|
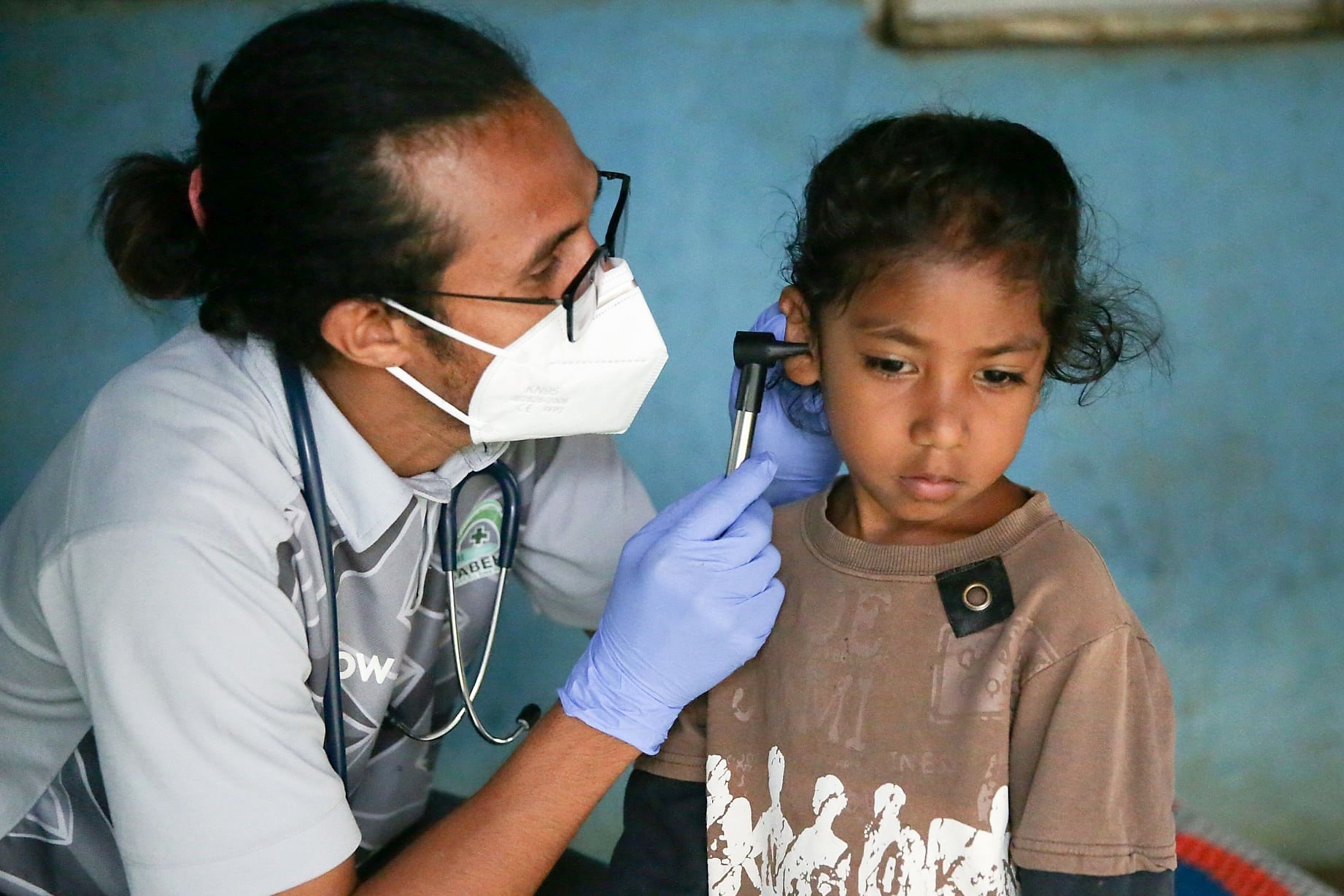
Audiologists
Audiology (from Latin , "to hear"; and from Greek , ''-logia'') is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies (e.g. behavioral hearing tests, otoacoustic emission measurements, and electrophysiologic tests), audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified, audiologists determine which portions of hearing (high, middle, or low frequencies) are affected, to what degree (severity of loss), and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found (outer ear, middle ear, inner ear, auditory nerve and/or central nervous system). If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present, they will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation (e.g. hearing aids, cochlear implants, appropriate medical referrals). In addition to diagnos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audiological Exam
Audiology (from Latin , "to hear"; and from Ancient Greek, Greek , ''wikt:-logia, -logia'') is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies (e.g. behavioral hearing tests, otoacoustic emission measurements, and electrophysiologic tests), audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified, audiologists determine which portions of hearing (high, middle, or low frequencies) are affected, to what degree (severity of loss), and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found (outer ear, middle ear, inner ear, auditory nerve and/or central nervous system). If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present, they will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation (e.g. hearing aids, cochlear implants, appropriate medical referra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditory Processing Disorder
Auditory processing disorder (APD), rarely known as King-Kopetzky syndrome or auditory disability with normal hearing (ADN), is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting the way the brain processes auditory information. Individuals with APD usually have normal structure and function of the outer, middle, and inner ear (peripheral hearing). However, they cannot process the information they hear in the same way as others do, which leads to difficulties in recognizing and interpreting sounds, especially the sounds composing speech. It is thought that these difficulties arise from dysfunction in the central nervous system. It is highly prevalent in individuals with other neurodevelopmental disorders, such as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Autism Spectrum Disorders, Dyslexia, and Sensory Processing Disorder. The American Academy of Audiology notes that APD is diagnosed by difficulties in one or more auditory processes known to reflect the function of the central auditory nervo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor Of Audiology
The Doctor of Audiology (AuD) is a professional degree for an audiologist. The AuD program is designed to produce audiologists who are skilled in providing diagnostic, rehabilitative, and other services associated with hearing, balance, tinnitus management, and related audiological fields. These individuals help patients with hearing problems primarily by diagnosing hearing loss and fitting hearing assistive devices. There is an emphasis on the clinical learning experience, though most programs also have a research component. As of 2007, the AuD has replaced Masters-level audiology programs as the entry-level degree in the United States. Other countries, such as Australia, Canada and India, still offer the master's degree. In the United States, after an AuD is obtained, some states may require a license before practicing audiology clinically. The majority of AuD programs include three years of didactic and clinical instruction and a one-year externship, similar to a medical resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
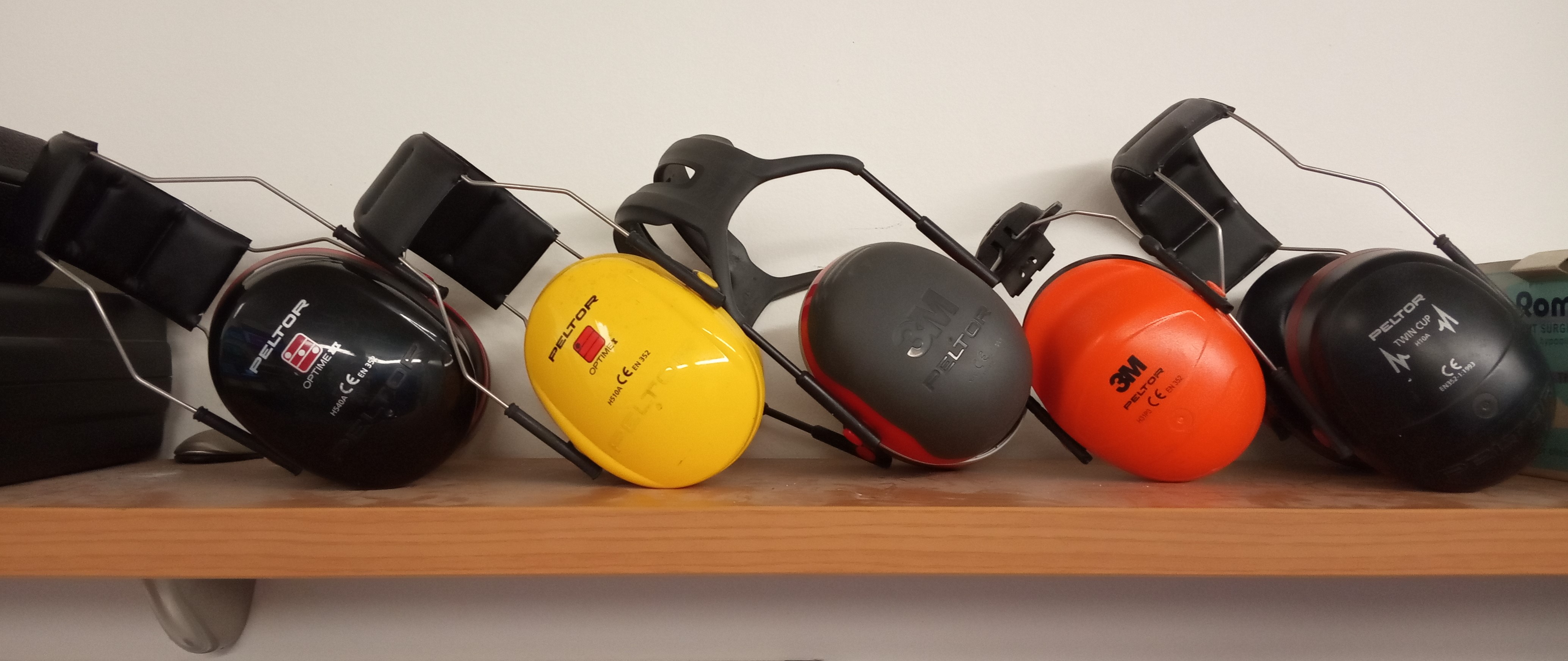
Hearing Protection Device
A hearing protection device, also known as a HPD, is an ear protection device worn in or over the ears while exposed to hazardous noise and provide hearing protection to help prevent noise-induced hearing loss. HPDs reduce the level of the noise entering the ear. HPDs can also protect against other effects of noise exposure such as tinnitus and hyperacusis. There are many different types of HPDs available for use, including earmuffs, earplugs, electronic hearing protection devices, and semi-insert devices. The use of the HPD without individual selection, training and fit testing does not significantly reduce the risk of hearing loss. For example, one study covered more than 19 thousand workers, some of whom usually used hearing protective devices, and some did not use them at all. There was no statistically significant difference in the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. Exposure limits In the context of work, adequate hearing protection is that which reduces noise exposur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Conduction
Bone conduction is the conduction of sound to the inner ear primarily through the bones of the skull, allowing the hearer to perceive audio content without blocking the ear canal. Bone conduction transmission occurs constantly as sound waves vibrate bone, specifically the bones in the skull, although it is hard for the average individual to distinguish sound being conveyed through the bone as opposed to the sound being conveyed through the air via the ear canal. Intentional transmission of sound through bone can be used with individuals with normal hearing — as with bone-conduction headphones — or as a treatment option for certain types of hearing impairment. Bone generally conveys lower-frequency sounds better than higher frequency sounds. Overview Bone conduction is one reason why a person's voice sounds different to them when it is recorded and played back. Because the skull conducts lower frequencies better than air, people perceive their own voices to be lower a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
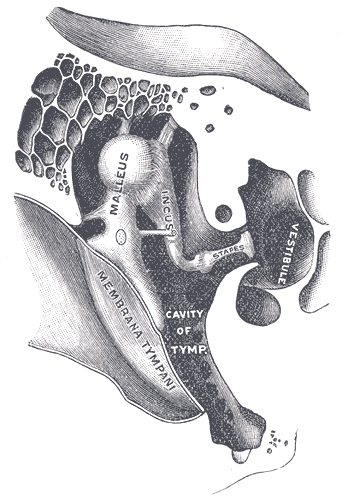
Hearing (sense)
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sensitivity to the movement of molecules in the world outside the organism. Both hearing and touch are types of mechanosensation. Hearing mechanism There are three main components of the human auditory system: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Outer ear The outer ear in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochlear Implant
A cochlear implant (CI) is a surgically implanted neuroprosthesis that provides a person who has moderate-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss with sound perception. With the help of therapy, cochlear implants may allow for improved speech understanding in both quiet and noisy environments. A CI bypasses acoustic hearing by direct electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve. Through everyday listening and auditory training, cochlear implants allow both children and adults to learn to interpret those signals as speech and sound. The implant has two main components. The outside component is generally worn behind the ear, but could also be attached to clothing, for example, in young children. This component, the sound processor, contains microphones, electronics that include digital signal processor (DSP) chips, battery, and a coil that transmits a signal to the implant across the skin. The inside component, the actual implant, has a coil to receive signals, electronics, and an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otology
Otology is a branch of medicine which studies normal and pathological anatomy and physiology of the ear (hearing and vestibular sensory systems and related structures and functions) as well as their diseases, diagnosis and treatment. Otologic surgery generally refers to surgery of the middle ear and mastoid related to chronic otitis media, such as tympanoplasty, or ear drum surgery, ossiculoplasty, or surgery of the hearing bones, and mastoidectomy. Otology also includes surgical treatment of conductive hearing loss, such as stapedectomy surgery for otosclerosis. Neurotology, a related field of medicine and subspecialty of otolaryngology, is the study of diseases of the inner ear, which can lead to hearing and balance disorders. Neurotologic surgery generally refers to surgery of the inner ear or surgery that involves entering the inner ear with risk to the hearing and balance organs, including labyrinthectomy, cochlear implant surgery, and surgery for tumors of the temporal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a disorder arising from a problem in the inner ear. Symptoms are repeated, brief periods of vertigo with movement, characterized by a spinning sensation upon changes in the position of the head. * This can occur with turning in bed or changing position. Each episode of vertigo typically lasts less than one minute. Nausea is commonly associated. BPPV is one of the most common causes of vertigo. BPPV is a type of balance disorder along with labyrinthitis and Ménière's disease. It can result from a head injury or simply occur among those who are older. Often, a specific cause is not identified. When found, the underlying mechanism typically involves a small calcified otolith moving around loose in the inner ear. Diagnosis is typically made when the Dix–Hallpike test results in nystagmus (a specific movement pattern of the eyes) and other possible causes have been ruled out. In typical cases, medical imaging is not needed. BPPV is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ear Plugs
An earplug is a device that is inserted in the ear canal to protect the user's ears from loud noises, intrusion of water, foreign bodies, dust or excessive wind. Since they reduce the sound volume, earplugs are often used to help prevent hearing loss and tinnitus (ringing of the ears). History The first recorded mention of the use of earplugs is in the Greek tale ''Odyssey,'' wherein Odysseus's crew is warned about the Sirens that sing from an island they will sail past. Circe, their hostess, tells them of the Sirens' bewitching song that makes men drive their boats ashore and perish. She advised Odysseus to fashion earplugs for his men from beeswax so they would not be lured to their deaths by the sirens' song. In 1907, the German company Ohropax, which would produce mainly wax earplugs, was started by the German inventor Max Negwer. Ray and Cecilia Benner invented the first moldable pure silicone ear plug in 1962. These earplugs were valued by swimmers because of their waterpro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Neonatal Hearing Screening
Universal neonatal hearing screening (UNHS), also known as early hearing detection and intervention (EHDI) programmes in several countries, refer to those services aimed at the early identification, intervention, and follow-up of infants and young children who are deaf or hard-of-hearing. It is a strategy for early detection of permanent congenital hearing loss. It describes the use of objective testing methods (usually otoacoustic emission (OAE) testing or automated auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing) to screen the hearing of well newborns in a particular target region. Overview Even among developed countries, until the 1990s, it could take years for hearing-impaired child to be diagnosed and to benefit from a health intervention and amplification. This delay still can happen in developing countries. If children are not exposed to sounds and language during their first years of life because of a hearing loss, they will have difficulty in developing spoken or signed lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Safety
Occupational safety and health (OSH), also commonly referred to as occupational health and safety (OHS), occupational health, or occupational safety, is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the safety, health, and welfare of people at work (i.e. in an occupation). These terms also refer to the goals of this field, so their use in the sense of this article was originally an abbreviation of ''occupational safety and health program/department'' etc. The goal of an occupational safety and health program is to foster a safe and healthy occupational environment. OSH also protects all the general public who may be affected by the occupational environment.Fanning, Fred E. (2003). Basic Safety Administration: A Handbook for the New Safety Specialist, Chicago: American Society of Safety Engineers Globally, more than 2.78 million people die annually as a result of workplace-related accidents or diseases, corresponding to one death every fifteen seconds. There are an additional 374 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |