|
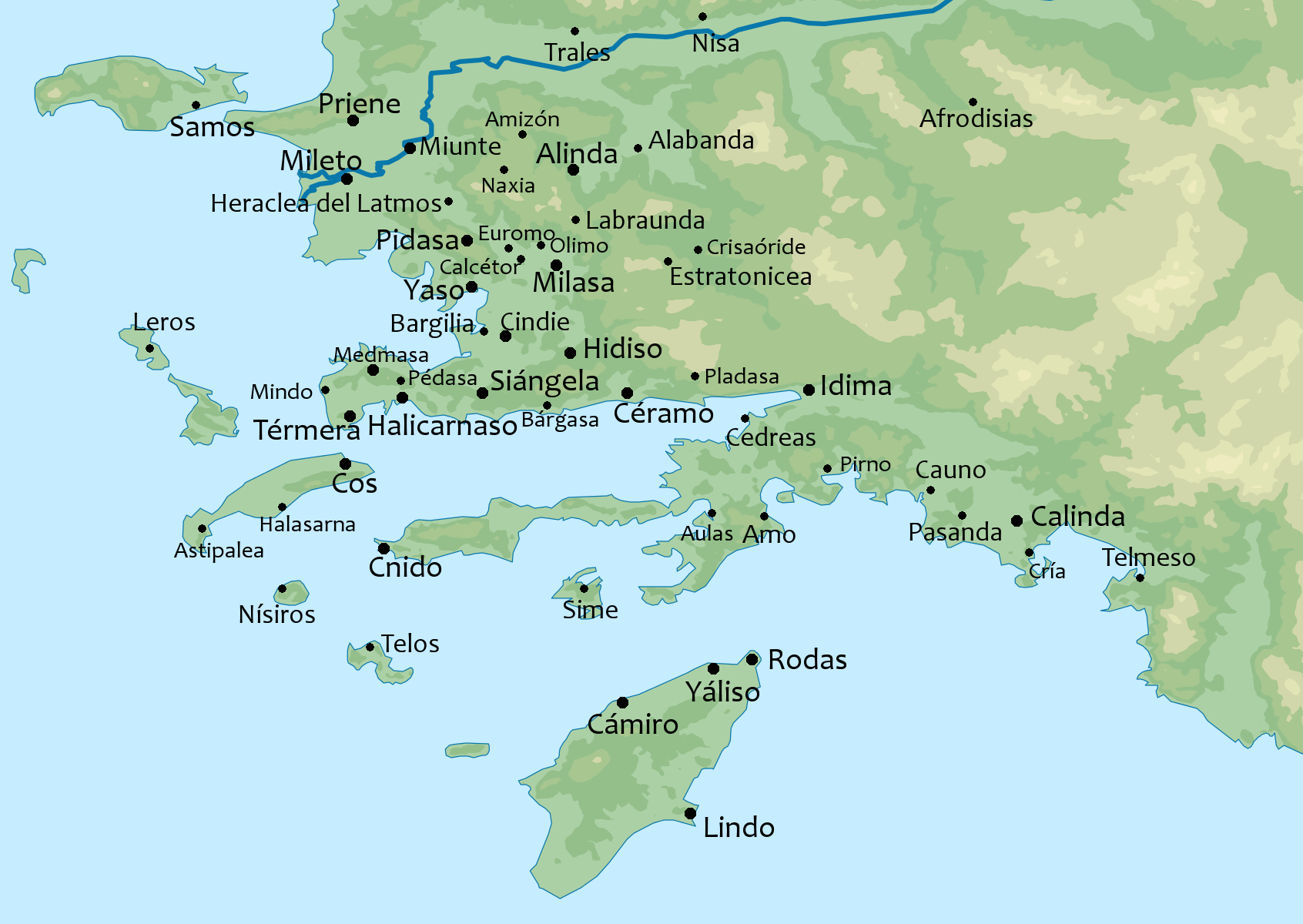
Aurelia Neapolis
Aurelia Neapolis, or Neapolis ( grc, Νεάπολις), was an inland town of ancient Caria, between Orthosia and Aphrodisias, at the foot of Mount Cadmus, in the neighbourhood of Harpasa. During Roman times, it bore the name of Aurelia Neapolis. Its site is located near modern Inebolu, Turkey Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with .... References Populated places in ancient Caria Former populated places in Turkey History of Aydın Province {{Aydın-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there. Carians were described by Herodotus as being of Minoan descent,''The Histories'', Book I Section 171. while he reports that the Carians themselves maintained that they were Anatolian mainlanders intensely engaged in seafaring and were akin to the Mysians and the Lydians. The Carians spoke Carian, a native Anatolian language closely related to Luwian. Also closely associated with the Carians were the Leleges, which could be an earlier name for Carians. Municipalities of Caria Cramer's detailed catalog of Carian towns in classical Greece is based entirely on ancient sources. The multiple names of towns and geomorphic features, such as bays and headlands, reveal an ethnic layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthosia (Caria)
Orthosia ( grc, Ὀρθωσία) was a town of ancient Caria, inhabited during Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine times. It was not far from Alabanda, on the left bank of the Maeander River, and apparently on or near a hill of the same name. Near this town the Rhodians gained a victory over the Carians. It was the seat of a bishop from an early date, and, while no longer a residential bishopric, it remains under the name Orthosias in Caria a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a .... Its site is located near Yenipazar in Asiatic Turkey. References Catholic titular sees in Asia Populated places in ancient Caria Former populated places in Turkey Roman towns and cities in Turkey Populated places of the Byzantine Empire H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphrodisias
Aphrodisias (; grc, Ἀφροδισιάς, Aphrodisiás) was a small Ancient Greece, ancient Greek Hellenistic_period, Hellenistic city in the historic Caria cultural region of western Anatolia, Turkey. It is located near the modern village of Geyre, about east/inland from the coast of the Aegean Sea, and southeast of İzmir. Aphrodisias was named after Aphrodite, the Greek goddess of love, who had here her unique cult image, the ''Aphrodite of Aphrodisias''. According to the Suda, a Byzantine encyclopedic compilation, before the city became known as Aphrodisias (c.3rd century BCE) it had three previous names: ''Lelégōn Pólis'' (Λελέγων πόλις, "City of the Leleges"), ''Megálē Pólis'' (Μεγάλη Πόλις, "Great City"), and ''Ninó''ē (Νινόη). Sometime before 640, in the Late Antiquity, Late Antique period when it was within the Byzantine Empire, the city was renamed ''Stauropolis'' (Σταυρούπολις, "City of the Cross").Siméon Vailhé, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Cadmus
Mount is often used as part of the name of specific mountains, e.g. Mount Everest. Mount or Mounts may also refer to: Places * Mount, Cornwall, a village in Warleggan parish, England * Mount, Perranzabuloe, a hamlet in Perranzabuloe parish, Cornwall, England * Mounts, Indiana, a community in Gibson County, Indiana, United States People * Mount (surname) * William L. Mounts (1862–1929), American lawyer and politician Computing and software * Mount (computing), the process of making a file system accessible * Mount (Unix), the utility in Unix-like operating systems which mounts file systems Displays and equipment * Mount, a fixed point for attaching equipment, such as a hardpoint on an airframe * Mounting board, in picture framing * Mount, a hanging scroll for mounting paintings * Mount, to display an item on a heavy backing such as foamcore, e.g.: ** To pin a biological specimen, on a heavy backing in a stretched stable position for ease of dissection or display ** To p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harpasa
Harpasa ( grc, Ἅρπασα) was a city and bishopric in ancient Caria in Roman Asia Minor (Asian Turkey), which only remains a Latin Catholic titular see. History Little is known of the history of this town, situated on the east bank of the Harpasus, a tributary of the Büyük Menderes River, Mæander. It is mentioned by Ptolemy, by Stephanus Byzantius, by Hierocles (author of Synecdemus), Hierocles, and by Pliny the Elder. According to Pliny, there was in the neighbourhood a rocking-stone which could be set in motion by a finger-touch, whereas the force of the whole body could not move it. The Ancient Armenian village that resided in present-day Turkey hosts the ruined castle of Arpaz, in the district of Nazilli, nearly preserves the old name as does the Turkish form Harpaskale. Bishopric It was important enough in the late Roman province of Caria (civil Diocese of Asia) to become a bishopric, a suffragan of the archbishopric of Stauropolis , in the sway of the Patriarchat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Anatolia
Classical Anatolia is Anatolia during Classical Antiquity. Early in that period, Anatolia was divided into several Iron Age kingdoms, most notably Lydia in the west, Phrygia in the center and Urartu in the east. Anatolia fell under Achaemenid Persian rule c. 550 BC. In the aftermath of the Greco-Persian Wars, all of Anatolia remained under Persian control except for the Aegean coast, which was incorporated in the Delian League in the 470s BC. Alexander the Great finally wrested control of the whole region from Persia in the 330s BC. After Alexander's death, his conquests were split amongst several of his trusted generals, but were under constant threat of invasion from both the Gauls and other powerful rulers in Pergamon, Pontus, and Egypt. The Seleucid Empire, the largest of Alexander's territories, and which included Anatolia, became involved in a disastrous war with Rome culminating in the battles of Thermopylae and Magnesia. The resulting Treaty of Apamea in (188 BC) saw th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a East Thrace, small portion on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It shares borders with the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia to the northeast; Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq to the southeast; Syria and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; the Aegean Sea to the west; and Greece and Bulgaria to the northwest. Cyprus is located off the south coast. Turkish people, Turks form the vast majority of the nation's population and Kurds are the largest minority. Ankara is Turkey's capital, while Istanbul is its list of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city and financial centre. One of the world's earliest permanently Settler, settled regions, present-day Turkey was home to important Neol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Ancient Caria
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Turkey
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |