|
Audio Video Bridging
Audio Video Bridging (AVB) is a common name for the set of technical standards which provide improved synchronization, low-latency, and reliability for switched Ethernet networks. AVB embodies the following technologies and standards: * IEEE 802.1AS-2011: Timing and Synchronization for Time-Sensitive Applications (gPTP); * IEEE 802.1Qav-2009: Forwarding and Queuing for Time-Sensitive Streams (FQTSS); * IEEE 802.1Qat-2010: Stream Reservation Protocol (SRP); * IEEE 802.1BA-2011: Audio Video Bridging (AVB) Systems; * IEEE 1722-2011 Layer 2 Transport Protocol for Time Sensitive Applications (AV Transport Protocol, AVTP); and * IEEE 1722.1-2013 Device Discovery, Enumeration, Connection Management and Control Protocol (AVDECC). IEEE 802.1Qat and 802.1Qav amendments have been incorporated to the base IEEE 802.1Q-2011 document, which specifies the operation of Media Access Control (MAC) Bridges and Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks. AVB was initially developed by the Institute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE 1394
IEEE 1394 is an interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. It was developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple in cooperation with a number of companies, primarily Sony and Panasonic. Apple called the interface FireWire. It is also known by the brand names i.LINK (Sony), and Lynx (Texas Instruments). The copper cable used in its most common implementation can be up to long. Power and data is carried over this cable, allowing devices with moderate power requirements to operate without a separate power supply. FireWire is also available in Cat 5 and optical fiber versions. The 1394 interface is comparable to USB. USB was developed subsequently and gained much greater market share. USB requires a host controller whereas IEEE 1394 is cooperatively managed by the connected devices. History and development FireWire is Apple's name for the IEEE 1394 High Speed Serial Bus. Its development was initiated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admission Control
Admission control is a validation process in communication systems where a check is performed before a connection is established to see if current resources are sufficient for the proposed connection. Applications For some applications, dedicated resources (such as a wavelength across an optical network) may be needed in which case admission control has to verify availability of such resources before a request can be admitted. For more elastic applications, a total volume of resources may be needed prior to some deadline in order to satisfy a new request, in which case admission control needs to verify availability of resources at the time and perform scheduling to guarantee satisfaction of an admitted request. Admission control systems *Asynchronous Transfer Mode *Audio Video Bridging using Stream Reservation Protocol *IEEE 1394 *Integrated services In computer networking, integrated services or IntServ is an architecture that specifies the elements to guarantee quality of servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VLAN
A virtual local area network (VLAN) is any broadcast domain that is partitioned and isolated in a computer network at the data link layer (OSI layer 2).IEEE 802.1Q-2011, ''1.4 VLAN aims and benefits'' In this context, virtual, refers to a physical object recreated and altered by additional logic, within the local area network. VLANs work by applying tags to network frames and handling these tags in networking systems – creating the appearance and functionality of network traffic that is physically on a single network but acts as if it is split between separate networks. In this way, VLANs can keep network applications separate despite being connected to the same physical network, and without requiring multiple sets of cabling and networking devices to be deployed. VLANs allow network administrators to group hosts together even if the hosts are not directly connected to the same network switch. Because VLAN membership can be configured through software, this can greatly simplif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traffic Shaping
Traffic shaping is a bandwidth management technique used on computer networks which delays some or all datagrams to bring them into compliance with a desired ''traffic profile''. Traffic shaping is used to optimize or guarantee performance, improve latency, or increase usable bandwidth for some kinds of packets by delaying other kinds. It is often confused with traffic policing, the distinct but related practice of packet dropping and packet marking. The most common type of traffic shaping is application-based traffic shaping. In application-based traffic shaping, fingerprinting tools are first used to identify applications of interest, which are then subject to shaping policies. Some controversial cases of application-based traffic shaping include bandwidth throttling of peer-to-peer file sharing traffic. Many application protocols use encryption to circumvent application-based traffic shaping. Another type of traffic shaping is route-based traffic shaping. Route-based traffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
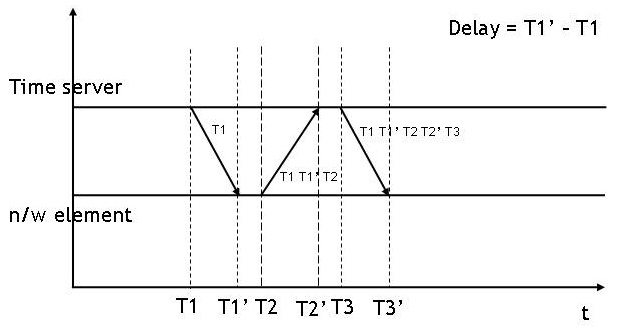
Precision Time Protocol
The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a protocol used to synchronize clocks throughout a computer network. On a local area network, it achieves clock accuracy in the sub-microsecond range, making it suitable for measurement and control systems. PTP is employed to synchronize financial transactions, mobile phone tower transmissions, sub-sea acoustic arrays, and networks that require precise timing but lack access to satellite navigation signals. The first version of PTP, IEEE 1588-2002, was published in 2002. IEEE 1588-2008, also known as PTP Version 2 is not backward compatible with the 2002 version. IEEE 1588-2019 was published in November 2019 and includes backward-compatible improvements to the 2008 publication. IEEE 1588-2008 includes a ''profile'' concept defining PTP operating parameters and options. Several profiles have been defined for applications including telecommunications, electric power distribution and audiovisual. is an adaptation of PTP for use with Audio Vid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lip Sync
Lip sync or lip synch (pronounced , the same as the word ''sink'', short for lip synchronization) is a technical term for matching a speaking or singing person's lip movements with sung or spoken vocals. Audio for lip syncing is generated through the sound reinforcement system in a live performance or via television, computer, cinema speakers, or other forms of audio output. The term can refer to any of a number of different techniques and processes, in the context of live performances and audiovisual recordings. In film production, lip syncing is often part of the post-production phase. Dubbing foreign-language films and making animated characters appear to speak both require elaborate lip syncing. Many video games make extensive use of lip-synced sound files to create an immersive environment in which on-screen characters appear to be speaking. In the music industry, lip syncing is used by singers for music videos, television and film appearances and some types of live perf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Layer 2
The data link layer, or layer 2, is the second layer of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. This layer is the protocol layer that transfers data between nodes on a network segment across the physical layer. The data link layer provides the functional and procedural means to transfer data between network entities and may also provide the means to detect and possibly correct errors that can occur in the physical layer. The data link layer is concerned with local delivery of frames between nodes on the same level of the network. Data-link frames, as these protocol data units are called, do not cross the boundaries of a local area network. Inter-network routing and global addressing are higher-layer functions, allowing data-link protocols to focus on local delivery, addressing, and media arbitration. In this way, the data link layer is analogous to a neighborhood traffic cop; it endeavors to arbitrate between parties contending for access to a medium, without conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Network
A tree topology, or star-bus topology, is a hybrid network topology in which star networks are interconnected via bus networks. Tree networks are hierarchical, and each node In general, a node is a localized swelling (a "knot") or a point of intersection (a vertex). Node may refer to: In mathematics *Vertex (graph theory), a vertex in a mathematical graph *Vertex (geometry), a point where two or more curves, lines, ... can have an arbitrary number of child nodes. Regular tree networks A regular tree network's topology is characterized by two parameters: the branching, d, and the number of generations, G. The total number of the nodes, N, and the number of peripheral nodes N_p, are given by : N= \frac,\quad N_p=d^G Random tree networks Three parameters are crucial in determining the statistics of random tree networks, first, the branching probability, second the maximum number of allowed progenies at each branching point, and third the maximum number of generation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet Switch
A network switch (also called switching hub, bridging hub, and, by the IEEE, MAC bridge) is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device. A network switch is a multiport network bridge that uses MAC addresses to forward data at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model. Some switches can also forward data at the network layer (layer 3) by additionally incorporating routing functionality. Such switches are commonly known as layer-3 switches or multilayer switches. Switches for Ethernet are the most common form of network switch. The first MAC Bridge was invented in 1983 by Mark Kempf, an engineer in the Networking Advanced Development group of Digital Equipment Corporation. The first 2 port Bridge product (LANBridge 100) was introduced by that company shortly after. The company subsequently produced multi-port switches for both Ethernet and FDDI such as GigaSwitch. Digital d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Of Service
Quality of service (QoS) is the description or measurement of the overall performance of a service, such as a telephony or computer network, or a cloud computing service, particularly the performance seen by the users of the network. To quantitatively measure quality of service, several related aspects of the network service are often considered, such as packet loss, bit rate, throughput, transmission delay, availability, jitter, etc. In the field of computer networking and other packet-switched telecommunication networks, quality of service refers to traffic prioritization and resource reservation control mechanisms rather than the achieved service quality. Quality of service is the ability to provide different priorities to different applications, users, or data flows, or to guarantee a certain level of performance to a data flow. Quality of service is particularly important for the transport of traffic with special requirements. In particular, developers have introduced Voice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |