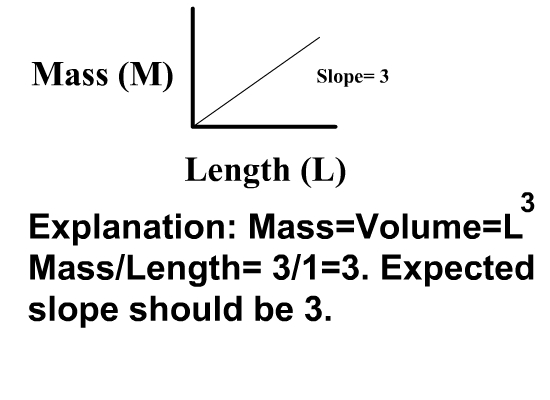
|
Aulacocephalodon
''Aulacephalodon'' is an extinct genus of medium-sized dicynodonts, or non-mammalian synapsids, that lived during Permian period, about 299-252 million years ago. Individuals of ''Aulacephalodon'' are commonly found in the Lower Beaufort Group of the Karoo Supergroup of South Africa and Zambia. Rising to dominance during the Late Permian, ''Aulacephalodon'' were the dominant terrestrial vertebrate herbivores until they became extinct during the Triassic. No living relatives of ''Aulacephalodon'' exist today. Two species have been named, the type species, ''A. bainii,'' and a second species, ''A. peavoti''. However, debate exists among paleontologists if ''A. peavoti'' is a true member of the genus ''Aulacephalodon''. Therefore, a majority of the information known about ''Aulacephalodon'' is in reference to discoveries about ''A. bainii''. The name ''Aulacephalodon'' combines the Greek words aulak- (aulax), meaning "a furrow", kephale, meaning "head," and odon, meaning tooth. Toge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomodont
Anomodontia is an extinct group of non-mammalian therapsids from the Permian and Triassic periods. By far the most speciose group are the dicynodonts, a clade of beaked, tusked herbivores.Chinsamy-Turan, A. (2011) ''Forerunners of Mammals: Radiation - Histology - Biology''p.39.Indiana University Press, . Retrieved May 2012 Anomodonts were very diverse during the Middle Permian, including primitive forms like ''Anomocephalus'' and ''Patranomodon'' and groups like Venyukovioidea and Dromasauria. Dicynodonts became the most successful and abundant of all herbivores in the Late Permian, filling ecological niches ranging from large browsers down to small burrowers. Few dicynodont families survived the Permian–Triassic extinction event, but one lineage (Kannemeyeriiformes) evolved into large, stocky forms that became dominant terrestrial herbivores right until the Late Triassic, when changing conditions caused them to decline, finally going extinct during the Triassic-Jurassic ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1898 In Paleontology
Dinosaurs Plesiosaurs New taxa Synapsids Non-mammalian {, class="wikitable sortable" align="center" width="100%" , - ! Name ! Status ! Authors ! Age ! Unit ! Location ! width="33%" class="unsortable" , Notes ! class="unsortable", Images , - , '' Aulacocephalodon'' , Valid , Seeley , , , , , rowspan="99", , - , ''Aulacephalodon'' , Valid , Seeley , , , , , - , ''Rhachiocephalus ''Rhachiocephalus'' is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsid Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their orig ...'' , Valid , Seeley , , , , , - References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geikiidae
Geikiidae is a family of Late Permian dicynodonts. Fossils are known from Scotland, South Africa, and Tanzania. The family was first named by Franz Nopcsa in 1923, although Friedrich von Huene's 1948 description of the family brought it into common usage. Von Huene established Geikiidae as a monotypic family for ''Geikia'', then known from Scotland. He distinguished ''Geikia'' from all other dicynodonts because it lacked a preparietal bone. The outlines on the bones of the skull roof could not be seen however, meaning that this characteristic was uncertain in geikiids. Geikiids were originally classified as close relatives of ''Dicynodon'' and ''Lystrosaurus ''Lystrosaurus'' (; 'shovel lizard'; proper Greek is λίστρον ''lístron'' ‘tool for leveling or smoothing, shovel, spade, hoe’) is an extinct genus of herbivorous dicynodont therapsids from the late Permian and Early Triassic epochs (a ...'', but the characters that linked these dicynodonts are also seen in many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicynodont
Dicynodontia is an extinct clade of anomodonts, an extinct type of non-mammalian therapsid. Dicynodonts were herbivorous animals with a pair of tusks, hence their name, which means 'two dog tooth'. Members of the group possessed a horny, typically toothless beak, unique amongst all synapsids. Dicynodonts first appeared in Southern Pangaea during the mid-Permian, ca. 270–260 million years ago, and became globally distributed and the dominant herbivorous animals in the Late Permian, ca. 260–252 Mya. They were devastated by the end-Permian Extinction that wiped out most other therapsids ca. 252 Mya. They rebounded during the Triassic but died out towards the end of that period. They were the most successful and diverse of the non-mammalian therapsids, with over 70 genera known, varying from rat-sized burrowers to elephant-sized browsers. Characteristics The dicynodont skull is highly specialised, light but strong, with the synapsid temporal openings at the rear of the skull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oudenodon
''Oudenodon'' is an extinct genus of dicynodont. It was common throughout southern Africa during the Late Permian. Several species of ''Oudenodon'' are known. Both ''O. bainii'', the type species, and ''O. grandis'' are known from South Africa. Specimens of ''O. luangwensis'' have been found from Zambia. One species, ''O. sakamenensis'', is the only Permian therapsid yet known from Madagascar.Mazin, J. M. and King, G. M. (1991). The first dicynodont from the Late Permian of Malagasy. ''Palaeontology'' 34:837–842. It is the type genus of the family Oudenodontidae, which includes members such as '' Tropidostoma''. See also * List of therapsids References The main groups of non-mammalian synapsids at Mikko's Phylogeny Archive External links ''Oudenodon''in the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistecephalus Assemblage Zone
The ''Cistecephalus'' Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod assemblage zone or biozone found in the Adelaide Subgroup of the Beaufort Group, a majorly fossiliferous and geologically important geological group of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. This biozone has outcrops located in the Teekloof Formation north-west of Beaufort West in the Western Cape, in the upper Middleton and lower Balfour Formations respectively from Colesberg of the Northern Cape to east of Graaff-Reinet in the Eastern Cape. The ''Cistecephalus'' Assemblage Zone is one of eight biozones found in the Beaufort Group, and is considered to be Late Permian in age. The name of the biozone refers to ''Cistecephalus'', a small, burrowing dicynodont therapsid. It is characterized by the presence of this species, known especially from the upper sections of this biozone, and the first appearance of the dicynodont ''Aulacephalodon''. History The first fossils to be found in the Beaufort Group rocks that encompass the cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biostratigraphy
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock Stratum, strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of Biology'', 8th ed., Oxford University Press, 2019. The primary objective of biostratigraphy is ''correlation'', demonstrating that a particular Horizon (geology), horizon in one geological section represents the same period of time as another horizon at a different section. Fossils within these strata are useful because sediments of the same age can look completely different, due to local variations in the Sedimentary depositional environment, sedimentary environment. For example, one section might have been made up of clays and marls, while another has more chalky limestones. However, if the fossil species recorded are similar, the two sediments are likely to have been laid down around the same time. Ideally these fossils are used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will , image_map = , map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1 = State , subdivision_type2 = Counties , subdivision_name1 = Illinois , subdivision_name2 = Cook and DuPage , established_title = Settled , established_date = , established_title2 = Incorporated (city) , established_date2 = , founder = Jean Baptiste Point du Sable , government_type = Mayor–council , governing_body = Chicago City Council , leader_title = Mayor , leader_name = Lori Lightfoot ( D) , leader_title1 = City Clerk , leader_name1 = Anna Valencia ( D) , unit_pref = Imperial , area_footnotes = , area_tot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following: * jawless fish, which include hagfish and lampreys * jawed vertebrates, which include: ** cartilaginous fish (sharks, rays, and ratfish) ** bony vertebrates, which include: *** ray-fins (the majority of living bony fish) *** lobe-fins, which include: **** coelacanths and lungfish **** tetrapods (limbed vertebrates) Extant vertebrates range in size from the frog species ''Paedophryne amauensis'', at as little as , to the blue whale, at up to . Vertebrates make up less than five percent of all described animal species; the rest are invertebrates, which lack vertebral columns. The vertebrates traditionally include the hagfish, which do no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allometry
Allometry is the study of the relationship of body size to shape, anatomy, physiology and finally behaviour, first outlined by Otto Snell in 1892, by D'Arcy Thompson in 1917 in ''On Growth and Form'' and by Julian Huxley in 1932. Overview Allometry is a well-known study, particularly in statistical shape analysis for its theoretical developments, as well as in biology for practical applications to the differential growth rates of the parts of a living organism's body. One application is in the study of various insect species (e.g., Hercules beetles), where a small change in overall body size can lead to an enormous and disproportionate increase in the dimensions of appendages such as legs, antennae, or horns The relationship between the two measured quantities is often expressed as a power law equation (Allometric equation) which expresses a remarkable scale symmetry: : y = kx^a \,\! or in a logarithmic form: : \log y = a \log x + \log k\,\! or similarly \ln y = a \ln x ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontology
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek (, "old, ancient"), (, ( gen. ), "being, creature"), and (, "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics, and engineering. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |