|
Asus ZenFone 8
The Asus ZenFone 8 is an Android-based phone designed, developed and manufactured by Asus as part of its Asus ZenFone series. It was announced on 12 May 2021. History On 13 May Asus announced the ZenFone8 and ZenFone8 Pro, which were announced and sold in Hong Kong on the same day. The devices were launched on 28 May in Malaysia. On 12 May 2021, ASUS announced ZenFone 8 ''(ZenFone 8 Compact)'' and ZenFone 8 Flip under the slogan ''"Big on Performance. Compact in Size."'' They were released later on 13 May 2021, featuring a Qualcomm Snapdragon 888 5G chipset, with Corning Gorilla Glass 6 (Victus in ''Compact ver.'') protection and they support 5G. Their display design is Samsung Super AMOLED AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode, ) is a type of OLED display device technology. OLED describes a specific type of thin-film-display technology in which organic compounds form the electroluminescent material, and active matrix ... screen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asus ZenFone
Asus ZenFone is a series of Android smartphones designed, marketed and produced by Asus. The first-generation ZenFones were announced at the 2014 Consumer Electronic Show in Las Vegas, Nevada. Various models are powered by a series of Intel Atom, Qualcomm Snapdragon, and MediaTek processors. Some ZenFone also features the Zen UI, a user interface from Asus. First generation (2014) ZenFone 4 The ZenFone 4 is the 4-inch WVGA (800×480) TFT display model. The ZenFone 4 features a 1.2 GHz dual-core Intel Atom Z2520 saltwell processor, a 5 MP rear & 0.3 MP front camera and 1 GB RAM. However, ZenFone 4 does not have an LED flash unlike the rest of the models in the ZenFone series. ZenFone 4.5 The ZenFone 4.5 is the 4.5-inch WVGA (854×480) TFT display model. Using the same processor as the ZenFone 4 and having 8GB of internal storage, 1GB of RAM and a MicroSD Card Slot supporting up to 64GB Storage, it does have a better rear camera than the ZenFone 4. The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation (spin axis) is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, according to the conservation of angular momentum. Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the microchip-packaged MEMS gyroscopes found in electronic devices (sometimes called gyrometers), solid-state ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, and the extremely sensitive quantum gyroscope. Applications of gyroscopes include inertial navigation systems, such as in the Hubble Space Telescope, or inside the steel hull of a submerged submarine. Due to their precision, gyroscopes are also used in gyrotheodolites to maintain direction in tunnel mining. Gyroscopes ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panorama
A panorama (formed from Greek πᾶν "all" + ὅραμα "view") is any wide-angle view or representation of a physical space, whether in painting, drawing, photography, film, seismic images, or 3D modeling. The word was originally coined in the 18th century by the English (Irish descent) painter Robert Barker to describe his panoramic paintings of Edinburgh and London. The motion-picture term ''panning'' is derived from ''panorama''. A panoramic view is also purposed for multimedia, cross-scale applications to an outline overview (from a distance) along and across repositories. This so-called "cognitive panorama" is a panoramic view over, and a combination of, cognitive spaces used to capture the larger scale. History The device of the panorama existed in painting, particularly in murals, as early as 20 A.D., in those found in Pompeii, as a means of generating an immersive "panoptic" experience of a vista. Cartographic experiments during the Enlightenment era prec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
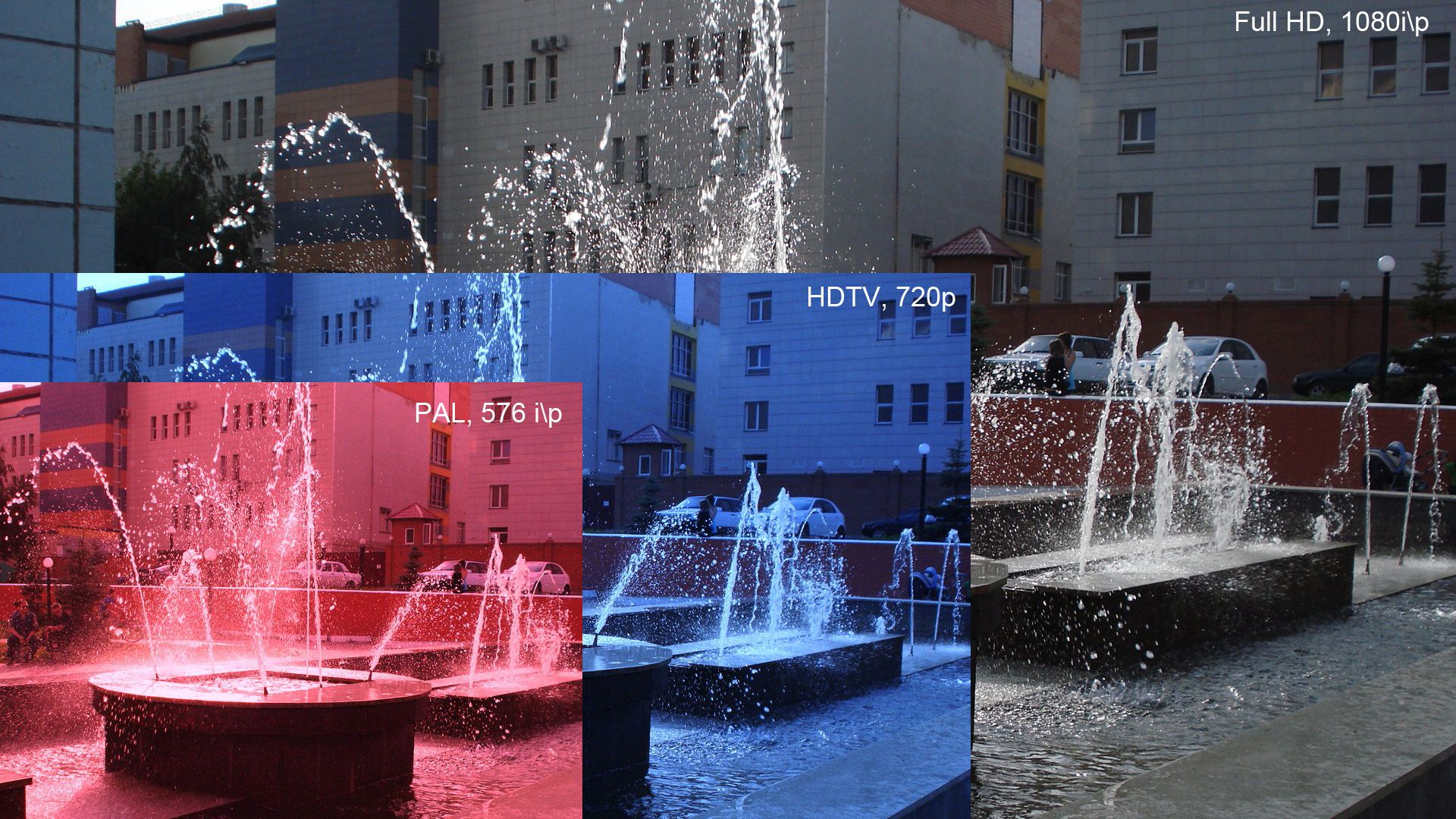
720p
720p (1280×720 px; also called HD ready, standard HD or just HD) is a progressive HDTV signal format with 720 horizontal lines/1280 columns and an aspect ratio (AR) of 16:9, normally known as widescreen HDTV (1.78:1). All major HDTV broadcasting standards (such as SMPTE 292M) include a 720p format, which has a resolution of 1280×720; however, there are other formats, including HDV Playback and AVCHD for camcorders, that use 720p images with the standard HDTV resolution. The frame rate is standards-dependent, and for conventional broadcasting appears in 50 progressive frames per second in former PAL/SECAM countries (Europe, Australia, others), and 59.94 frames per second in former NTSC countries (North America, Japan, Brazil, others). The number ''720'' stands for the 720 horizontal scan lines of image display resolution (also known as 720 pixels of vertical resolution). The ''p'' stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. When broadcast at 60 frames per second, 720p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1080p
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movies, consumer-grade televisions and projector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4K Resolution
4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 38402160 (4K Ultra-high-definition television, UHD) is the dominant 4K standard, whereas the digital cinema, movie projection industry uses 40962160 (Digital Cinema Initiatives, DCI 4K). The 4K television market share increased as prices fell dramatically during 2014 and 2015. 4K standards and terminology The term "4K" is generic and refers to any resolution with a horizontal pixel count of approximately 4,000. Several different 4K resolutions have been standardized by various organizations. The terms "4K" and "Ultra HD" are used more widely in marketing than "2160p". While typically referring to motion pictures, some digital camera vendors have used the term "4K photo" for still photographs, making it appear like an especially high resolution even though 3840×2160 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8K Resolution
8K resolution refers to an image or display resolution with a width of approximately 8,000 pixels. 8K UHD () is the highest resolution defined in the Rec. 2020 (UHDTV) standard. 8K display resolution is the successor to 4K resolution. TV manufacturers pushed to make 4K a new standard by 2017. At CES 2019, the first 8K TVs were unveiled. The feasibility of a fast transition to this new standard is questionable in view of the absence of broadcasting resources. It is predicted (2018 forecast by Strategy Analytics) that 8K-ready devices will still only account for 3% of UHD TVs by 2023 with global sales of 11 million units a year. However, TV manufacturers remain optimistic as the 4K market grew much faster than expected, with actual sales exceeding projections nearly six-fold in 2016. In 2013, a transmission network's capability to carry HDTV resolution was limited by internet speeds and relied on satellite broadcast to transmit the high data rates. The demand is expected to dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Stabilization
Image stabilization (IS) is a family of techniques that reduce blurring associated with the motion of a camera or other imaging device during exposure. Generally, it compensates for pan and tilt (angular movement, equivalent to yaw and pitch) of the imaging device, though electronic image stabilization can also compensate for rotation. It is mainly used in high-end image-stabilized binoculars, still and video cameras, astronomical telescopes, and also smartphones. With still cameras, camera shake is a particular problem at slow shutter speeds or with long focal length lenses (telephoto or zoom). With video cameras, camera shake causes visible frame-to-frame jitter in the recorded video. In astronomy, the problem of lens shake is added to variation in the atmosphere, which changes the apparent positions of objects over time. Application in still photography In photography, image stabilization can facilitate shutter speeds 2 to 5.5 stops slower (exposures 4 to times l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megapixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software. Each pixel is a sample of an original image; more samples typically provide more accurate representations of the original. The intensity of each pixel is variable. In color imaging systems, a color is typically represented by three or four component intensities such as red, green, and blue, or cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. In some contexts (such as descriptions of camera sensors), ''pixel'' refers to a single scalar element of a multi-component representation (called a ''photosite'' in the camera sensor context, although ''sensel'' is sometimes used), while in yet other contexts (like MRI) it may refer to a set of component intensities for a spatial position. Etymology The w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HDR10+
HDR10+ is a high dynamic range (HDR) video technology that adds dynamic metadata to HDR10 source files. The dynamic metadata are used to adjust and optimize each frame of the HDR video to the consumer display's capabilities in a way based on the content creator's intents. HDR10+ is a competitor to Dolby Vision, which also uses dynamic metadata. HDR10+ is the default variant of dynamic metadata as part of the HDMI 2.1 standard. HDR10+ Adaptive is an update designed to optimize HDR10+ content according to the ambient light. Description HDR10+, also known as HDR10 Plus, was announced on 20 April 2017, by Samsung and Amazon Video. HDR10+ updates HDR10 by adding dynamic metadata that can be used to more accurately adjust brightness levels up to 10,000 nits maximum brightness on a scene-by-scene or frame-by-frame basis and supports up to 10-bit colour depth and 8K resolution. This function is based on Samsung variant of metadata format defined in SMPTE ST 2094-40. HDR10+ is an open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
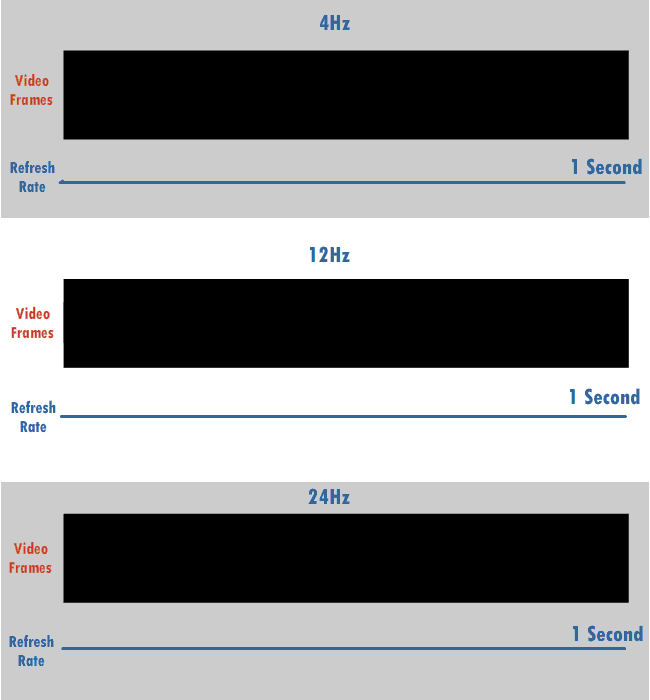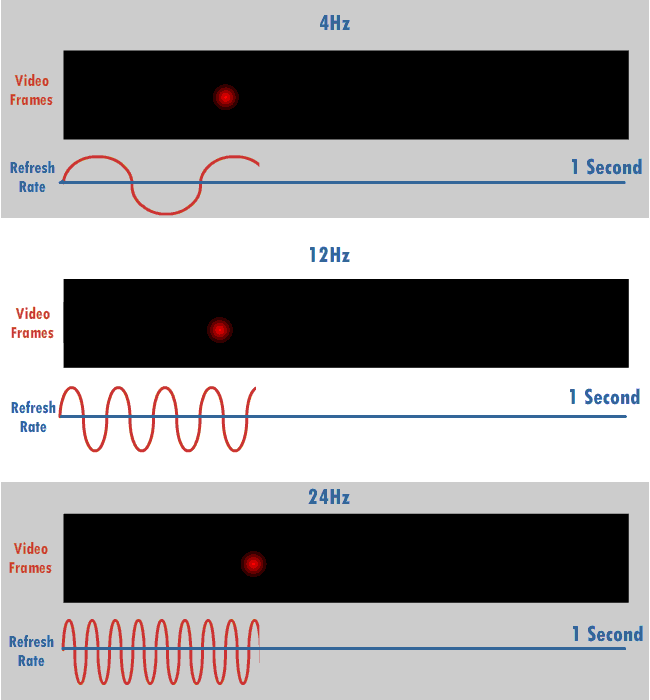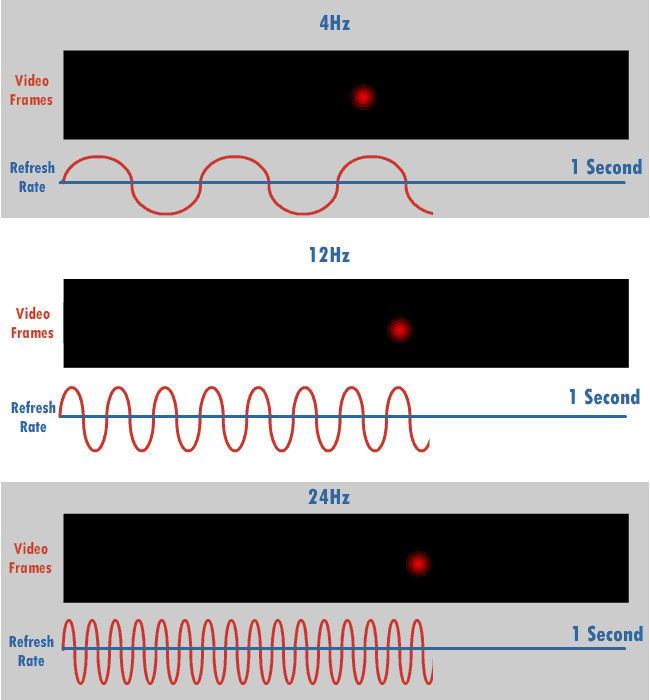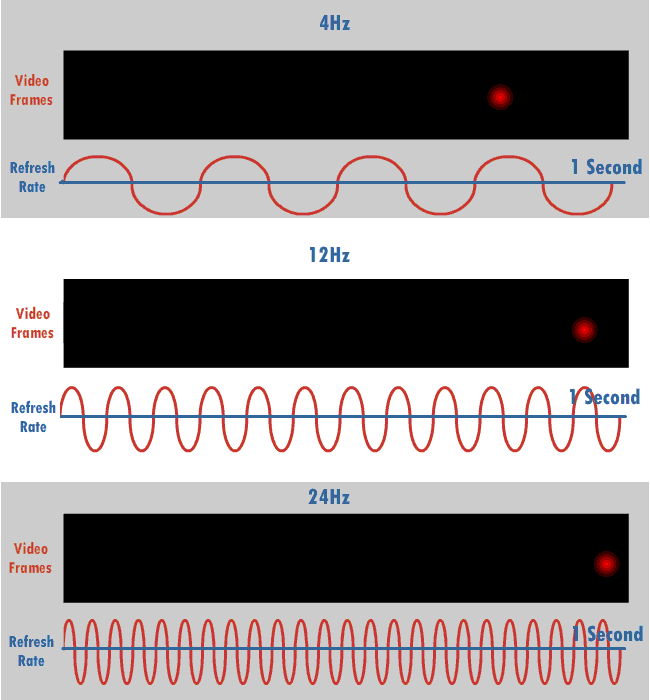
Refresh Rate
The refresh rate (or "vertical refresh rate", "vertical scan rate", terminology originating with the cathode ray tubes) is the number of times per second that a raster-based display device displays a new image. This is independent from frame rate, which describes how many images are stored or generated every second by the device driving the display. On cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, higher refresh rates produce less flickering, thereby reducing eye strain. In other technologies such as liquid-crystal displays, the refresh rate affects only how often the image can potentially be updated. Non-raster displays may not have a characteristic refresh rate. Vector displays, for instance, do not trace the entire screen, only the actual lines comprising the displayed image, so refresh speed may differ by the size and complexity of the image data. For computer programs or telemetry, the term is sometimes applied to how frequently a datum is updated with a new external value from anothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |