|
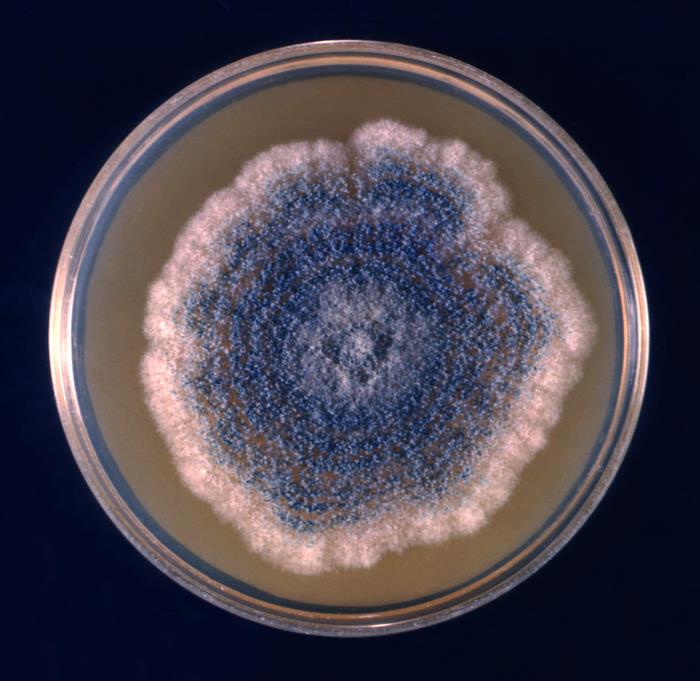
Aspergillus Clavatus
''Aspergillus clavatus'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Aspergillus'' with conidia dimensions 3–4.5 x 2.5–4.5 μm. It is found in soil and animal manure. The fungus was first described scientifically in 1834 by the French mycologist John Baptiste Henri Joseph Desmazières. The fungus can produce the toxin patulin, which may be associated with disease in humans and animals. This species is only occasionally pathogenic. Other sources have identified many species of ''Aspergillus'' as producing dry, hydrophobic spores that are easily inhaled by humans and animals. Due to the small size of the spores, about 70% of spores of ''A. fumigatus'' are able to penetrate into the trachea and primary bronchi and close to 1% into alveoli. Inhalation of spores of ''Aspergillus'' is a health risk. ''A. clavatus'' is allergenic, causing the occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis known as malt-worker's lung. History and taxonomy ''Aspergillus clavatus'' is a species of ''Aspergill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Baptiste Henri Joseph Desmazières
Jean Baptiste Henri Joseph Desmazières (10 July 1786 in Lille – 23 June 1862 in Lambersart) was a merchant of Lille and an amateur mycologist. He was the editor of the scientific journals "'' Annales des sciences naturelles''" and the "'' Bulletin de la société des sciences de Lille''". He was creator of the exsiccatae series "Plantes cryptogames du Nord de la France" (1825–1851) and "Plantes cryptogames de France" (1853–1861). In 1827 he published a treatise on the genus '' Mycoderma'', titled "''Recherches microscopiques et physiologiques sur le genre Mycoderma''". He was the binomial author of the fungi species '' Agaricus radians'' and ''Aspergillus clavatus''. Aspergillus clavatus Eponymous taxa *''[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycelial
Mycelium (plural mycelia) is a root-like structure of a fungus consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. Fungal colonies composed of mycelium are found in and on soil and many other substrate (biology), substrates. A typical single spore germinates into a Monokaryon, monokaryotic mycelium, which cannot reproduce sexually; when two compatible monokaryotic mycelia join and form a dikaryotic mycelium, that mycelium may form sporocarp (fungi), fruiting bodies such as mushrooms. A mycelium may be minute, forming a colony that is too small to see, or may grow to span thousands of acres as in ''Armillaria''. Through the mycelium, a fungus absorbs nutrients from its environment. It does this in a two-stage process. First, the hyphae secrete enzymes onto or into the food source, which break down biopolymers, biological polymers into smaller units such as monomers. These monomers are then absorbed into the mycelium by facilitated diffusion and active transport. Mycelia are v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czapek Medium
Czapek medium, also called Czapek's agar (CZA) or Czapek-Dox medium, is a growth medium for propagating fungi and other organisms in a laboratory. It was named after its inventors, Czech botanist Friedrich Johann Franz Czapek (May 16, 1868 – July 31, 1921) and American chemist Arthur Wayland Dox (September 19, 1882 – 1954). It was developed to grow ''Aspergillus niger'' and '' Penicillium camemberti''. It works well for many saprophytic fungi and soil bacteria such as species of ''Aspergillus'', '' Candida'', ''Penicillium'', and ''Paecilomyces''. Friedrich Czapek's original recipe is as follows: *1000 g distilled water *30 g cane sugar – energy source and sole source of carbon *1 g dipotassium phosphate – buffering agent *0.5 g magnesium sulfate – source of cations *0.5 g potassium chloride – source of essential ions *0.01 g iron sulfate – source of cations Arthur Wayland Dox added 2 g of sodium nitrate in his version, to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyphal
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 µm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membrane. The S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterigmata
In biology, a sterigma (pl. sterigmata) is a small supporting structure. It commonly refers to an extension of the basidium (the spore-bearing cells) consisting of a basal filamentous part and a slender projection which carries a spore at the tip. The sterigmata are formed on the basidium as it develops and undergoes meiosis, to result in the production of (typically) four nuclei. The nuclei gradually migrate to the tips of the basidium, and one nucleus will migrate into each spore that develops at the tip of each sterigma. In less common usage, a sterigma is a structure within the posterior end of the genitalia of female Lepidoptera. It also refers to the stem-like structure, also called a "woody peg" at the base of the leaves of some, but not all conifers, specifically ''Picea'' and ''Tsuga ''Tsuga'' (, from Japanese (), the name of ''Tsuga sieboldii'') is a genus of conifers in the subfamily Abietoideae of Pinaceae, the pine family. The common name hemlock is derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phialide
The phialide ( ; el, phialis, diminutive of phiale, a broad, flat vessel) is a flask-shaped projection from the vesicle (dilated part of the top of conidiophore) of certain fungi. It projects from the mycelium without increasing in length unless a subsequent increase in the formation of conidia occurs. It is the end cell of a phialosphore. See also *Ascomycete Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defi ... References Fungal morphology and anatomy {{mycology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singular Number
In linguistics, grammatical number is a grammatical category of nouns, pronouns, adjectives and verb agreement that expresses count distinctions (such as "one", "two" or "three or more"). English and other languages present number categories of singular or plural, both of which are cited by using the hash sign (#) or by the numero signs "No." and "Nos." respectively. Some languages also have a dual, trial and paucal number or other arrangements. The count distinctions typically, but not always, correspond to the actual count of the referents of the marked noun or pronoun. The word "number" is also used in linguistics to describe the distinction between certain grammatical aspects that indicate the number of times an event occurs, such as the semelfactive aspect, the iterative aspect, etc. For that use of the term, see "Grammatical aspect". Overview Most languages of the world have formal means to express differences of number. One widespread distinction, found in English and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergillus Clavatonanicus
''Aspergillus clavatonanicus'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Aspergillus ' () is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. ''Aspergillus'' was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli. Viewing the fungi under a microscope, Miche ...''. It is from the ''Clavati'' section. The species was first described in 1955.Batista, A.C.; Silva Maia, H. da; Alecrim, I. da C. 1955. Onicomicose produizida por 'Aspergillus clavato-nanica' n. sp. Anais da Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade do Recife. 15(2):197-203 ''A. clavatonanicus'' has been reported to produce antafumicins, glyanthrypine, kotanins, tryptoquivalines, and tryptoquivalones. References clavatonanicus Fungi described in 1955 {{Eurotiomycetes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergillus Longivesica
''Aspergillus longivesica'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Aspergillus''. It is from the ''Clavati'' section. The species was first described in 1971.Huang, L.H.; Raper, K.B. 1971. Aspergillus longivesica, a new species from Nigerian soil. Mycologia. 63(1):50-57 ''A. longivesica'' has been reported to produce patulin Patulin is an organic compound classified as a polyketide. It is a white powder soluble in acidic water and in organic solvents. It is a lactone that is heat-stable, so it is not destroyed by pasteurization or thermal denaturation.http://www.sig ..., tryptoquivalones, tryptoquivalines, antafumicins, and pyripyropen. Growth and morphology ''A. longivesica'' has been cultivated on both Czapek yeast extract agar (CYA) plates and Malt Extract Agar Oxoid® (MEAOX) plates. The growth morphology of the colonies can be seen in the pictures below. Aspergillus_longivesica_cya.png, ''Aspergillus longivesica'' growing on CYA plate Aspergillus_longivesica_meaox.png, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergillus Rhizopodus
''Aspergillus rhizopodus'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Aspergillus''. It is from the ''Clavati'' section. The species was first described in 1975.Rai, J.N.; Wadhwani, K.; Agarwal, S.C. 1975. Aspergillus rhizopodus sp.nov. from Indian alkaline soils. Transactions of the British Mycological Society. 64(3):515-517 ''A. rhizopodus'' has been reported to produce pseurotins, dehydrocarolic acid, tryptoquivalines, tryptoquivalones, kotanins, and cytochalasin Cytochalasins are fungal metabolites that have the ability to bind to actin filaments and block polymerization and the elongation of actin. As a result of the inhibition of actin polymerization, cytochalasins can change cellular morphology, inhibit ...s. Growth and morphology ''A. rhizopodus'' has been cultivated on both Czapek yeast extract agar (CYA) plates and Malt Extract Agar Oxoid® (MEAOX) plates. The growth morphology of the colonies can be seen in the pictures below. Aspergillus_rhizopodus_cya.png, ''Aspergillu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |