|
Ashlar-Vellum
Ashlar-Vellum, a dba of Ashlar Incorporated, is a developer of Computer-aided design (CAD) and 3D modeling software for both the Macintosh and Microsoft Windows platforms. Ashlar-Vellum's interface, designed in 1988 by Dr. Martin Newell and Dan Fitzpatrick, featured an automated Drafting Assistant that found useful points in the geometry and allowed the artist to quickly connect to locations like the "midpoint" or "tangent". Their original 2D product, Vellum, underwent numerous upgrades and gained 3D surface modelling capabilities over time. This product is now known as Graphite. In 1998 Vellum was joined by Solids, which added full solid modeling support. This product is now known as Cobalt, and is also offered in several sub-versions with different feature sets and price points. Founded in Sunnyvale, California, Ashlar Incorporated is now headquartered in Austin, Texas, with additional offices in Kiev, Ukraine. The Designer Elements Product Family The Ashlar-Vellum product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashlar-Vellum
Ashlar-Vellum, a dba of Ashlar Incorporated, is a developer of Computer-aided design (CAD) and 3D modeling software for both the Macintosh and Microsoft Windows platforms. Ashlar-Vellum's interface, designed in 1988 by Dr. Martin Newell and Dan Fitzpatrick, featured an automated Drafting Assistant that found useful points in the geometry and allowed the artist to quickly connect to locations like the "midpoint" or "tangent". Their original 2D product, Vellum, underwent numerous upgrades and gained 3D surface modelling capabilities over time. This product is now known as Graphite. In 1998 Vellum was joined by Solids, which added full solid modeling support. This product is now known as Cobalt, and is also offered in several sub-versions with different feature sets and price points. Founded in Sunnyvale, California, Ashlar Incorporated is now headquartered in Austin, Texas, with additional offices in Kiev, Ukraine. The Designer Elements Product Family The Ashlar-Vellum product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Newell (computer Scientist)
Martin Edward Newell is a British-born computer scientist specializing in computer graphics who is perhaps best known as the creator of the Utah teapot computer model. Career Before emigrating to the US, he worked at what was then the Computer-Aided Design Centre ( CADCentre) in Cambridge, UK, along with his brother Dick Newell (who went on to co-found two of the most important UK graphics software companies – Cambridge Interactive Systems (CIS) in 1977 and Smallworld in 1987). At CADCentre, the two Newells and Tom Sancha developed Newell's algorithm, a technique for eliminating cyclic dependencies when ordering polygons to be drawn by a computer graphics system. Newell developed the Utah teapot while working on a Ph.D. at the University of Utah, where he also helped develop a version of the painter's algorithm for rendering. He graduated in 1975, and was on the Utah faculty from 1977 to 1979. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doing Business As
A trade name, trading name, or business name, is a pseudonym used by companies that do not operate under their registered company name. The term for this type of alternative name is a "fictitious" business name. Registering the fictitious name with a relevant government body is often required. In a number of countries, the phrase "trading as" (abbreviated to t/a) is used to designate a trade name. In the United States, the phrase "doing business as" (abbreviated to DBA, dba, d.b.a., or d/b/a) is used, among others, such as assumed business name or fictitious business name. In Canada, "operating as" (abbreviated to o/a) and "trading as" are used, although "doing business as" is also sometimes used. A company typically uses a trade name to conduct business using a simpler name rather than using their formal and often lengthier name. Trade names are also used when a preferred name cannot be registered, often because it may already be registered or is too similar to a name that is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Companies Based In Texas
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work. At the lowest programming level, executable code consists of machine language instructions supported by an individual processor—typically a central processing unit (CPU) or a graphics processing unit (GPU). Machine language consists of groups of binary values signifying processor instructions that change the state of the computer from its preceding state. For example, an instruction may change the value stored in a particular storage location in the computer—an effect that is not directly observable to the user. An instruction may also invoke one of many input or output operations, for example displaying some text on a computer screen; causing state changes which should be visible to the user. The processor executes the instructions in the order they are provided, unless it is instructed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Companies Established In 1988
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work. At the lowest programming level, executable code consists of machine language instructions supported by an individual processor—typically a central processing unit (CPU) or a graphics processing unit (GPU). Machine language consists of groups of binary values signifying processor instructions that change the state of the computer from its preceding state. For example, an instruction may change the value stored in a particular storage location in the computer—an effect that is not directly observable to the user. An instruction may also invoke one of many input or output operations, for example displaying some text on a computer screen; causing state changes which should be visible to the user. The processor executes the instructions in the order they are provided, unless it is instructed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
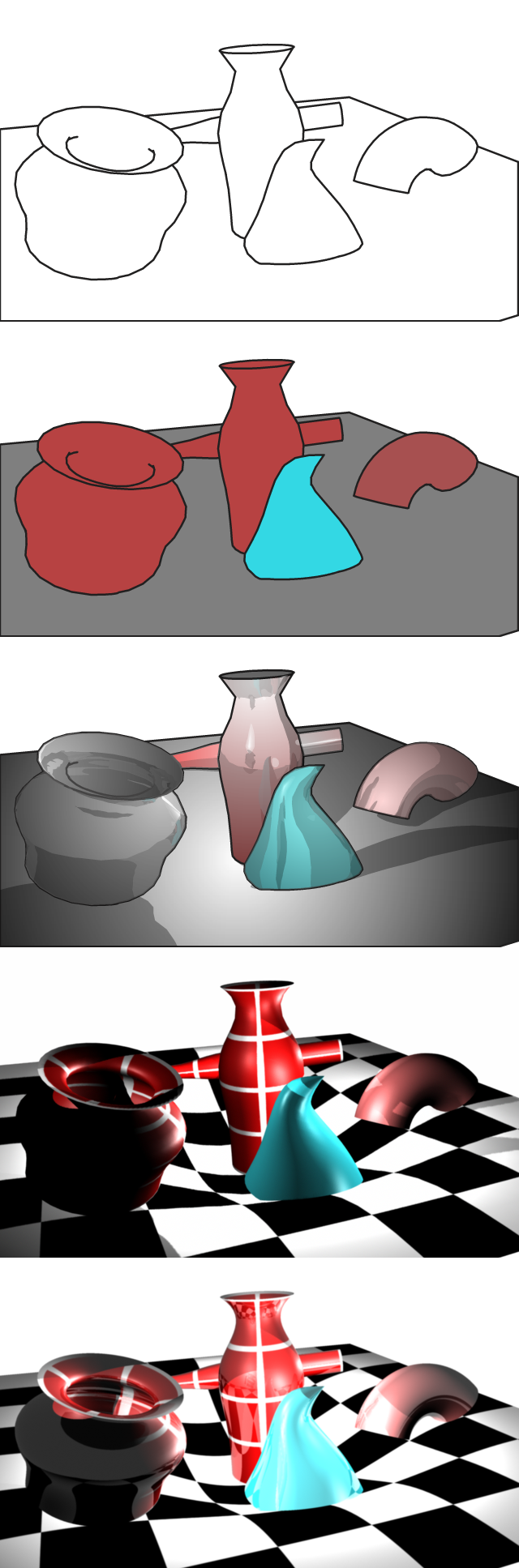
Utah Teapot
The Utah teapot, or the Newell teapot, is a 3D test model that has become a standard reference object and an in-joke within the computer graphics community. It is a mathematical model of an ordinary Melitta-brand teapot that appears solid with a nearly rotationally symmetrical body. Using a teapot model is considered the 3D equivalent of a "Hello, World!" program, a way to create an easy 3D scene with a somewhat complex model acting as the basic geometry for a scene with a light setup. Some programming libraries, such as the OpenGL Utility Toolkit, even have functions dedicated to drawing teapots. The teapot model was created in 1975 by early computer graphics researcher Martin Newell, a member of the pioneering graphics program at the University of Utah. It was one of the first to be modeled using bézier curves rather than precisely measured. History For his work, Newell needed a simple mathematical model of a familiar object. His wife, Sandra Newell, suggested mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid
Solid is one of the State of matter#Four fundamental states, four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and Plasma (physics), plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to a force applied to the surface. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire available volume like a gas. The atoms in a solid are bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystal, crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice), or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass). Solids cannot be compressed with little pressure whereas gases can be compressed with little pressure because the molecules in a gas are loosely packed. The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rendering (computer Graphics)
Rendering or image synthesis is the process of generating a photorealistic or non-photorealistic image from a 2D or 3D model by means of a computer program. The resulting image is referred to as the render. Multiple models can be defined in a ''scene file'' containing objects in a strictly defined language or data structure. The scene file contains geometry, viewpoint, texture, lighting, and shading information describing the virtual scene. The data contained in the scene file is then passed to a rendering program to be processed and output to a digital image or raster graphics image file. The term "rendering" is analogous to the concept of an artist's impression of a scene. The term "rendering" is also used to describe the process of calculating effects in a video editing program to produce the final video output. Rendering is one of the major sub-topics of 3D computer graphics, and in practice it is always connected to the others. It is the last major step in the gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens NX
NX, formerly known as "unigraphics", is an advanced high-end CAD/CAM/ CAE, which has been owned since 2007 by Siemens Digital Industries Software. In 2000, Unigraphics purchased SDRC I-DEAS and began an effort to integrate aspects of both software packages into a single product which became Unigraphics NX or NX. It is used, among other tasks, for: * Design (parametric and direct solid/surface modelling) * Engineering analysis (static; dynamic; electro-magnetic; thermal, using the finite element method; and fluid, using the finite volume method). * Manufacturing finished design by using included machining modules. NX is a direct competitor to CATIA, Creo, Autodesk Inventor. History 1972: United Computing, Inc. releases UNIAPT, one of the world's first end-user CAM products. 1973: The company purchases the Automated Drafting and Machining (ADAM) software code from MCS in 1973. The code became a foundation for a product called UNI-GRAPHICS, later sold commercially as Unigraphic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Edge
Solid Edge is a 3D CAD, parametric feature and synchronous technology solid modeling software. It runs on Microsoft Windows and provides solid modeling, assembly modelling and 2D orthographic view functionality for mechanical designers. Through third party applications it has links to many other Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) technologies. Originally developed and released by Intergraph in 1996 using the ACIS geometric modeling kernel, it changed to using the Parasolid kernel when it was purchased and further developed by UGS Corp in 1998. In 2007, UGS was acquired by the Automation & Drives Division of Siemens AG. UGS company was renamed Siemens Digital Industries Software on October 1, 2007. Since September 2006, Siemens has also offered a free 2D version called Solid Edge 2D Drafting. Solid Edge is available in Design and Drafting, Foundation, Classic or Premium. The "Premium" package includes all of the features of "Classic" plus mechanical and electrical routing sof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Associativity
In mathematics, the associative property is a property of some binary operations, which means that rearranging the parentheses in an expression will not change the result. In propositional logic, associativity is a valid rule of replacement for expressions in logical proofs. Within an expression containing two or more occurrences in a row of the same associative operator, the order in which the operations are performed does not matter as long as the sequence of the operands is not changed. That is (after rewriting the expression with parentheses and in infix notation if necessary), rearranging the parentheses in such an expression will not change its value. Consider the following equations: \begin (2 + 3) + 4 &= 2 + (3 + 4) = 9 \,\\ 2 \times (3 \times 4) &= (2 \times 3) \times 4 = 24 . \end Even though the parentheses were rearranged on each line, the values of the expressions were not altered. Since this holds true when performing addition and multiplication on any real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-aided Design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software are helpful in protecting products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used. Its use in designing electronic systems is known as '' electronic design automation'' (''EDA''). In mechanical design it is known as ''mechanical design automation'' (''MDA''), which includes the process of creating a technical drawing with the use of computer software. CAD software for mechanical design uses either vector-based graphics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.stl/1200px-Utah_teapot_(solid).stl.png)