|
Auricle Of Ear
Auricle is an Anglicization of Latin , from ''auris'' 'ear' and ''-cula'', a diminutive suffix. Auricle and auricula may refer to: * Auricle Ensemble, chamber ensemble * Auricular style, ornamental style based on parts of the human anatomy Medicine * Ear ** Auricle (anatomy), the external portion of the ear ** Auriculectomy, surgical removal of the ear ** Auricular branch (other), one of various nerves having to do with the ear or hearing ** Auricular muscles, muscles surrounding the ear * A small conical or ear-shaped pouch that projects from each atrium (heart); also, in some older texts, the atrium itself ** Left atrial appendage ** Right atrial appendage Biology * Auricle (botany), an earlike projection on the base of a leaf or petal (in some cyclamen species, for example) * An earlike projection at the base of the head of a planarium, which is sensitive to touch and the presence of certain chemicals * '' Primula auricula'', a species of primula, including t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auris
Auris may refer to: * Auris, Isère, a town in France * Auris, a snail genus, catalogued by George Washington Tryon * Toyota Auris, an automobile * Ear (Latin) * '' Auris'', the first ocean-going merchant ship powered by a gas turbine A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the directi ... See also * Auri (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
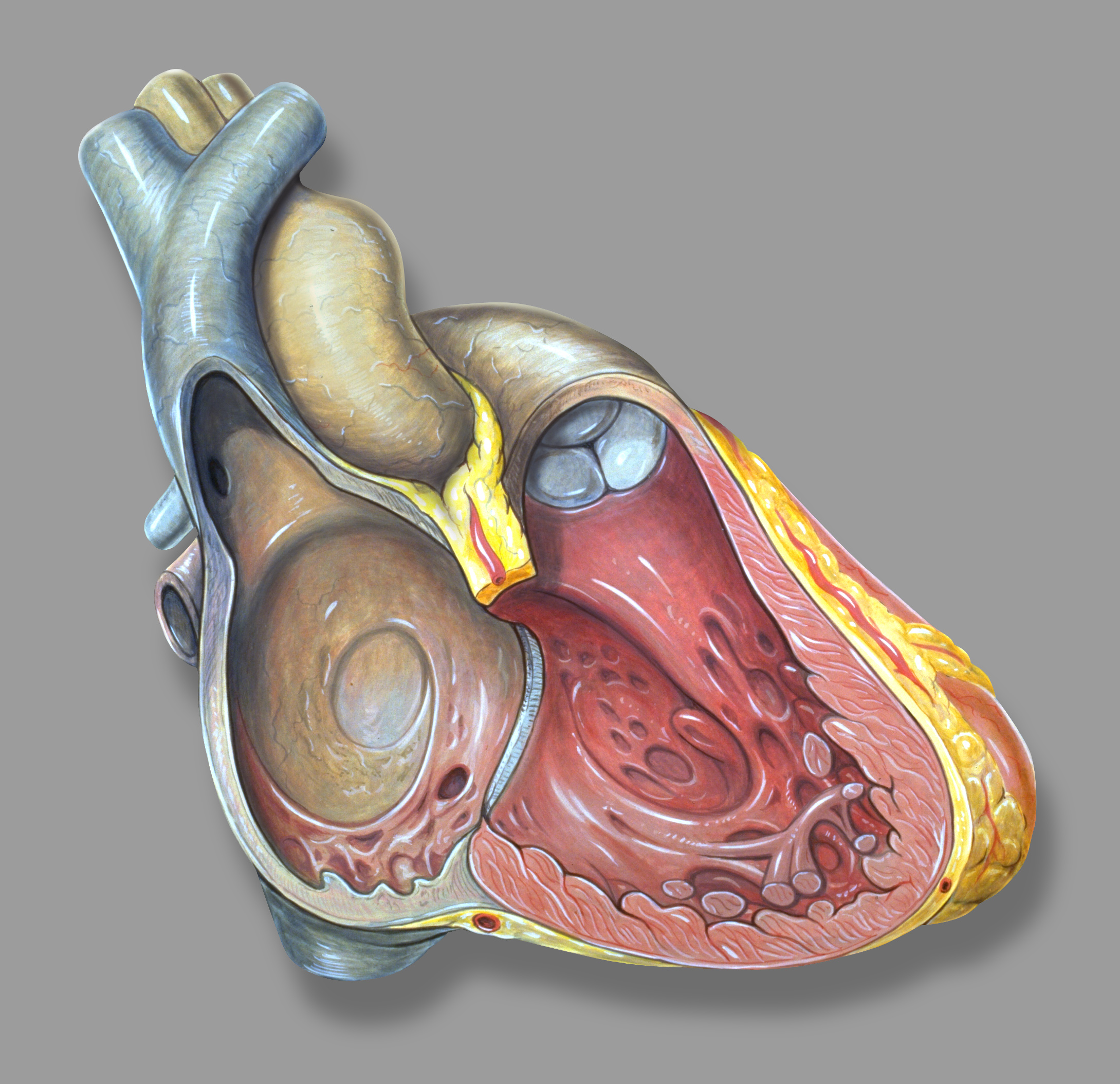
Atrium (heart)
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do. Structure Humans have a four-chambered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auricularia
''Auricularia'' is a genus of fungi in the family Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ... Auriculariaceae. Basidiocarps (fruit bodies) are typically gelatinous and ear-shaped, with a slightly downy to conspicuously hirsute upper surface and an under surface that is smooth, wrinkled or veined. All species grow on wood. Several ''Auricularia'' species are edible and commercially cultivated on a large scale in China and East Asia. Taxonomy The genus was first introduced in 1780 by French mycologist Jean Baptiste François Pierre Bulliard, Pierre Bulliard for a range of different fungi producing fruit bodies with an ear-like shape. In 1822 Christian Hendrik Persoon restricted the genus to two gelatinous species, ''Auricularia mesenterica'' (which became the type species) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auriculariales
The Auriculariales are an order of fungi in the class Agaricomycetes. Species within the order were formerly referred to the "heterobasidiomycetes" or "jelly fungi", since many have gelatinous basidiocarps (fruit bodies) that produce spores on septate basidia. Around 200 species are known worldwide, placed in six or more families, though the status of these families is currently uncertain. All species in the Auriculariales are believed to be saprotrophic, most growing on dead wood. Fruit bodies of several ''Auricularia'' species are cultivated for food on a commercial scale, especially in China. Taxonomy History The order was established in 1889 by German mycologist Joseph Schröter to accommodate species of fungi having "auricularioid" basidia (more or less cylindrical basidia with lateral septa), including many of the rusts and smuts. In 1922, British mycologist Carleton Rea recognized the order as containing the families Auriculariaceae and Ecchynaceae, as well as the rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primula Auricula
''Primula auricula'', often known as auricula, mountain cowslip or bear's ear (from the shape of its leaves), is a species of flowering plant in the family Primulaceae, that grows on basic rocks in the mountain ranges of central Europe, including the western Alps, Jura Mountains, the Vosges, the Black Forest and the Tatra Mountains. Description It is an evergreen perennial growing to tall by wide. The leaves are obovate and stalkless, with a cartilaginous edge, all growing in a basal rosette, and sometimes covered in a mealy white bloom. The yellow flowers grow in clusters on long stalks. The specific epithet ''auricula'' means "ear-shaped", and refers to the shape of the leaves. Taxonomy A recent study split the species into two, '' Primula lutea'' and ''P. auricula'', with the former being found further south and east (Apennines, Carpathians, Balkans, and the southern and eastern Alps). Prior to this study, ''P. lutea'' had been considered synonymous with ''P. auricula' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planarian
A planarian is one of the many flatworms of the traditional class Turbellaria. It usually describes free-living flatworms of the order Tricladida (triclads), although this common name is also used for a wide number of free-living platyhelminthes. Planaria are common to many parts of the world, living in both saltwater and freshwater ponds and rivers. Some species are terrestrial and are found under logs, in or on the soil, and on plants in humid areas. The triclads are characterized by triply branched intestine and anteriorly situated ovaries, next to the brain. Today the order Tricladida is split into three suborders, according to their phylogenetic relationships: Maricola, Cavernicola and Continenticola. Formerly, the Tricladida was split according to habitats: Maricola, which is marine; Paludicola which inhabits freshwater; and Terricola, which is land-dwelling. Planaria exhibit an extraordinary ability to regenerate lost body parts. For example, a planarian split lengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auricle (botany)
In botany, an auricle is a small ear-like projection from the base of a leaf or petal Petals are modified Leaf, leaves that surround the reproductive parts of flowers. They are often advertising coloration, brightly colored or unusually shaped to attract pollinators. All of the petals of a flower are collectively known as the ''c .... ReferencesDictionary of Botany Plant morphology {{botany-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrium (heart)
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do. Structure Humans have a four-chambered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auricular Muscles
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the external part of the ear, which consists of the auricle (also pinna) and the ear canal. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum (tympanic membrane). Structure Auricle The visible part is called the auricle, also known as the pinna, especially in other animals. It is composed of a thin plate of yellow elastic cartilage, covered with integument, and connected to the surrounding parts by ligaments and muscles; and to the commencement of the ear canal by fibrous tissue. Many mammals can move the pinna (with the auriculares muscles) in order to focus their hearing in a certain direction in much the same way that they can turn their eyes. Most humans do not have this ability. Ear canal From the pinna, the sound waves move into the ear canal (also known as the ''external acoustic meatus'') a simple tube running through to the middle ear. This tube leads inward from the bottom of the auricula and conducts the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auricular Branch (other)
Auricular branch (in Latin, "ramus auricularis") can refer to any one of several different structures having to do with the ear or hearing: *Nerves **The auricular branch of the vagus nerve - "ramus auricularis nervi vagi" (also known as the Alderman's nerve) **The auricular branch of the posterior auricular nerve - "ramus auricularis nervus auricularis posterioris" *Arteries **The auricular branch of the occipital artery - "ramus auricularis arteriae occipitalis" **The auricular branch of the posterior auricular artery - "ramus auricularis arteriae auricularis posterioris" **The anterior auricular branches of the superficial temporal artery - "rami auriculares anteriores arteriae temporalis superficialis" {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auriculectomy
Auriculectomy is the surgical removal of the ear due to disease or trauma Trauma most often refers to: *Major trauma, in physical medicine, severe physical injury caused by an external source *Psychological trauma, a type of damage to the psyche that occurs as a result of a severely distressing event *Traumatic inju ..., generally followed by rehabilitation involving an ear prosthesis., p. 124. References Surgical removal procedures {{surgery-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

