|
Atlas-Able
The Atlas-Able was an American expendable launch system derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas family of rockets, and was used to launch several Pioneer spacecraft towards the Moon. Of the five Atlas-Able rockets built, two failed during static firings, and the other three failed to reach orbit. The Atlas-Able was a three-and-a-half-stage rocket, with a stage-and-a-half Atlas missile as the first stage, an Able second stage, and an Altair third stage. The first Atlas-Able used an Atlas C as the first stage, but this exploded during a static fire test on 24 September 1959. The remaining launches used Atlas D missiles. Launches were conducted from Launch Complexes 12 and 14 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. One launch was planned from Launch Complex 13 Launch Complex 13 (LC-13) was a launch complex at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, the third-most southerly of the original launch complexes known as Missile Row, lying between LC-12 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pioneer Program
The Pioneer programs were two series of United States lunar and planetary space probes exploration. The first program, which ran from 1958 to 1960, unsuccessfully attempted to send spacecraft to orbit the Moon, successfully sent one spacecraft to fly by the Moon, and successfully sent one spacecraft to investigate interplanetary space between the orbits of Earth and Venus. The second program, which ran from 1965 to 1992, sent four spacecraft to measure interplanetary space weather, two to explore Jupiter and Saturn, and two to explore Venus. The two outer planet probes, ''Pioneer 10'' and ''Pioneer 11'', became the first two of five artificial objects to achieve the escape velocity that will allow them to leave the Solar System, and carried a golden plaque each depicting a man and a woman and information about the origin and the creators of the probes, in case any extraterrestrials find them someday. Naming Credit for naming the first probe has been attributed to Stephen A. Sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
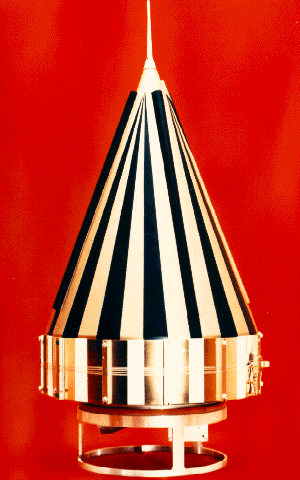
Pioneer P-30
Pioneer P-30 (also known as Able 5A, Atlas-Able 5A, or Pioneer Y) was intended to be a lunar orbiter probe, but the mission failed shortly after launch on September 25, 1960. The objectives were to place a highly instrumented probe in lunar orbit, to investigate the environment between the Earth and Moon, and to develop technology for controlling and maneuvering spacecraft from Earth. It was equipped to estimate the Moon's mass and topography of the poles, record the distribution and velocity of micrometeorites, and study radiation, magnetic fields, and low frequency electromagnetic waves in space. A mid-course propulsion system and injection rocket would have been the first United States self-contained propulsion system capable of operation many months after launch at great distances from Earth and the first U.S. tests of maneuvering a satellite in space. Mission Nearly a year passed between the first Atlas-Able launch in November 1959 and this second attempt due to a shortage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 12
Launch Complex 12 (LC-12) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida was a launch pad used by Atlas rockets and missiles between 1958 and 1967. It was the second-most southern of the pads known as Missile Row, between LC-11 to the south and LC-13 to the north. Along with Complexes 11, 13 and 14, 12 featured a more robust design than many contemporary pads, due to the greater power of the Atlas compared to other rockets of the time. It was larger, and featured a concrete launch pedestal that was tall and a reinforced blockhouse. The rockets were delivered to the launch pad by means of a ramp on the southwest side of the launch pedestal. Atlas A, C and D missiles were tested from the site. It was also used for orbital launches of Atlas-Able and later Atlas-Agena rockets, and two Project FIRE suborbital tests for Project Apollo, using Atlas D rockets. LC-12's first launch was Atlas 10A on January 10, 1958. During the second half of the year, a larger umbilical service t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Launch Complex 12
Launch Complex 12 (LC-12) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida was a launch pad used by Atlas rockets and missiles between 1958 and 1967. It was the second-most southern of the pads known as Missile Row, between LC-11 to the south and LC-13 to the north. Along with Complexes 11, 13 and 14, 12 featured a more robust design than many contemporary pads, due to the greater power of the Atlas compared to other rockets of the time. It was larger, and featured a concrete launch pedestal that was tall and a reinforced blockhouse. The rockets were delivered to the launch pad by means of a ramp on the southwest side of the launch pedestal. Atlas A, C and D missiles were tested from the site. It was also used for orbital launches of Atlas-Able and later Atlas-Agena rockets, and two Project FIRE suborbital tests for Project Apollo, using Atlas D rockets. LC-12's first launch was Atlas 10A on January 10, 1958. During the second half of the year, a larger umbilical service to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pioneer P-3
Pioneer P-3 (also known as Atlas-Able 4 or Pioneer X) was intended to be a lunar orbiter probe, but the mission failed shortly after launch. The objectives were to place a highly instrumented probe in lunar orbit, to investigate the environment between the Earth and Moon, and to develop technology for controlling and maneuvering spacecraft from Earth. It was equipped to take images of the lunar surface with a television-like system, estimate the Moon's mass and topography of the poles, record the distribution and velocity of micrometeorites, and study radiation, magnetic fields, and low frequency electromagnetic waves in space. A mid-course propulsion system and injection rocket would have been the first United States self-contained propulsion system capable of operation many months after launch at great distances from Earth and the first U.S. tests of maneuvering a satellite in space. Mission The probe was originally intended for launch on Atlas 9C in October, but the launch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SM-65 Atlas
The SM-65 Atlas was the first operational intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the United States and the first member of the Atlas rocket family. It was built for the U.S. Air Force by the Convair Division of General Dynamics at an assembly plant located in Kearny Mesa, San Diego. Atlas became operational in October 1959, but was soon made obsolete as an ICBM by new development, and was retired from this role by 1965. Atlas required long preparation times which made it unsuitable for a quick launch ICBM. However, this was not a requirement for planned space launches, and so Atlas-derived launch vehicles served a long history as space launchers. Even before its ICBM use ended in 1965, Atlas had placed four Project Mercury astronauts in orbit and was becoming the foundation for a family of successful space launch vehicles, most notably Atlas Agena and Atlas Centaur. Mergers led to the acquisition of the Atlas Centaur line by the United Launch Alliance. Tod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pioneer P-31
Pioneer P-31 (also known as Atlas-Able 5B or Pioneer Z) was intended to be a lunar orbiter probe, but the mission failed shortly after launch. The objectives were to place a highly instrumented probe in lunar orbit, to investigate the environment between the Earth and Moon, and to develop technology for controlling and maneuvering spacecraft from Earth. It was equipped to take images of the lunar surface with a television-like system, estimate the Moon's mass and topography of the poles, record the distribution and velocity of micrometeorites, and study radiation, magnetic fields, and low frequency electromagnetic waves in space. A midcourse propulsion system and injection rocket would have been the first United States self-contained propulsion system capable of operation many months after launch at great distances from Earth and the first U.S. tests of maneuvering a satellite in space. Mission The spacecraft was launched on Atlas vehicle 91D coupled to Thor-Able upper stages in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas (missile)
The SM-65 Atlas was the first operational intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the United States and the first member of the Atlas rocket family. It was built for the U.S. Air Force by the Convair Division of General Dynamics at an assembly plant located in Kearny Mesa, San Diego. Atlas became operational in October 1959, but was soon made obsolete as an ICBM by new development, and was retired from this role by 1965. Atlas required long preparation times which made it unsuitable for a quick launch ICBM. However, this was not a requirement for planned space launches, and so Atlas-derived launch vehicles served a long history as space launchers. Even before its ICBM use ended in 1965, Atlas had placed four Project Mercury astronauts in orbit and was becoming the foundation for a family of successful space launch vehicles, most notably Atlas Agena and Atlas Centaur. Mergers led to the acquisition of the Atlas Centaur line by the United Launch Alliance. Toda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Launch Complex 14
Launch Complex 14 (LC-14) is a launch site at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. LC-14 was used for various manned and unmanned Atlas launches, including the February 1962, ''Friendship 7'' flight aboard which John Glenn became the first American to orbit the Earth. History LC-14 was the first Atlas pad in operation and hosted the test flights in 1957–58. It was also the only one of the original four pads to never have a booster explode on it. By 1959, it was decided to convert the pad for the Atlas D missile and space launches, and a large service tower was added early in the year. The first Atlas flown from the renovated LC-14 was Missile 7D on May 18; however, a problem with the launcher hold-down arms damaged the missile and caused its explosion shortly after launch. This was traced to improper procedures during the renovation of the pad and was quickly fixed. The first space launch off of LC-14 was the Big Joe Mercury test in September. As the designated Merc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas (rocket Family)
Atlas is a family of US missiles and space launch vehicles that originated with the SM-65 Atlas. The Atlas intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) program was initiated in the late 1950s under the Convair Division of General Dynamics. Atlas was a liquid propellant rocket burning RP-1 fuel with liquid oxygen in three engines configured in an unusual "stage-and-a-half" or "parallel staging" design: two outboard booster engines were jettisoned along with supporting structures during ascent, while the center sustainer engine, propellant tanks and other structural elements remained connected through propellant depletion and engine shutdown. The Atlas name was originally proposed by Karel Bossart and his design team working at Convair on project MX-1593. Using the name of a mighty titan from Greek mythology reflected the missile's place as the biggest and most powerful at the time. It also reflected the parent company of Convair, the Atlas Corporation. The missiles saw only brief IC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 14
Launch Complex 14 (LC-14) is a launch site at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. LC-14 was used for various manned and unmanned Atlas launches, including the February 1962, ''Friendship 7'' flight aboard which John Glenn became the first American to orbit the Earth. History LC-14 was the first Atlas pad in operation and hosted the test flights in 1957–58. It was also the only one of the original four pads to never have a booster explode on it. By 1959, it was decided to convert the pad for the Atlas D missile and space launches, and a large service tower was added early in the year. The first Atlas flown from the renovated LC-14 was Missile 7D on May 18; however, a problem with the launcher hold-down arms damaged the missile and caused its explosion shortly after launch. This was traced to improper procedures during the renovation of the pad and was quickly fixed. The first space launch off of LC-14 was the Big Joe Mercury test in September. As the designated Merc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Able (rocket Stage)
Able rocket stage, is the second stage in the Vanguard rocket cutaway view Able rocket stage engine in the foreground The Able rocket stage was a rocket stage manufactured in the United States by Aerojet as the second of three stages of the Vanguard rocket used in the Vanguard project from 1957 to 1959. The rocket engine used nitric acid and UDMH as rocket propellants. The Able rocket stage was discontinued in 1960. The improved Ablestar version was used as the upper stage of the Thor-Ablestar two stage launcher. The Ablestar second stage was an enlarged version of the Able rocket stage, which gave the Thor-Ablestar a greater payload capacity compared to the earlier Thor-Able. It also incorporated restart capabilities, allowing a multiple-burn trajectory to be flown, further increasing payload, or allowing the rocket to reach different orbits. It was the first rocket to be developed with such a capability and development of the stage took a mere eight months. A version of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |