|
Autochrome Lumière
The Autochrome Lumière was an early color photography process patented in 1903 by the Lumière brothers in France and first marketed in 1907. Autochrome was an additive color "mosaic screen plate" process. It was the principal color photography process in use before the advent of subtractive color film in the mid-1930s. Prior to the Lumière brothers, Louis Ducos du Hauron utilized the separation technique to create colour images on paper with screen plates, producing natural colours through superimposition, which would become the foundation of all commercial colour photography. Descendants of photographer Antoine Lumière, inventors Louis and Auguste Lumière utilized Du Hauron's (1869) technique, which had already been improved upon by other inventors such as John Joly (1894) and James William McDonough (1896), making it possible to print photographic images in colour. One of the most broadly used forms of colour photography in the early twentieth century, autochrome was re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visible Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 terahertz, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). In physics, the term "light" may refer more broadly to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. The primary properties of light are intensity, propagation direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum and polarization. Its speed in a vacuum, 299 792 458 metres a second (m/s), is one of the fundamental constants of nature. Like all types of electromagnetic radiation, visible light propagates by massless elementary particles called photons that represents the quanta of electromagnetic field, and can be analyzed as both waves and particl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass
Glass is a non-Crystallinity, crystalline, often transparency and translucency, transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the Melting, molten form; some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring. The most familiar, and historically the oldest, types of manufactured glass are "silicate glasses" based on the chemical compound silicon dioxide, silica (silicon dioxide, or quartz), the primary constituent of sand. Soda–lime glass, containing around 70% silica, accounts for around 90% of manufactured glass. The term ''glass'', in popular usage, is often used to refer only to this type of material, although silica-free glasses often have desirable properties for applications in modern communications technology. Some objects, such as drinking glasses and glasses, eyeglasses, are so commonly made of silicate- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Science And Media Museum
The National Science and Media Museum (formerly The National Museum of Photography, Film & Television, 1983–2006 and then the National Media Museum, 2006–2017), located in Bradford, West Yorkshire, is part of the national Science Museum Group in the UK. The museum has seven floors of galleries with permanent exhibitions focusing on photography, television, animation, videogaming, the Internet and the scientific principles behind light and colour. It also hosts temporary exhibitions and maintains a collection of 3.5 million pieces in its research facility. The venue has three cinemas, including Europe's first opened IMAX screen, finished in April 1983. It hosts festivals dedicated to widescreen film, video games and science. It has hosted popular film festivals, including the Bradford International Film Festival, until 2014. In September 2011 the museum was voted the best indoor attraction in Yorkshire by the public, and it is one of the most visited museums in the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pictorialist
Pictorialism is an international style and aesthetic movement that dominated photography during the later 19th and early 20th centuries. There is no standard definition of the term, but in general it refers to a style in which the photographer has somehow manipulated what would otherwise be a straightforward photograph as a means of creating an image rather than simply recording it. Typically, a pictorial photograph appears to lack a sharp focus (some more so than others), is printed in one or more colors other than black-and-white (ranging from warm brown to deep blue) and may have visible brush strokes or other manipulation of the surface. For the pictorialist, a photograph, like a painting, drawing or engraving, was a way of projecting an emotional intent into the viewer's realm of imagination. Pictorialism as a movement thrived from about 1885 to 1915, although it was still being promoted by some as late as the 1940s. It began in response to claims that a photograph was nothin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photo Manipulation
Photograph manipulation involves the transformation or alteration of a photograph using various methods and techniques to achieve desired results. Some photograph manipulations are considered to be skillful artwork, while others are considered to be unethical practices, especially when used to deceive the public. Other examples include being used for political propaganda, or to improve the appearance of a product or person, or simply as entertainment or practical jokes. Depending on the application and intent, some photograph manipulations are considered an art form because it involves the creation of unique images and in some instances, signature expressions of art by photographic artists. Ansel Adams employed some of the more common manipulations using darkroom exposure techniques, burning (darkening) and dodging (lightening) a photograph. Other examples of photo manipulation include retouching photographs using ink or paint, airbrushing, double exposure, piecing photo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incandescent Light Bulb
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxidation. Current is supplied to the filament by terminals or wires embedded in the glass. A bulb socket provides mechanical support and electrical connections. Incandescent bulbs are manufactured in a wide range of sizes, light output, and voltage ratings, from 1.5 volts to about 300 volts. They require no external regulating equipment, have low manufacturing costs, and work equally well on either alternating current or direct current. As a result, the incandescent bulb became widely used in household and commercial lighting, for portable lighting such as table lamps, car headlamps, and flashlights, and for decorative and advertising lighting. Incandescent bulbs are much less efficient than other types of electric lighting, converting le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Lamp
An arc lamp or arc light is a lamp that produces light by an electric arc (also called a voltaic arc). The carbon arc light, which consists of an arc between carbon electrodes in air, invented by Humphry Davy in the first decade of the 1800s, was the first practical electric light. It was widely used starting in the 1870s for street and large building lighting until it was superseded by the incandescent light in the early 20th century. It continued in use in more specialized applications where a high intensity point light source was needed, such as searchlights and movie projectors until after World War II. The carbon arc lamp is now obsolete for most of these purposes, but it is still used as a source of high intensity ultraviolet light. The term is now used for gas discharge lamps, which produce light by an arc between metal electrodes through a gas in a glass bulb. The common fluorescent lamp is a low-pressure mercury arc lamp. The xenon arc lamp, which produces a high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereopticon
A stereopticon is a slide projector or relatively powerful "magic lantern", which has two lenses, usually one above the other, and has mainly been used to project photographic images. These devices date back to the mid 19th century, and were a popular form of entertainment and education before the advent of moving pictures. Magic lanterns originally used rather weak light sources, like candles or oil lamps, that produced projections that were just large and strong enough to entertain small groups of people. During the 19th century stronger light sources, like limelight, became available. For the " dissolving views" lantern shows that were popularized by Henry Langdon Childe since the late 1830s, lanternists needed to be able to project two aligned pictures in the same spot on a screen, gradually dimming a first picture while revealing a second one. This could be done with two lanterns, but soon biunial lanterns (with two objectives placed one above the other) became common. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Lantern
The magic lantern, also known by its Latin name , is an early type of image projector that used pictures—paintings, prints, or photographs—on transparent plates (usually made of glass), one or more lens (optics), lenses, and a light source. Because a single lens inverts an image projected through it (as in the phenomenon which inverts the image of a camera obscura), slides were inserted upside down in the magic lantern, rendering the projected image correctly oriented. It was mostly developed in the 17th century and commonly used for entertainment purposes. It was increasingly used for education during the 19th century. Since the late 19th century, smaller versions were also mass-produced as toys. The magic lantern was in wide use from the 18th century until the mid-20th century when it was superseded by a compact version that could hold many 35 mm photographic slides: the slide projector. Technology Apparatus The magic lantern used a concave mirror behind a light s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereoscope
A stereoscope is a device for viewing a stereoscopic pair of separate images, depicting left-eye and right-eye views of the same scene, as a single three-dimensional image. A typical stereoscope provides each eye with a lens that makes the image seen through it appear larger and more distant and usually also shifts its apparent horizontal position, so that for a person with normal binocular depth perception the edges of the two images seemingly fuse into one "stereo window". In current practice, the images are prepared so that the scene appears to be beyond this virtual window, through which objects are sometimes allowed to protrude, but this was not always the custom. A divider or other view-limiting feature is usually provided to prevent each eye from being distracted by also seeing the image intended for the other eye. Most people can, with practice and some effort, view stereoscopic image pairs in 3D without the aid of a stereoscope, but the physiological depth cues result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
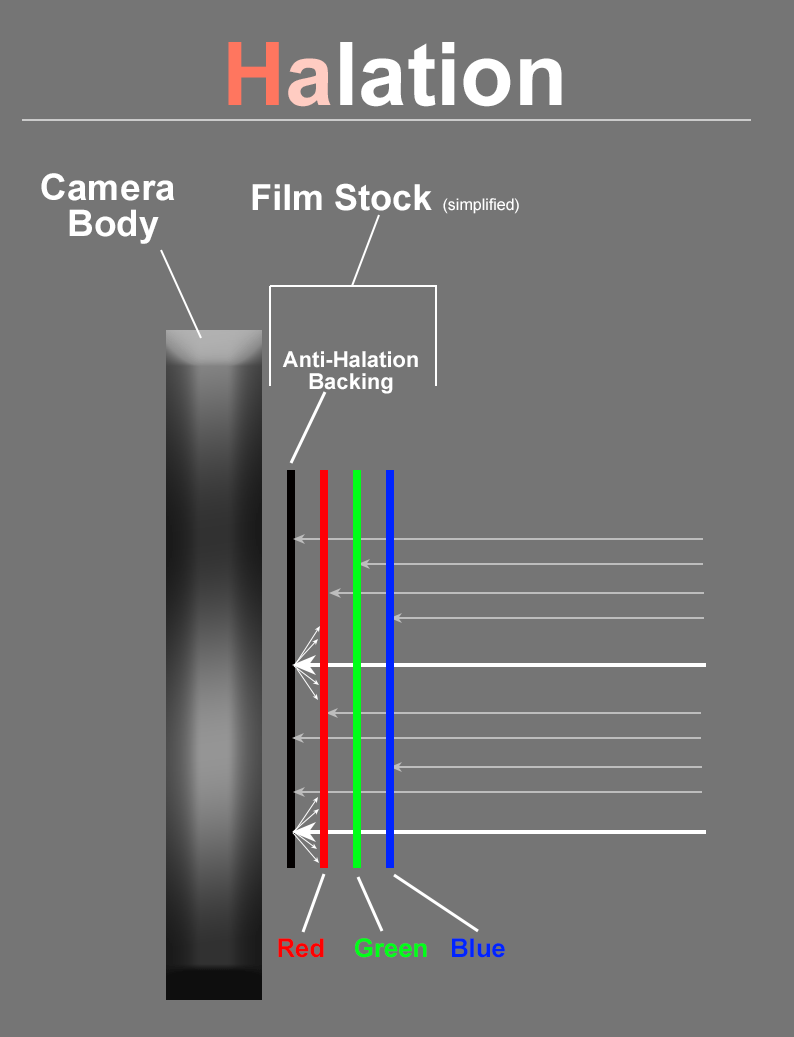
Anti-halation Backing
An anti-halation backing is a layer found in many photographic films—and almost all film intended for motion picture cameras—usually a coating on the back of the film base, though it is sometimes incorporated between the light-sensitive emulsion and the base. Its purpose is to absorb light that passes through the emulsion, thus preventing any light from being reflected back through the emulsion from the rear surface of the base, or from anything behind the film, such as the pressure plate of the camera. This prevents a halo-like effect (halation) from forming around bright points or edges in the image. Still cameras, which handle less film and thus contend with less wear, typically hold their film in the gate with components painted or treated to be black, so reflections are less of an issue and few still films made use of anti-halation backings. The notable exception was Kodak's Kodachrome, which incorporated such a backing to aid with a very sensitive innermost layer. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)







.jpg)