|
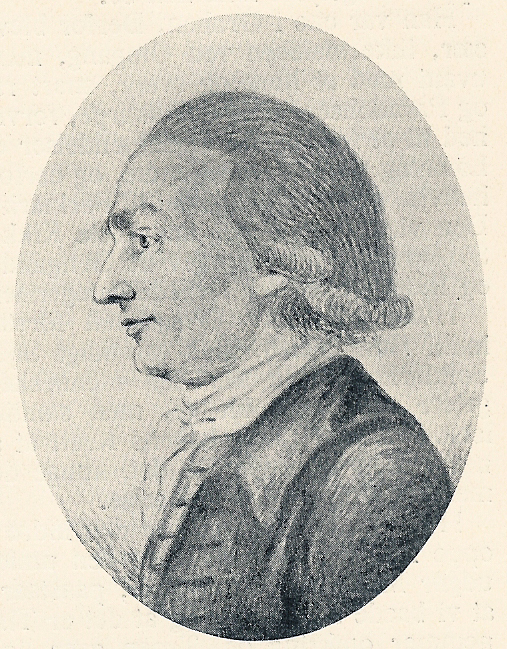
August Von Herder
August von Herder (18 August 1776 - 29 January 1838) was a German geologist and mineralogist. From 1813 he served in a succession of increasingly senior posts in the Saxon government mines service, ending up in 1826 as government mining director (''"Berghauptmann"''). He was an energetic and highly effective moderniser of the Saxon mining industry. Biography ''Sigismund August Wolfgang Herder'' was born in Bückeburg, an economically diversified hill-town to the west of Hanover. Bückeburg owed much of its prosperity and intellectual dynamism to its status as the long-established administrative and commercial hub of Schaumburg-Lippe. The adjacent Bückeberg hills were an important source of building stone. However, later during 1776, August's family relocated to Weimar after his father accepted a church appointment there, mediated through the intervention of his friend Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, as "Generalsuperintendent". August was the second son of the philosopher-poet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electorate Of Hanover
The Electorate of Hanover (german: Kurfürstentum Hannover or simply ''Kurhannover'') was an electorate of the Holy Roman Empire, located in northwestern Germany and taking its name from the capital city of Hanover. It was formally known as the Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg (german: Kurfürstentum Braunschweig-Lüneburg). For most of its existence, the electorate was ruled in personal union with Great Britain and Ireland following the Hanoverian Succession. The Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg had been split in 1269 between different branches of the House of Welf. The Principality of Calenberg, ruled by a cadet branch of the family, emerged as the largest and most powerful of the Brunswick-Lüneburg states. In 1692, the Holy Roman Emperor elevated the Prince of Calenberg to the College of Electors, creating the new Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg. The fortunes of the Electorate were tied to those of Great Britain by the Act of Settlement 1701 and Act of Union 1707, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss French
Swiss French (french: français de Suisse or ') is the variety of French spoken in the French-speaking area of Switzerland known as Romandy. French is one of the four official languages of Switzerland, the others being German, Italian, and Romansch. In 2020, around 2 million people in the country (22.8% of the population) spoke French as their primary language, and French was the most frequently used language for 28% of the labour market. The French spoken in Switzerland is very similar to that of France or Belgium due to historical French policy of education in Francien French only in schools after the French Revolution. The differences between the French of Switzerland and of France are mostly lexical, influenced by local substrate languages. This contrasts with the differences between Standard German and Swiss German, which are largely mutually unintelligible. Swiss French is characterized by some terms adopted from the Arpitan language, which was formerly spoken wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
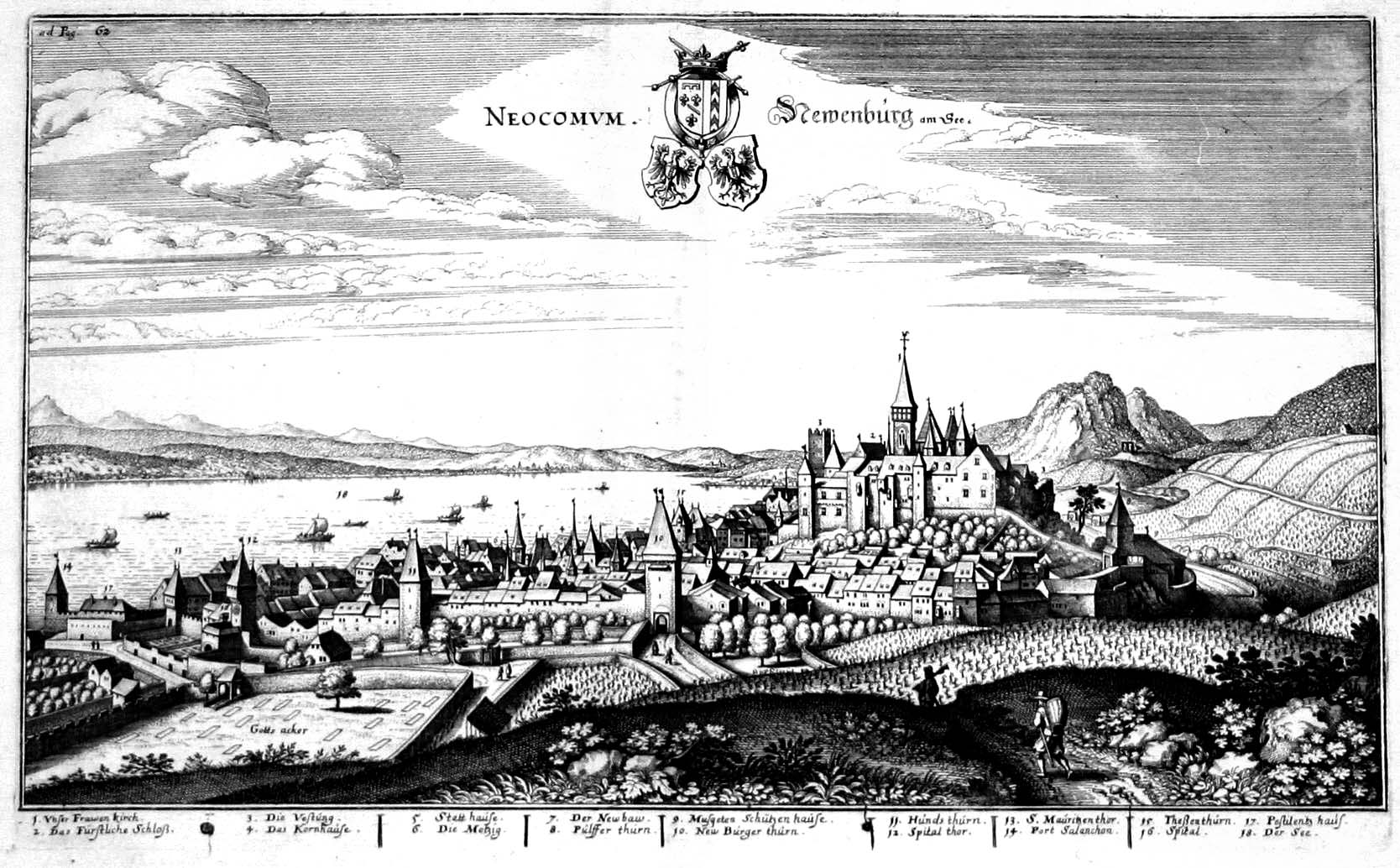
Neuchâtel
, neighboring_municipalities= Auvernier, Boudry, Chabrey (VD), Colombier, Cressier, Cudrefin (VD), Delley-Portalban (FR), Enges, Fenin-Vilars-Saules, Hauterive, Saint-Blaise, Savagnier , twintowns = Aarau (Switzerland), Besançon (France), Sansepolcro (Italy) Neuchâtel (, , ; german: Neuenburg) is the capital of the Swiss canton of Neuchâtel, situated on the shoreline of Lake Neuchâtel. Since the fusion in 2021 of the municipalities of Neuchâtel, Corcelles-Cormondrèche, Peseux, and Valangin, the city has approximately 45,000 inhabitants (80,000 in the metropolitan area). The city is sometimes referred to historically by the German name ; both the French and German names mean "New Castle". It was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy, then part of the Holy Roman Empire and later under Prussian control from 1707 until 1848, with an interruption during the Napoleonic Wars from 1802 to 1814. In 1848, Neuchâtel became a republic and a canton of Switzerland. Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm-Ernst-Gymnasium
The Wilhelm-Ernst-Gymnasium is a secondary school on Herderplatz 14 in Weimar, Germany. Founded in 1712 by Duke William Ernest of Saxe-Weimar, it is the oldest school building in the city. Numerous notable figures such as Johann Gottfried Herder, Johann Heinrich Voss, Friedrich Wilhelm Riemer and Johann Karl August Musäus studied here. It is a designated historic site and is one of the few secular buildings of the pre-classical period still remaining in Weimar. It is prominently located in the urban center and is one of three sites forming the UNESCO World Heritage Site Classical Weimar, created in 1998. History The Wilhelm-Ernst-Gymnasium was founded in 1712 at the behest of William Ernest, Duke of Saxe-Weimar, to replace the Stadt- und Landschule (school of the town and the region) of 1561. Among the teachers were Johann Heinrich Voss, Friedrich Wilhelm Riemer and Johann Karl August Musäus. In 1776 Weimar General Superintendent Johann Gottfried Herder took over as the direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the processes of mineral origin and formation, classification of minerals, their geographical distribution, as well as their utilization. History Early writing on mineralogy, especially on gemstones, comes from ancient Babylonia, the ancient Greco-Roman world, ancient and medieval China, and Sanskrit texts from ancient India and the ancient Islamic world. Books on the subject included the '' Naturalis Historia'' of Pliny the Elder, which not only described many different minerals but also explained many of their properties, and Kitab al Jawahir (Book of Precious Stones) by Persian scientist Al-Biruni. The German Renaissance specialist Georgius Agricola wrote works such as '' De re metallica'' (''On Metals'', 1556) and '' De Natura Fossilium' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Science
Natural science is one of the branches of science concerned with the description, understanding and prediction of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence from observation and experimentation. Mechanisms such as peer review and repeatability of findings are used to try to ensure the validity of scientific advances. Natural science can be divided into two main branches: life science and physical science. Life science is alternatively known as biology, and physical science is subdivided into branches: physics, chemistry, earth science, and astronomy. These branches of natural science may be further divided into more specialized branches (also known as fields). As empirical sciences, natural sciences use tools from the formal sciences, such as mathematics and logic, converting information about nature into measurements which can be explained as clear statements of the " laws of nature". Modern natural science succeeded more classical approaches to natural philosophy, usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthias Claudius
Matthias Claudius (15 August 1740 – 21 January 1815) was a German poet and journalist, otherwise known by the pen name of “Asmus”. Life Claudius was born at Reinfeld, near Lübeck, and studied at Jena. He spent the greater part of his life in the town of Wandsbeck, where he earned his first literary reputation by editing from 1771 to 1775, a newspaper called ''Der Wandsbecker Bote'' (The Wandsbeck Messenger) (''Wandsbeck'' until the year 1879 still written with "ck". Today only with "k".), in which he published a large number of prose essays and poems. They were written in pure and simple German, and appealed to the popular taste; in many there was a vein of extravagant humour or even burlesque, while others were full of quiet meditation and solemn sentiment. In his later days, perhaps through the influence of Klopstock, with whom he had formed an intimate acquaintance, Claudius became strongly pietistic, and the graver side of his nature showed itself. In 1814 he moved t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Georg Hamann
Johann Georg Hamann (; ; 27 August 1730 – 21 June 1788) was a German Lutheran philosopher from Königsberg known as "the Wizard of the North" who was one of the leader figures of post-Kantian philosophy. His work was used by his student J. G. Herder as the main support of the ''Sturm und Drang'' movement, and is associated with the Counter-Enlightenment and Romanticism. He introduced Kant, also from Königsberg, to the works of both Hume – waking him from his "dogmatic slumber" – and Rousseau. Hamann was influenced by Hume, but he used his views to argue for rather than against Christianity. Goethe and Kierkegaard were among those who considered him to be the finest mind of his time. He was also a key influence on Hegel and Jacobi. Long before the linguistic turn, Hamann believed epistemology should be replaced by the philosophy of language. Early life Hamann was born on 27 August 1730 in Königsberg (now Kaliningrad, Russia). Initially he studied theology at the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godparent
In infant baptism and denominations of Christianity, a godparent (also known as a sponsor, or '' gossiprede'') is someone who bears witness to a child's christening and later is willing to help in their catechesis, as well as their lifelong spiritual formation. In the past, in some countries, the role carried some legal obligations as well as religious responsibilities. In both religious and civil views, a godparent tends to be an individual chosen by the parents to take an interest in the child's upbringing and personal development, to offer mentorship or claim legal guardianship of the child if anything should happen to the parents. A male godparent is a godfather, and a female godparent is a godmother. The child is a godchild (i.e. godson for boys and goddaughter for girls). Christianity Origins and history As early as the 2nd century AD, infant baptism had begun to gain acceptance among Catholic Christians for the spiritual purification and social initiation of infa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intellectual and philosophical movement that dominated Europe in the 17th century, 17th and 18th century, 18th centuries with global influences and effects. The Enlightenment included a range of ideas centered on the value of human happiness, the pursuit of knowledge obtained by means of rationalism, reason and empiricism, the evidence of the senses, and ideals such as liberty, progress, toleration, fraternity (philosophy), fraternity, and constitutional government. The Enlightenment was preceded by the Scientific Revolution and the work of Francis Bacon, John Locke, and others. Some date the beginning of the Enlightenment to the publication of René Descartes' ''Discourse on the Method'' in 1637, featuring his famous dictum, ''Cogito, ergo sum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



