|
Australopristis
''Australopristis'' is an extinct genus of sawfish from the late Cretaceous epoch. Its name is derived from the Latin for "southern" and the Greek for "saw". It is known from a single species, ''A. wiffeni'' named for the late prominent fossil hunter Joan Wiffen. This species is currently known only from rostral teeth found at Mangahouanga stream and East Wing, Haumuri bluff, New Zealand. It's rostral teeth possess a smooth root which makes it unique among Sclerorhynchids. Rostral teeth appear to vary in morphology according to position and ontogenetic stage. Unlike the related ''Onchopristis'' and '' Atlanticopristis'', it lives in a marine rather than fluvial In geography and geology, fluvial processes are associated with rivers and streams and the deposits and landforms created by them. When the stream or rivers are associated with glaciers, ice sheets, or ice caps, the term glaciofluvial or fluviog ... environment and likely preferred cooler waters. References {{Taxon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onchopristis
''Onchopristis'' is an extinct genus of sclerorhynchoid from the Cretaceous of North Africa, Europe, and North America. Its name is derived from the Ancient Greek ''ónkos'' ( ὄγκος, 'barb') and ''prístis'' ( πρίστις, 'saw' or 'sawfish'). It contains two valid species, ''O. numida'' and ''O. dunklei''. ''Onchopristis'' first appeared in the Barremian and its latest occurrence dates to the Campanian, making it one of the oldest and longest-lived sclerorhynchoid genera. Description Specimens of ''O. numida'', IPUW 353500 and IGR 2818, suggest a length estimate of and , respectively; such individuals would have weighed . Like other sclerorhynchoids, it had a long rostrum with large denticles similar to sawfishes and sawsharks. This feature was convergently evolved and its closest living relatives are actually skates. Isolated rostral denticles are the most common fossils of ''Onchopristis'', but rostra, chondrocrania, jaws, oral teeth, vertebrae, and dermal den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerorhynchiformes
Sclerorhynchoidei is an extinct suborder of rajiform rays that had long rostra with large denticles similar to sawfishes and sawsharks. This feature was convergently evolved and their closest living relatives are actually skates. While they are often called "sawfishes", sawskates is a more accurate common name for sclerorhynchoids. The suborder contains five named families: Ganopristidae, Ischyrhizidae, Onchopristidae, Ptychotrygonidae, and Schizorhizidae. Several genera (see below) are not currently placed in any of these families. Sclerorhynchoids first appeared in the Barremian and went extinct during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, with former Paleocene occurrences being misidentifications or reworked specimens. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram of Sclerorhynchoidei, with the topology based on Villalobos-Segura ''et al.'' (2021b) and the family taxonomy based on Greenfield (2021). Other genera *†''Agaleorhynchus'' *†''Ankistrorhynchus'' *†''Arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animalia
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
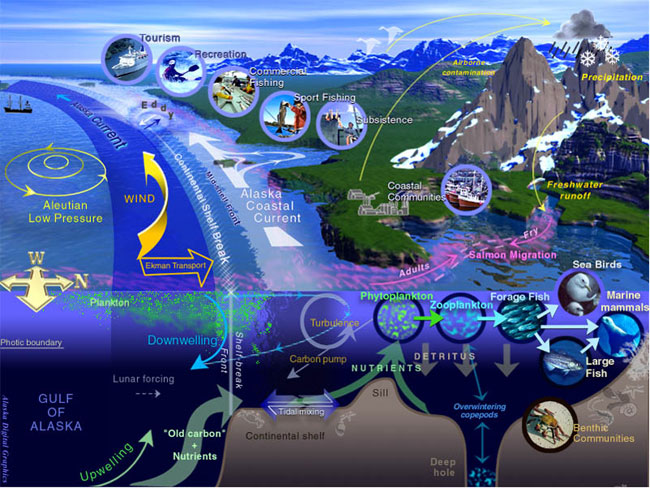
Marine Life
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. Marine organisms, mostly microorganisms, produce oxygen and sequester carbon. Marine life in part shape and protect shorelines, and some marine organisms even help create new land (e.g. coral building reefs). Most life forms evolved initially in marine habitats. By volume, oceans provide about 90% of the living space on the planet. The earliest vertebrates appeared in the form of fish, which live exclusively in water. Some of these evolved into amphibians, which spend portions of their lives in water and portions on land. One group of amphibians evolved into reptiles and mammals and a few subsets of each returned to the ocean as sea snakes, sea turtles, seals, manatees, and whales. Plant forms such as kelp and other algae grow in the wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlanticopristis
''Atlanticopristis'' (meaning "Atlantic saw") is an extinct genus of sclerorhynchid (a sawfish-like chondrichthyan) that lived during the Middle Cretaceous (Cenomanian) of what is now the Northeast Region of Brazil, between 100.5 and 93.9 million years ago. Fourteen fossil teeth from ''Atlanticopristis'' were found in the Alcântara Formation, and referred to the closely related ''Onchopristis'' in 2007; a redescription in 2008 by Brazilian paleontologists Manuel Medeiros and Agostinha Pereira assigned it to a new genus containing one species, ''Atlanticopristis equatorialis.'' Like all sawfish, it would have had a long snout armed with modified fish scales shaped into "teeth", but ''Atlanticopristis's'' teeth had barbs on both sides. ''Atlanticopristis'' inhabited fresh to brackish water estuaries near large conifer forests, and lived in the same time and place as many species of bony fish, cartilaginous fish, and lobe finned fish, as well as some crocodilians, and several di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontogenetic Stage
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the study of the entirety of an organism's lifespan. Ontogeny is the developmental history of an organism within its own lifetime, as distinct from phylogeny, which refers to the evolutionary history of a species. Another way to think of ontogeny is that it is the process of an organism going through all of the developmental stages over its lifetime. The developmental history includes all the developmental events that occur during the existence of an organism, beginning with the changes in the egg at the time of fertilization and events from the time of birth or hatching and afterward (i.e., growth, remolding of body shape, development of secondary sexual characteristics, etc.). While developmental (i.e., ontogenetic) processes can influence sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haumuri Bluff
Haumuri Bluff (also known as Amuri Bluff) is a headland on the coast of New Zealand's South Island on the south side of Piripaua (Spyglass Point), located several kilometres south of Oaro. It has been a major palaeontological site since the mid-19th century,Campbell, H.Haumuri Bluff, ''Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand'', 9 July 2013. Retrieved 24 June 2016. and has lent its name to the Haumurian stage in the New Zealand geologic time scale While also using the international geologic time scale, many nations–especially those with isolated and therefore non-standard prehistories–use their own systems of dividing geologic time into epochs and faunal stages. In New Zealand, these epo .... The bluff has also been the site of numerous shipwrecks. References Paleontological sites of New Zealand Headlands of Canterbury, New Zealand Kaikōura District {{CanterburyNZ-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joan Wiffen
Joan Wiffen (née Pederson, 4 February 1922 – 30 June 2009) was a self-taught New Zealand paleontologist known for discovering the first dinosaur fossils in New Zealand. Early life Wiffen was born in 1922 and was brought up in Havelock North, New Zealand, Havelock North and the King Country. She only had a very short secondary school education as her father believed that higher education was wasted on girls, resulting in her education opportunities being limited during her youth. At the age of 16, Wiffen joined the New Zealand Women's Auxiliary Air Force, Women's Auxiliary Air Force during World War II where she served for six years. Career In 1975 Wiffen discovered the first dinosaur fossils in New Zealand in the Mangahouanga Valley in Northern Hawkes Bay. Her first discovery was the tail bone of a Joan Wiffen's Theropod, theropod dinosaur. Her later finds included bones from a hypsilophodont, a pterosaur, an Ankylosauria, ankylosaur, mosasaurs and plesiosaurs. In 1999, W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordata
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These five synapomorphies include a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. The name “chordate” comes from the first of these synapomorphies, the notochord, which plays a significant role in chordate structure and movement. Chordates are also Bilateral symmetry, bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a circulatory system, and exhibit Metameric, metameric segmentation. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and mitochondrial inner membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |