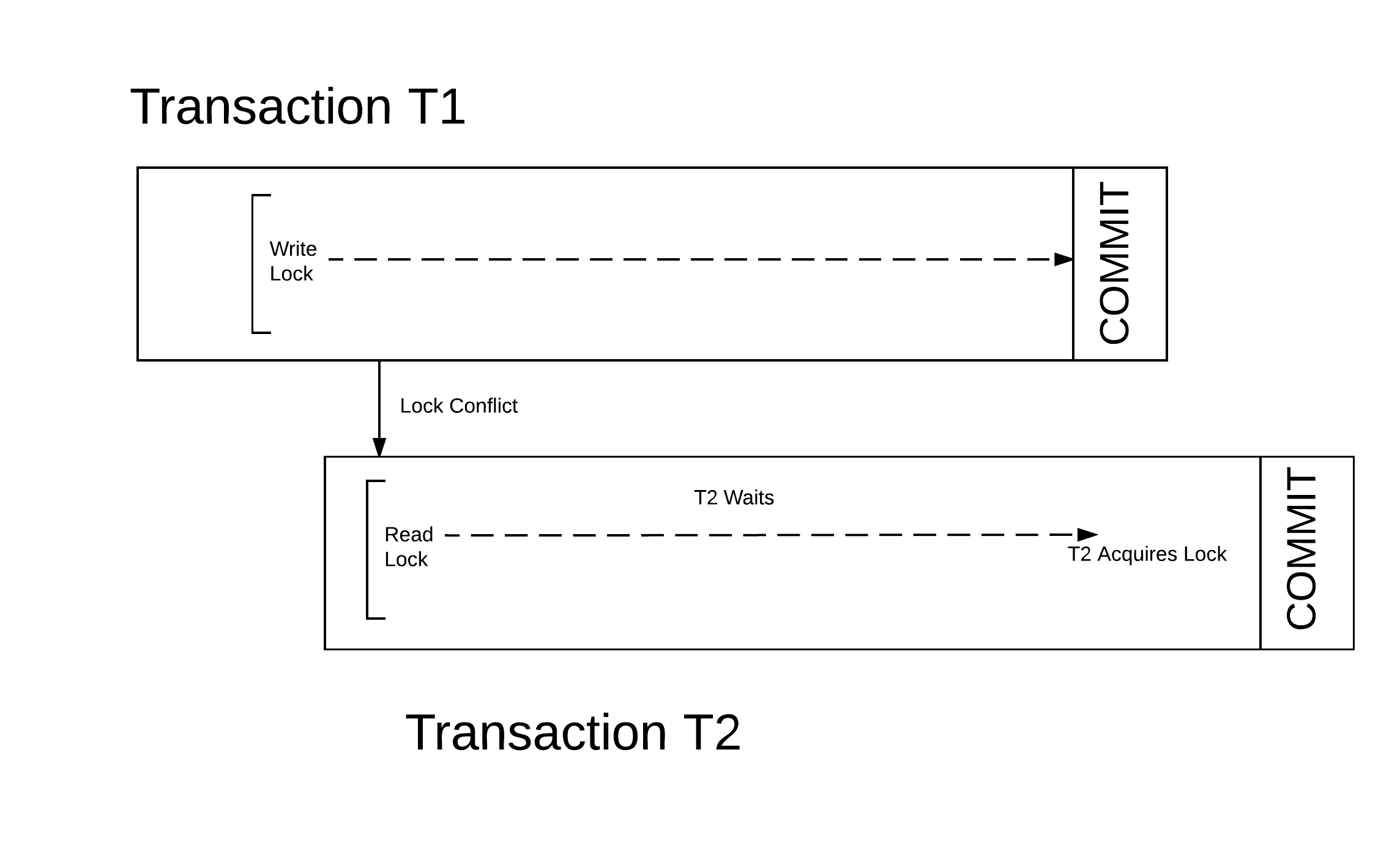
Transactional Memory
In computer science and engineering, transactional memory attempts to simplify concurrent programming by allowing a group of load and store instructions to execute in an atomic way. It is a concurrency control mechanism analogous to database transactions for controlling access to shared memory in concurrent computing. Transactional memory systems provide high-level abstraction as an alternative to low-level thread synchronization. This abstraction allows for coordination between concurrent reads and writes of shared data in parallel systems. Motivation In concurrent programming, synchronization is required when parallel threads attempt to access a shared resource. Low-level thread synchronization constructs such as locks are pessimistic and prohibit threads that are outside a critical section from making any changes. The process of applying and releasing locks often functions as additional overhead in workloads with little conflict among threads. Transactional memory provides o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulk Synchronous Parallel
The bulk synchronous parallel (BSP) abstract computer is a bridging model for designing parallel algorithms. It is similar to the parallel random access machine (PRAM) model, but unlike PRAM, BSP does not take communication and synchronization for granted. In fact, quantifying the requisite synchronization and communication is an important part of analyzing a BSP algorithm. History The BSP model was developed by Leslie Valiant of Harvard University during the 1980s. The definitive article was published in 1990.Leslie G. Valiant, A bridging model for parallel computation, Communications of the ACM, Volume 33 Issue 8, Aug. 199/ref> Between 1990 and 1992, Leslie Valiant and Bill McColl of Oxford University worked on ideas for a distributed memory BSP programming model, in Princeton and at Harvard. Between 1992 and 1997, McColl led a large research team at Oxford that developed various BSP programming libraries, languages and tools, and also numerous massively parallel BSP algorithm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Computing
Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but has gained broader interest due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling.S.V. Adve ''et al.'' (November 2008)"Parallel Computing Research at Illinois: The UPCRC Agenda" (PDF). Parallel@Illinois, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "The main techniques for these performance benefits—increased clock frequency and smarter but increasingly complex architectures—are now hitting the so-called power wall. The computer industry has accepted that future performance increases must largely come from increasing the number of processors (or cores) on a die, rather than m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |