|
Aschoff Cell
In pathology, Aschoff cells (or Aschoff giant cells) are cells associated with rheumatic heart disease. They are found in Aschoff bodies surrounding centres of fibrinoid necrosis. In comparison with Anitschkow cells their cytoplasm is more basophilic and can contain up to four nuclei.Aschoff Body. nline it. 2014-02-25 Retrieved from http://www.histopathology-india.net/Asch.htm Aschoff believed that Aschoff giant cells were some type of connective or endothelial tissue. Today Aschoff cells are considered to be derived from cardiac myocytes rather than connective tissue cells. Aschoff cells were named after the German physician and pathologist Ludwig Aschoff Karl Albert Ludwig Aschoff (10 January 1866 – 24 June 1942) was a German physician and pathologist. He is considered to be one of the most influential pathologists of the early 20th century and is regarded as the most important German patholog .... References {{Cardiovascular system symptoms and signs Chroni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatic Heart Disease - 2 - Very High Mag
Rheumatology (Greek ''ῥεῦμα'', ''rheûma'', flowing current) is a branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis and management of disorders whose common feature is inflammation in the bones, muscles, joints, and internal organs. Rheumatology covers more than 100 different complex diseases, collectively known as rheumatic diseases, which includes many forms of arthritis as well as lupus and Sjögren's syndrome. Doctors who have undergone formal training in rheumatology are called rheumatologists. Many of these diseases are now known to be disorders of the immune system, and rheumatology has significant overlap with immunology, the branch of medicine that studies the immune system. Rheumatologist A rheumatologist is a physician who specializes in the field of medical sub-specialty called rheumatology. A rheumatologist holds a board certification after specialized training. In the United States, training in this field requires four years undergraduate school, four yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatic Heart Disease
Rheumatic fever (RF) is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a streptococcal throat infection. Signs and symptoms include fever, multiple painful joints, involuntary muscle movements, and occasionally a characteristic non-itchy rash known as erythema marginatum. The heart is involved in about half of the cases. Damage to the heart valves, known as rheumatic heart disease (RHD), usually occurs after repeated attacks but can sometimes occur after one. The damaged valves may result in heart failure, atrial fibrillation and infection of the valves. Rheumatic fever may occur following an infection of the throat by the bacterium ''Streptococcus pyogenes''. If the infection is left untreated, rheumatic fever occurs in up to three percent of people. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve the production of antibodies against a person's own tissues. Due to their genetics, some peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aschoff Bodies
In medicine, Aschoff bodies are nodules found in the hearts of individuals with rheumatic fever. They result from inflammation in the heart muscle and are characteristic of rheumatic heart disease. These nodules were discovered independently by Ludwig Aschoff and Paul Rudolf Geipel, and for this reason they are occasionally called Aschoff-Geipel bodies. Appearance Microscopically, Aschoff bodies are areas of inflammation of the connective tissue of the heart, or focal interstitial inflammation. Fully developed Aschoff bodies are granulomatous structures consisting of fibrinoid change, lymphocytic infiltration, occasional plasma cells, and characteristically abnormal macrophages surrounding necrotic centres. Some of these macrophages may fuse to form multinucleated giant cells. Others may become Anitschkow cells or "caterpillar cells," so named because of the appearance of their chromatin. They are pathognomic foci of fibrinoid necrosis found in many sites, most often the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrinoid Necrosis
Fibrinoid necrosis is a specific pattern of irreversible, uncontrolled cell death that occurs when antigen-antibody complexes are deposited in the walls of blood vessels along with fibrin. It is common in the immune-mediated vasculitides which are a result of type III hypersensitivity. When stained with hematoxylin and eosin, they appear brightly eosinophilic and smudged. Diseases Fibrinoid necrosis is not limited to the immune-mediated vasculitides; many pathologic processes can lead to areas of fibrinoid necrosis. In systemic lupus erythematosus, the dermis The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided i ... is often affected by fluid accumulation and inflammation around the small vessels in the skin, which may show prominent fibrinoid necrosis. Also it's seen in rheumatoid no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anitschkow Cell
In pathology, Anitschkow (or Anichkov) cells are often cells associated with rheumatic heart disease. Anitschkow cells are enlarged macrophages found within granulomas (called Aschoff bodies) associated with the disease. The cells are also called caterpillar cells, as they have an ovoid nucleus and chromatin that is condensed toward the center of the nucleus in a wavy rod-like pattern that to some resembles a caterpillar. Larger Anitschkow cells may coalesce to form multinucleated Aschoff giant cells. Anitschkow cells were named after the Russian pathologist Nikolay Anichkov. Squamous epithelial cells with nuclear changes resembling Anitschkow cells have also been observed in recurrent aphthous stomatitis, iron deficiency anemia, children receiving chemotherapy Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
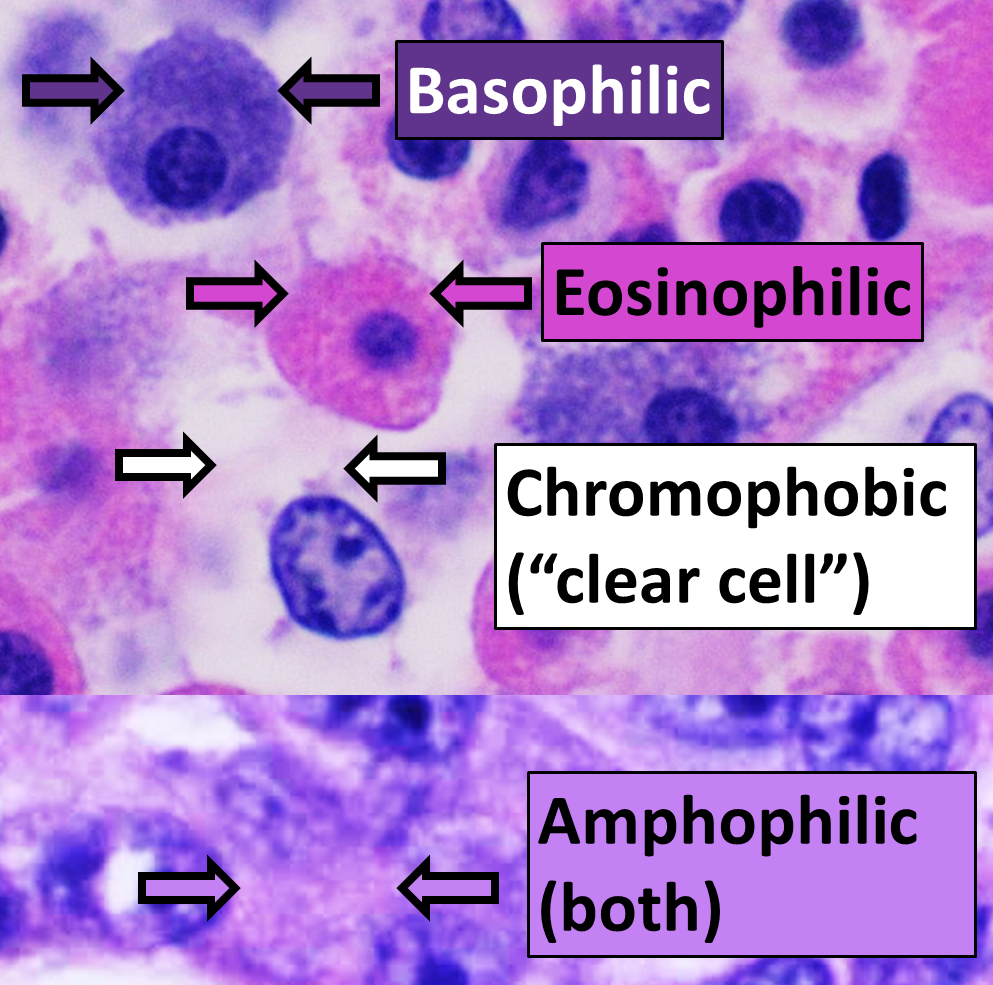
Basophilic
Basophilic is a technical term used by pathologists. It describes the appearance of cells, tissues and cellular structures as seen through the microscope after a histological section has been stained with a basic dye. The most common such dye is haematoxylin. The name basophilic refers to the characteristic of these structures to be stained very well by basic dyes. This can be explained by their charges. Basic dyes are cationic, i.e. contain positive charges, and thus they stain anionic structures (i.e. structures containing negative charges), such as the phosphate backbone of DNA in the cell nucleus and ribosomes. "Basophils" are cells that "love" (from greek "-phil") basic dyes, for example haematoxylin, azure and methylene blue. Specifically, this term refers to: * basophil granulocytes * anterior pituitary basophils An abnormal increase in basophil granulocytes is therefore also described as basophilia.https://www.collinsdictionary.com/de/worterbuch/englisch/basophilia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelial Tissue
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. Endothelial cells form the barrier between vessels and tissue and control the flow of substances and fluid into and out of a tissue. Endothelial cells in direct contact with blood are called vascular endothelial cells whereas those in direct contact with lymph are known as lymphatic endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillaries. These cells have unique functions that include fluid filtration, such as in the glomerulus of the kidney, blood vessel tone, hemostasis, neutrophil recruitment, and hormone trafficking. Endothelium of the interior surfaces of the heart chambers is called endocardium. An impaired function can lead to serious health issues throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)