|
Attenuated Virus
An attenuated vaccine (or a live attenuated vaccine, LAV) is a vaccine created by reducing the virulence of a pathogen, but still keeping it viable (or "live"). Attenuation takes an infectious agent and alters it so that it becomes harmless or less virulent. These vaccines contrast to those produced by "killing" the virus (inactivated vaccine). Attenuated vaccines stimulate a strong and effective immune response that is long-lasting. In comparison to inactivated vaccines, attenuated vaccines produce a stronger and more durable immune response with a quick immunity onset. Attenuated vaccines function by encouraging the body to create antibodies and memory immune cells in response to the specific pathogen which the vaccine protects against. Common examples of live attenuated vaccines are measles, mumps, rubella, yellow fever, and some influenza vaccines. Development Attenuated viruses Viruses may be attenuated using the principles of evolution via serial passage of the virus thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or Antigen, killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and to further recognize and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future. Vaccines can be prophylaxis, prophylactic (to prevent or ameliorate the effects of a future infection by a natural or "wild" pathogen), or therapeutic vaccines, therapeutic (to fight a disease that has already occurred, such as cancer vaccine, cancer). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoid Vaccine
Typhoid vaccines are vaccines that prevent typhoid fever. Several types are widely available: typhoid conjugate vaccine (TCV), Ty21a (a live oral vaccine) and Vi capsular polysaccharide vaccine (ViPS) (an injectable subunit vaccine). They are about 30 to 70% effective in the first two years, depending on the specific vaccine in question. The Vi-rEPA vaccine has been shown to be efficacious in children. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends vaccinating all children in areas where the disease is common. Otherwise they recommend vaccinating those at high risk. Vaccination campaigns can also be used to control outbreaks of disease. Depending on the vaccine, additional doses are recommended every three to seven years. In the United States the vaccine is only recommended in those at high risk such as travelers to areas of the world where the disease is common. The vaccines available as of 2018 are very safe. Minor side effects may occur at the site of injection. The inje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholera Vaccine
Cholera vaccines are vaccines that are effective at preventing cholera. For the first six months after vaccination they provide about 85percent protection, which decreases to 50percent or 62percent during the first year. After two years the level of protection decreases to less than 50percent. When enough of the population is immunized, it may protect those who have not been immunized (known as herd immunity). The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the use of cholera vaccines in combination with other measures among those at high risk. With the oral vaccine, two or three doses are typically recommended. The duration of protection is two years in adults and six months in children aged 2–5 years. A single dose vaccine is available for those traveling to an area where cholera is common. In 2010, in some countries an injectable cholera vaccine was available. The available types of oral vaccine are generally safe. Mild abdominal pain or diarrhea may occur. They are safe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome. Recombinant DNA is the general name for a piece of DNA that has been created by combining at least two fragments from two different sources. Recombinant DNA is possible because DNA molecules from all organisms share the same chemical structure, and differ only in the nucleotide sequence within that identical overall structure. Recombinant DNA molecules are sometimes called chimeric DNA, because they can be made of material from two different species, like the mythical chimera. R-DNA technology uses palindromic sequences and leads to the production of sticky and blunt ends. The DNA sequences used in the construction of recombinant DNA molecules can originate from any species. For example, plant DNA may be joined to bacter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Polio Vaccine
Polio vaccines are vaccines used to prevent poliomyelitis (polio). Two types are used: an inactivated poliovirus given by injection (IPV) and a weakened poliovirus given by mouth (OPV). The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends all children be fully vaccinated against polio. The two vaccines have eliminated polio from most of the world, and reduced the number of cases reported each year from an estimated 350,000 in 1988 to 33 in 2018. The inactivated polio vaccines are very safe. Mild redness or pain may occur at the site of injection. Oral polio vaccines cause about three cases of vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis per million doses given. This compares with 5,000 cases per million who are paralysed following a polio infection. Both types of vaccine are generally safe to give during pregnancy and in those who have HIV/AIDS but are otherwise well. However, the emergence of circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus (cVDPV), a form of the vaccine virus that has revert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine
Live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) is a type of influenza vaccine in the form of a nasal spray that is recommended for the prevention of influenza. It is an attenuated vaccine, unlike most influenza vaccines, which are inactivated vaccines. LAIV is administered intranasally, while inactivated vaccines are administered by intramuscular injection. LAIV is sold under the brand name FluMist Quadrivalent in the United States and the brand name Fluenz Tetra in the European Union. FluMist was first introduced in 2003 by MedImmune. Medical uses The live attenuated influenza vaccine is used to provide protection against the flu caused by infection with influenza viruses. Contraindications The use of the live attenuated influenza vaccine is contraindicated, and should therefore not be used, in the following populations: * children <24 months of age, due to increased risk of wheezing * individuals with a history of hypersensitiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
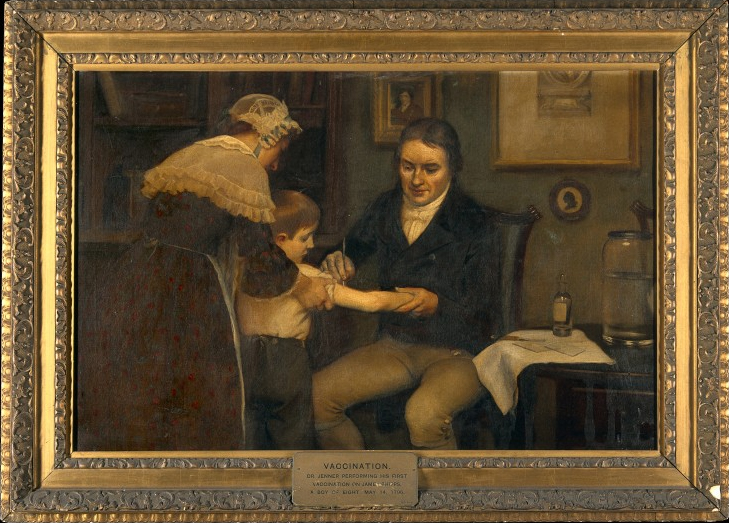
Smallpox Vaccine
The smallpox vaccine is the first vaccine to be developed against a contagious disease. In 1796, British physician Edward Jenner demonstrated that an infection with the relatively mild cowpox virus conferred immunity against the deadly smallpox virus. Cowpox served as a natural vaccine until the modern smallpox vaccine emerged in the 20th century. From 1958 to 1977, the World Health Organization (WHO) conducted a global vaccination campaign that eradicated smallpox, making it the only human disease to be eradicated. Although routine smallpox vaccination is no longer performed on the general public, the vaccine is still being produced to guard against bioterrorism, biological warfare, and monkeypox.Anderson MG, Frenkel LD, Homann S, and Guffey J. (2003), "A case of severe monkeypox virus disease in an American child: emerging infections and changing professional values"; '' Pediatr Infect Dis J'';22(12): 1093–96; discussion 1096–98. The term ''vaccine'' derives from the Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis Vaccines
Tuberculosis (TB) vaccines are vaccinations intended for the prevention of tuberculosis. Immunotherapy as a defence against TB was first proposed in 1890 by Robert Koch.Prabowo, S. et al. "Targeting multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) by therapeutic vaccines." Med Microbiol Immunol 202 (2013): 95–1041. Print. Today, the only effective tuberculosis vaccine in common use is the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine, first used on humans in 1921.White, A. et al. "Evaluation of the Safety and Immunogenicity of a Candidate Tuberculosis Vaccine, MVA85A, Delivered by Aerosol to the Lungs of Macaques." Clinical and Vaccine Immunology 20 (2013): 663–672. Print. About three out of every 10,000 people who get the vaccine experience side effects, which are usually minor except in severely immuno-depressed individuals. While BCG immunization provides fairly effective protection for infants and young children (including defence against TB meningitis and miliary TB),Hussey, G, T Haw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Fever Vaccine
Yellow fever vaccine is a vaccine that protects against yellow fever. Yellow fever is a viral infection that occurs in Africa and South America. Most people begin to develop immunity within ten days of vaccination and 99 percent are protected within one month, and this appears to be lifelong. The vaccine can be used to control outbreaks of disease. It is given either by injection into a muscle or just under the skin. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends routine immunization in all countries where the disease is common. This should typically occur between nine and twelve months of age. Those traveling to areas where the disease occurs should also be immunized. Additional doses after the first are generally not needed. The yellow fever vaccine is generally safe. This includes in those with HIV infection but without symptoms. Mild side effects may include headache, muscle pains, pain at the injection site, fever, and rash. Severe allergies occur in about eight per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varicella Vaccine
Varicella vaccine, also known as chickenpox vaccine, is a vaccine that protects against chickenpox. One dose of vaccine prevents 95% of moderate disease and 100% of severe disease. Two doses of vaccine are more effective than one. If given to those who are not immune within five days of exposure to chickenpox it prevents most cases of disease. Vaccinating a large portion of the population also protects those who are not vaccinated. It is given by injection just under the skin. Another vaccine, known as zoster vaccine, is used to prevent diseases caused by the same virus – the varicella zoster virus. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends routine vaccination only if a country can keep more than 80% of people vaccinated. If only 20% to 80% of people are vaccinated it is possible that more people will get the disease at an older age and outcomes overall may worsen. Either one or two doses of the vaccine is recommended. In the United States two doses are recommended sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MMR Vaccine
The MMR vaccine is a vaccine against measles, mumps, and rubella (German measles), abbreviated as ''MMR''. The first dose is generally given to children around 9 months to 15 months of age, with a second dose at 15 months to 6 years of age, with at least four weeks between the doses. After two doses, 97% of people are protected against measles, 88% against mumps, and at least 97% against rubella. The vaccine is also recommended for those who do not have evidence of immunity, those with well-controlled HIV/AIDS, and within 72 hours of exposure to measles among those who are incompletely immunized. It is given by injection. The MMR vaccine is widely used around the world. Worldwide over 500 million doses were administered between 1999 and 2004, and 575 million doses have been administered since the vaccine's introduction worldwide. Measles resulted in 2.6 million deaths per year before immunization became common. This has decreased to 122,000 deaths per year , mostly in low-in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |