|
Atmosphere Of Triton
The atmosphere of Triton is the layer of gases surrounding Triton. The surface pressure is only 14 microbars (1.4 Pa or 0.0105 mmHg), of the surface pressure on Earth, and it is composed of nitrogen, similar to those of Titan and Earth. It extends 800 kilometers above its surface. Observations obtained in 1998 showed an increase in temperature. Composition Nitrogen is the main gas in Triton's atmosphere. The two other known components are methane and carbon monoxide, whose abundances are a few hundredths of a percent of that of the nitrogen. Carbon monoxide, which was discovered only in 2010 by the ground-based observations, is slightly more abundant than methane. The abundance of methane relative to nitrogen increased by four to five times since 1986 due to the seasonal warming observed on Triton, which passed its southern-hemisphere solstice in 2001. Other possible components of the Triton's atmosphere include argon and neon. Because they were not detected in the ultraviole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triton (moon)
Triton is the largest natural satellite of the planet Neptune, and was the first Neptunian moon to be discovered, on October 10, 1846, by English astronomer William Lassell. It is the only large moon in the Solar System with a retrograde orbit, an orbit in the direction opposite to its planet's rotation. Because of its retrograde orbit and composition similar to Pluto, Triton is thought to have been a dwarf planet, captured from the Kuiper belt. At in diameter, it is the seventh-largest moon in the Solar System, the only satellite of Neptune massive enough to be in hydrostatic equilibrium, the second-largest planetary moon in relation to its primary (after Earth's Moon), and larger than Pluto. Triton is one of the few moons in the Solar System known to be geologically active (the others being Jupiter's Io and Europa, and Saturn's Enceladus and Titan). As a consequence, its surface is relatively young, with few obvious impact craters. Intricate cryovolcanic and tectonic te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photolysis
Photodissociation, photolysis, photodecomposition, or photofragmentation is a chemical reaction in which molecules of a chemical compound are broken down by photons. It is defined as the interaction of one or more photons with one target molecule. Photodissociation is not limited to visible light. Any photon with sufficient energy can affect the chemical bonds of a chemical compound. Since a photon energy, photon's energy is inversely proportional to its wavelength, electromagnetic radiations with the energy of visible light or higher, such as ultraviolet light, x-rays, and gamma rays can induce such reactions. Photolysis in photosynthesis Photolysis is part of the light-dependent reactions, light-dependent reaction or light phase or photochemical phase or Hill reaction of photosynthesis. The general reaction of photosynthetic photolysis can be given in terms of photons as: :\ce + 2 \text \longrightarrow \ce The chemical nature of "A" depends on the type of organism. Purple su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
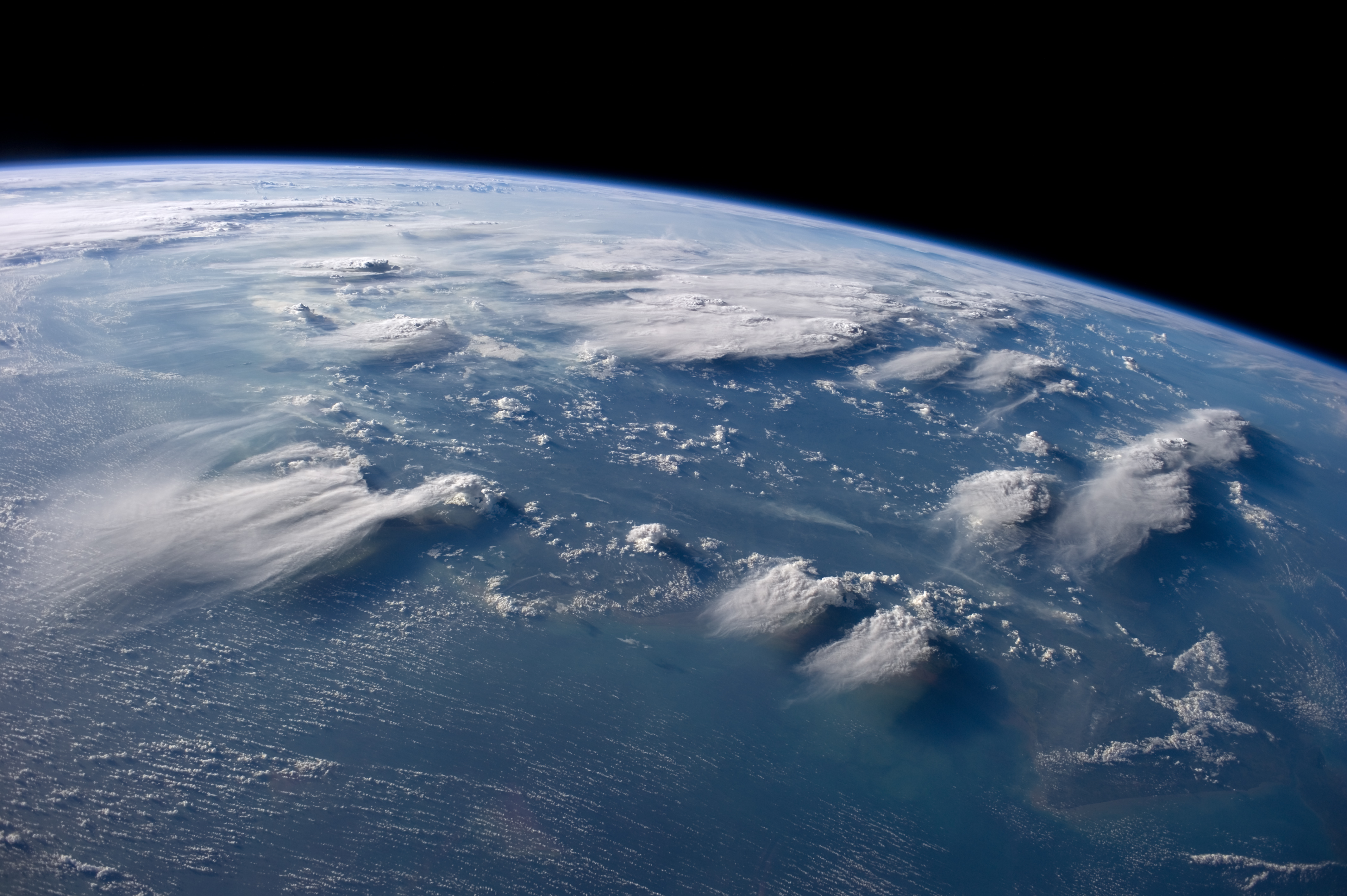
Clouds
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may compose the droplets and crystals. On Earth, clouds are formed as a result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its dew point, or when it gains sufficient moisture (usually in the form of water vapor) from an adjacent source to raise the dew point to the ambient temperature. They are seen in the Earth's homosphere, which includes the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere. Nephology is the science of clouds, which is undertaken in the cloud physics branch of meteorology. There are two methods of naming clouds in their respective layers of the homosphere, Latin and common name. Genus types in the troposphere, the atmospheric layer closest to Earth's surface, have Latin names because of the universal adoption of Luke Howard's n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exosphere
The exosphere ( grc, ἔξω "outside, external, beyond", grc, σφαῖρα "sphere") is a thin, atmosphere-like volume surrounding a planet or natural satellite where molecules are gravitationally bound to that body, but where the density is so low that the molecules are essentially collisionless. In the case of bodies with substantial atmospheres, such as Earth's atmosphere, the exosphere is the uppermost layer, where the atmosphere thins out and merges with outer space. It is located directly above the thermosphere. Very little is known about it due to lack of research. Mercury, the Moon, Ceres, Europa, and Ganymede have surface boundary exospheres, which are exospheres without a denser atmosphere underneath. The Earth's exosphere is mostly hydrogen and helium, with some heavier atoms and molecules near the base. Surface boundary exosphere Mercury, Ceres and several large natural satellites, such as the Moon, Europa, and Ganymede, have exospheres without a denser a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermosphere
The thermosphere is the layer in the Earth's atmosphere directly above the mesosphere and below the exosphere. Within this layer of the atmosphere, ultraviolet radiation causes photoionization/photodissociation of molecules, creating ions; the thermosphere thus constitutes the larger part of the ionosphere. Taking its name from the Greek θερμός (pronounced ''thermos'') meaning heat, the thermosphere begins at about 80 km (50 mi) above sea level. At these high altitudes, the residual atmospheric gases sort into strata according to molecular mass (see turbosphere). Thermospheric temperatures increase with altitude due to absorption of highly energetic solar radiation. Temperatures are highly dependent on solar activity, and can rise to or more. Radiation causes the atmospheric particles in this layer to become electrically charged, enabling radio waves to be refracted and thus be received beyond the horizon. In the exosphere, beginning at about 600 km (375&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Press
Academic Press (AP) is an academic book publisher founded in 1941. It was acquired by Harcourt, Brace & World in 1969. Reed Elsevier bought Harcourt in 2000, and Academic Press is now an imprint of Elsevier. Academic Press publishes reference books, serials and online products in the subject areas of: * Communications engineering * Economics * Environmental science * Finance * Food science and nutrition * Geophysics * Life sciences * Mathematics and statistics * Neuroscience * Physical sciences * Psychology Well-known products include the ''Methods in Enzymology'' series and encyclopedias such as ''The International Encyclopedia of Public Health'' and the ''Encyclopedia of Neuroscience''. See also * Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft (AVG) — the German predecessor, founded in 1906 by Leo Jolowicz (1868–1940), the father of Walter Jolowicz Walter may refer to: People * Walter (name), both a surname and a given name * Little Walter, American blues harmonica player Marion Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is an atmospheric layer composed of stratified temperature layers, with the warm layers of air high in the sky and the cool layers of air in the low sky, close to the planetary surface of the Earth. The increase of temperature with altitude is a result of the absorption of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation by the ozone layer. The temperature inversion is in contrast to the troposphere, near the Earth's surface, where temperature decreases with altitude. Between the troposphere and stratosphere is the tropopause border that demarcates the beginning of the temperature inversion. Near the equator, the lower edge of the stratosphere is as high as , at midlatitudes around , and at the poles about . Temperatures range from an average of near the tropopause to an average of near the mesosphere. Stratospheric temperatures also vary w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropopause
The tropopause is the atmospheric boundary that demarcates the troposphere from the stratosphere; which are two of the five layers of the atmosphere of Earth. The tropopause is a thermodynamic gradient-stratification layer, that marks the end of the troposphere, and lies approximately above the equatorial regions, and approximately above the polar regions. Definition Rising from the planetary surface of the Earth, the tropopause is the atmospheric level where the air ceases to become cool with increased altitude, and becomes dry, devoid of water vapor. The tropopause is the boundary that demarcates the troposphere from the stratosphere, and is the part of the atmosphere where there occurs an abrupt change in the environmental lapse rate (ELR), from a positive rate in the troposphere to a negative rate in the stratosphere. The ELR indicates the lowest level at which the lapse rate decreases to 2°C/km or less, provided that the average lapse-rate, between that level and all othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troposphere
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the planetary surface of the Earth, the average height of the troposphere is in the tropics; in the middle latitudes; and in the high latitudes of the polar regions in winter; thus the average height of the troposphere is . The term ''troposphere'' derives from the Greek words ''tropos'' (rotating) and '' sphaira'' (sphere) indicating that rotational turbulence mixes the layers of air and so determines the structure and the phenomena of the troposphere. The rotational friction of the troposphere against the planetary surface affects the flow of the air, and so forms the planetary boundary layer (PBL) that varies in height from hundreds of meters up to . The measures of the PBL vary according to the latitude, the landform, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convection is unspecified, convection due to the effects of thermal expansion and buoyancy can be assumed. Convection may also take place in soft solids or mixtures where particles can flow. Convective flow may be transient (such as when a multiphase mixture of oil and water separates) or steady state (see Convection cell). The convection may be due to gravitational, electromagnetic or fictitious body forces. Heat transfer by natural convection plays a role in the structure of Earth's atmosphere, its oceans, and its mantle. Discrete convective cells in the atmosphere can be identified by clouds, with stronger convection resulting in thunderstorms. Natural convection also plays a role in stellar physics. Convection is often categorised or d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Nitrogen
Solid nitrogen is a number of solid forms of the element nitrogen, first observed in 1884. Solid nitrogen is mainly the subject of academic research, but low-temperature, low-pressure solid nitrogen is a substantial component of bodies in the outer Solar System and high-temperature, high-pressure solid nitrogen is a powerful explosive, with higher energy density than any other non-nuclear material. Generation Karol Olszewski first observed solid nitrogen in 1884, by first liquefying hydrogen with evaporating liquid nitrogen, and then allowing the liquid hydrogen to freeze the nitrogen. By evaporating vapour from the solid nitrogen, Olszewski also generated the extremely low temperature of , at the time a world record. Modern techniques usually take a similar approach: solid nitrogen is normally made in a laboratory by evaporating liquid nitrogen in a vacuum. The solid produced is porous. Occurrence in nature Solid nitrogen forms a large part of the surface of Pluto (where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)