|
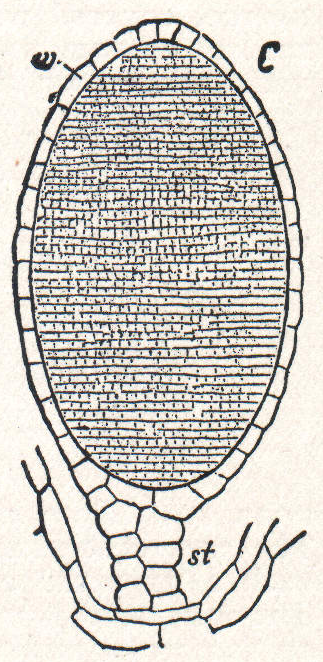
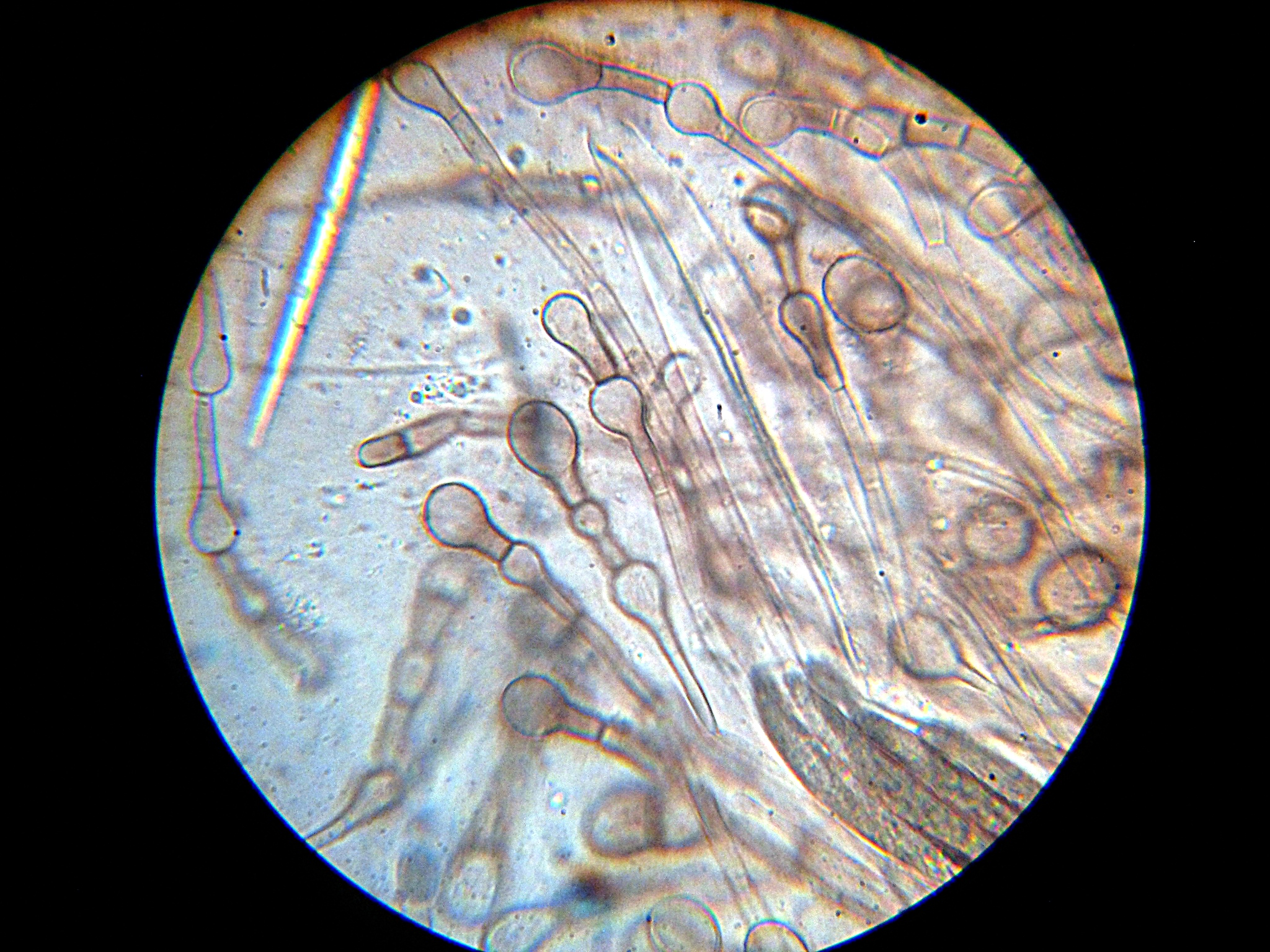
Ascodesmis Nigricans
''Ascodesmis nigricans'' is a coprophilous fungus that could be isolated from the dung of various animals. It was firstly introduced by Philippe Édouard Léon Van Tieghem, a French botanist, and was the type species of the genus ''Ascodesmis''. It is an uncommon species but its development of the fruit body has been the subject of much laboratory study due to the easy nature of its cultivation. ''Ascodesmis nigricans'' is not pathogenic to human, animals or plants. This species has world-wide distribution. History and taxonomy ''Ascodesmis nigricans'' is firstly introduced in by Philippe Édouard Léon Van Tieghem in France in 1876 as a representative type species of genus ''Ascodesmis''. The genus ''Ascodesmis'' belonged to discomycetes which is characterized by species contained disc-shaped ascocarps called apothecia. "Ascodesmis" was given as the genus name because of all the species that under it have a fruit body which only contained an exposed bundle of asci. The growth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oogonium
An oogonium (plural oogonia) is a small diploid cell which, upon maturation, forms a primordial follicle in a female fetus or the female (haploid or diploid) gametangium of certain thallophytes. In the mammalian fetus Oogonia are formed in large numbers by mitosis early in fetal development from primordial germ cells. In humans they start to develop between weeks 4 and 8 and are present in the fetus between weeks 5 and 30. Structure Normal oogonia in human ovaries are spherical or ovoid in shape and are found amongst neighboring somatic cells and oocytes at different phases of development. Oogonia can be distinguished from neighboring somatic cells, under an electron microscope, by observing their nuclei. Oogonial nuclei contain randomly dispersed fibrillar and granular material whereas the somatic cells have a more condensed nucleus that creates a darker outline under the microscope. Oogonial nuclei also contain dense prominent nucleoli. The chromosomal material in the nucleu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antheridia
An antheridium is a haploid structure or organ producing and containing male gametes (called ''antherozoids'' or sperm). The plural form is antheridia, and a structure containing one or more antheridia is called an androecium. Androecium is also the collective term for the stamens of flowering plants. Antheridia are present in the gametophyte phase of cryptogams like bryophytes and ferns. Many algae and some Fungus, fungi, for example ascomycetes and water moulds, also have antheridia during their reproductive stages. In gymnosperms and angiosperms, the male gametophytes have been reduced to Pollen, pollen grains and in most of these the antheridia have been reduced to a single generative cell within the pollen grain. During pollination, this generative cell divides and gives rise to sperm cells. The female counterpart to the antheridium in cryptogams is the archegonium, and in flowering plants is the gynoecium. An antheridium typically consists of sterile cell (biology), cells a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gametangia
A gametangium (plural: gametangia) is an organ or cell in which gametes are produced that is found in many multicellular protists, algae, fungi, and the gametophytes of plants. In contrast to gametogenesis in animals, a gametangium is a haploid structure and formation of gametes does not involve meiosis. Types of gametangia Depending on the type of gamete produced in a gametangium, several types can be distinguished. Female Female gametangia are most commonly called archegonia. They produce egg cells and are the sites for fertilization. Archegonia are common in algae and primitive plants as well as gymnosperms. In flowering plants, they are replaced by the embryo sac inside the ovule. Male The male gametangia are most commonly called antheridia. They produce sperm cells that they release for fertilization. Antheridia producing non-motile sperm (spermatia) are called spermatangia. Some antheridia do not release their sperm. For example, the oomycete antheridium is a syncytium wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epispore
The following is a glossary of terms used in the description of lichens, composite organisms that arise from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungus species in a mutualistic relationship. Until the end of the 18th century, only a couple of lichen-specific terms had been proposed. Johann Dillenius introduced ' in 1742 to describe the cup-shaped structures associated with genus ''Cladonia'', while in 1794 Michel Adanson used ' for the furrowed fruitbodies of the genus '' Graphis''. Erik Acharius, the "father of lichenology", conceived many new terms to describe lichen structures in several of his seminal publications in the early 1800s. Examples include , , , , , , and . In 1825, Friedrich Wallroth published the first of his multi-volume work ''Naturgeschichte der Flechten'' ("Natural History of Lichens"), in which he proposed an alternative terminology based largely on roots from the Greek language. His work, presented as an alternative to that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endospore
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form (''endo'' means 'within'), but it is not a true spore (i.e., not an offspring). It is a stripped-down, dormant form to which the bacterium can reduce itself. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients, and usually occurs in gram-positive bacteria. In endospore formation, the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. Endospores enable bacteria to lie dormant for extended periods, even centuries. There are many reports of spores remaining viable over 10,000 years, and revival of spores millions of years old has been claimed. There is one report of viable spores of ''Bacillus marismortui'' in salt crystals approximately 250 million years old. When the environment becomes more favorable, the endospore can reactivate itself into a vegetative state. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operculum (botany)
In botany, an operculum () or calyptra () is a cap-like structure in some flowering plants, mosses, and fungus, fungi. It is a covering, hood or lid, describing a feature in plant morphology. Flowering plants In flowering plants, the operculum, also known as a calyptra, is the cap-like covering or "lid" of the flower or fruit that detaches at maturity. The operculum is formed by the fusion of sepals and/or petals and is usually shed as a single structure as the flower or fruit matures. The name is also used for the capping tissue of roots, the root cap. In eucalypts, (including ''Eucalyptus'' and ''Corymbia'' but not ''Angophora'') there may be two opercula - an outer operculum formed by the fusion of the united sepals and an inner operculum formed by the fusion of the sepals. In that case, the outer operculum is shed early in the development of the bud leaving a scar around the bud. In those species that lack an outer operculum, there is no bud scar. The inner operculum is sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyses
Paraphyses are erect sterile filament-like support structures occurring among the reproductive apparatuses of fungi, ferns, bryophytes and some thallophytes. The singular form of the word is paraphysis. In certain fungi, they are part of the fertile spore-bearing layer. More specifically, paraphyses are sterile filamentous hyphal end cells composing part of the hymenium of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota interspersed among either the asci or basidia respectively, and not sufficiently differentiated to be called cystidia A cystidium (plural cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that ar ..., which are specialized, swollen, often protruding cells. The tips of paraphyses may contain the pigments which colour the hymenium. In ferns and mosses, they are filament-like structures that are found on sporangia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatia
Sperm is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, which are known as spermatozoa, while some red algae and fungi produce non-motile sperm cells, known as spermatia. Flowering plants contain non-motile sperm inside pollen, while some more basal plants like ferns and some gymnosperms have motile sperm. Sperm cells form during the process known as spermatogenesis, which in amniotes (reptiles and mammals) takes place in the seminiferous tubules of the testes. This process involves the production of several successive sperm cell precursors, starting with spermatogonia, which Cellular differentiation, differentiate into spermatocytes. The spermatocytes then undergo meiosis, reducing their Ploidy, chromosome number by half, which produces spermatids. The spermatids then mature and, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conidia
A conidium ( ; ), sometimes termed an asexual chlamydospore or chlamydoconidium (), is an asexual, non-motile spore of a fungus. The word ''conidium'' comes from the Ancient Greek word for dust, ('). They are also called mitospores due to the way they are generated through the cellular process of mitosis. The two new haploid cells are genetically identical to the haploid parent, and can develop into new organisms if conditions are favorable, and serve in biological dispersal. Asexual reproduction in ascomycetes (the phylum Ascomycota) is by the formation of conidia, which are borne on specialized stalks called conidiophores. The morphology of these specialized conidiophores is often distinctive between species and, before the development of molecular techniques at the end of the 20th century, was widely used for identification of (''e.g.'' ''Metarhizium'') species. The terms microconidia and macroconidia are sometimes used. Conidiogenesis There are two main types of conidium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyphae
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 µm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membrane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)