|
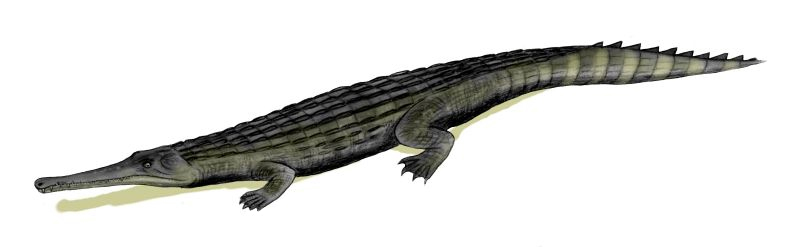
Atlantosuchus
''Atlantosuchus'' is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodylomorph from Morocco. One defining characteristic that distinguishes it from other long-snouted dyrosaurids was its proportionally elongate snout, the longest in proportion to body size of any dyrosaurid. '' Rhabdognathus'', a hyposaurine dyrosaurid, is believed to have been the closest relative of the genus.Jouve, S., B. Bouya, and M. Amaghzaz (2008). A long-snouted dyrosaurid (Crocodyliformes, Mesoeucrocodylia) from the Paleocene of Morocco: phylogenetic and palaoebiogeographic implications. Palaeontology 51(2):281-294. References External links ''Atlantosuchus''in the Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale ... Paleocene crocodylomorphs Fossils of Morocco Dyrosaurids Prehistoric ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyrosaurids
Dyrosauridae is a family of extinct neosuchian crocodyliforms that lived from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to the Eocene. Dyrosaurid fossils are globally distributed, having been found in Africa, Asia, Europe, North America and South America. Over a dozen species are currently known, varying greatly in overall size and cranial shape. A majority were aquatic, some terrestrial and others fully marine (see locomotion below), with species inhabiting both freshwater and marine environments. Ocean-dwelling dyrosaurids were among the few marine reptiles to survive the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. The dyrosaurids were a group of mostly marine, long jawed, crocodile-like quadrupeds up to long. The largest dyrosaurid was probably ''Phosphatosaurus'' estimated at in length. Based on bone tissue evidence, it has been hypothesized that they were slow-growing near-shore marine animals with interlocking closed jaws, able to swim as well as walk on land. External nostrils at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyrosauridae
Dyrosauridae is a family of extinct neosuchian crocodyliforms that lived from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to the Eocene. Dyrosaurid fossils are globally distributed, having been found in Africa, Asia, Europe, North America and South America. Over a dozen species are currently known, varying greatly in overall size and cranial shape. A majority were aquatic, some terrestrial and others fully marine (see locomotion below), with species inhabiting both freshwater and marine environments. Ocean-dwelling dyrosaurids were among the few marine reptiles to survive the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. The dyrosaurids were a group of mostly marine, long jawed, crocodile-like quadrupeds up to long. The largest dyrosaurid was probably ''Phosphatosaurus'' estimated at in length. Based on bone tissue evidence, it has been hypothesized that they were slow-growing near-shore marine animals with interlocking closed jaws, able to swim as well as walk on land. External nostrils at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhabdognathus
''Rhabdognathus'' is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodylomorph. It is known from rocks dating to the Paleocene epoch from western Africa, and specimens dating back to the Maastrichtian era were identified in 2008. It was named by Swinton in 1930 for a lower jaw fragment from Nigeria. The type species is ''Rhabdognathus rarus''. Stéphane Jouve subsequently assessed ''R. rarus'' as indeterminate at the species level, but not at the genus level, and thus dubious. Two skulls which were assigned to the genus ''Rhabdognathus'' but which could not be shown to be identical to ''R. rarus'' were given new species: ''R. aslerensis'' and ''R. keiniensis'', both from Mali. The genus formerly contained the species ''Rhabdognathus compressus'', which was reassigned to ''Congosaurus compressus'' after analysis of the lower jaw of a specimen found that it was more similar to that of the species ''Congosaurus bequaerti''. ''Rhabdognathus'' is believed to be the closest relative to the extinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by an asteroid impact and possibly volcanism, marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of living species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Paleocene, the continents of the Northern Hemisphere were still connected via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 In Paleontology
Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ... Paleontology 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodylomorpha
Crocodylomorpha is a group of pseudosuchian archosaurs that includes the crocodilians and their extinct relatives. They were the only members of Pseudosuchia to survive the end-Triassic extinction. During Mesozoic and early Cenozoic times, crocodylomorphs were far more diverse than they are now. Triassic forms were small, lightly built, active terrestrial animals. The earliest and most primitive crocodylomorphs are represented by " sphenosuchians", a paraphyletic assemblage containing small-bodied forms with elongated limbs that walked upright, which represents the ancestral morphology of Crocodylomorpha. These forms persisted until the end of the Jurassic. During the Jurassic, Crocodylomorphs morphologically diversified into numerous niches, including into the aquatic and marine realms. Evolutionary history When their extinct species and stem group are examined, the crocodylian lineage (clade Pseudosuchia, formerly Crurotarsi) proves to have been a very diverse and adaptive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert L
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate Paleontology And Evolution
''Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution'' is an advanced textbook on vertebrate paleontology by Robert L. Carroll, published in 1988 by WH Freeman. It provides a very detailed technical account of various groups of living and fossil vertebrates. The book, which is written in the style of Alfred Sherwood Romer's ''Vertebrate Paleontology'', presented more recent overall coverage of the subject. At the rear of the book is a 53-page Classification list which lists every genus known at the time of publication, along with locality and stratigraphic range. ''Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution'' appeared in print in 1988, just before the cladistic taxonomy became popular in vertebrate paleontology. The books thus uses the classical systematic scheme, including a number of paraphyletic taxa that are not recognised under phylogenetic nomenclature Phylogenetic nomenclature is a method of nomenclature for taxa in biology that uses phylogenetic definitions for taxon names as explaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Mauritania lies to the south of Western Sahara. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It spans an area of or , with a population of roughly 37 million. Its official and predominant religion is Islam, and the official languages are Arabic and Berber; the Moroccan dialect of Arabic and French are also widely spoken. Moroccan identity and culture is a mix of Arab, Berber, and European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. In a region inhabited since the Paleolithic Era over 300,000 years ago, the first Moroccan s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleobiology Database
The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Paleofaunal Database initiative, which operated from August 1998 through August 2000. From 2000 to 2015, PBDB received funding from the National Science Foundation. PBDB also received support form the Australian Research Council. From 2000 to 2010 it was housed at the National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis, a cross-disciplinary research center within the University of California, Santa Barbara. It is currently housed at University of Wisconsin-Madison and overseen by an international committee of major data contributors. The Paleobiology Database works closely with the Neotoma Paleoecology Database, which has a similar intellectual history, but has focused on the Quaternary (with an emphasis on the late Pleistocene and Holocen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene Crocodylomorphs
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by an asteroid impact and possibly volcanism, marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of living species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Paleocene, the continents of the Northern Hemisphere were still connected via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |