|
Ascending Palatine Artery
The ascending palatine artery is an artery in the head that branches off the facial artery and runs up the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. Structure The ascending palatine artery arises close to the origin of the facial artery and passes up between the styloglossus and stylopharyngeus to the side of the pharynx along which it is continued between the superior pharyngeal constrictor and the medial pterygoid muscle to near the base of the skull. It divides near the levator veli palatini muscle into two branches: one supplies and follows the course of this muscle, and, winding over the upper border of the superior pharyngeal constrictor, supplies the soft palate and the palatine glands, anastomosing with its fellow of the opposite side and with the descending palatine branch of the maxillary artery; the other pierces the superior pharyngeal constrictor and supplies the palatine tonsil and auditory tube, anastomosing with the tonsillar branch of the facial artery and the as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Carotid Artery
The internal carotid artery (Latin: arteria carotis interna) is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotids arise from the common carotid arteries, where these bifurcate at cervical vertebrae C3 or C4. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain, including the eyes, while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as the face, scalp, skull, and meninges. Classification Terminologia Anatomica in 1998 subdivided the artery into four parts: "cervical", "petrous", "cavernous", and "cerebral". However, in clinical settings, the classification system of the internal carotid artery usually follows the 1996 recommendations by Bouthillier, describing seven anatomical segments of the internal carotid artery, each with a corresponding alphanumeric identifier—C1 cervical, C2 petrous, C3 lacerum, C4 cavernous, C5 clinoid, C6 ophthalmic, and C7 communicating. The Bouthillier nomenclat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
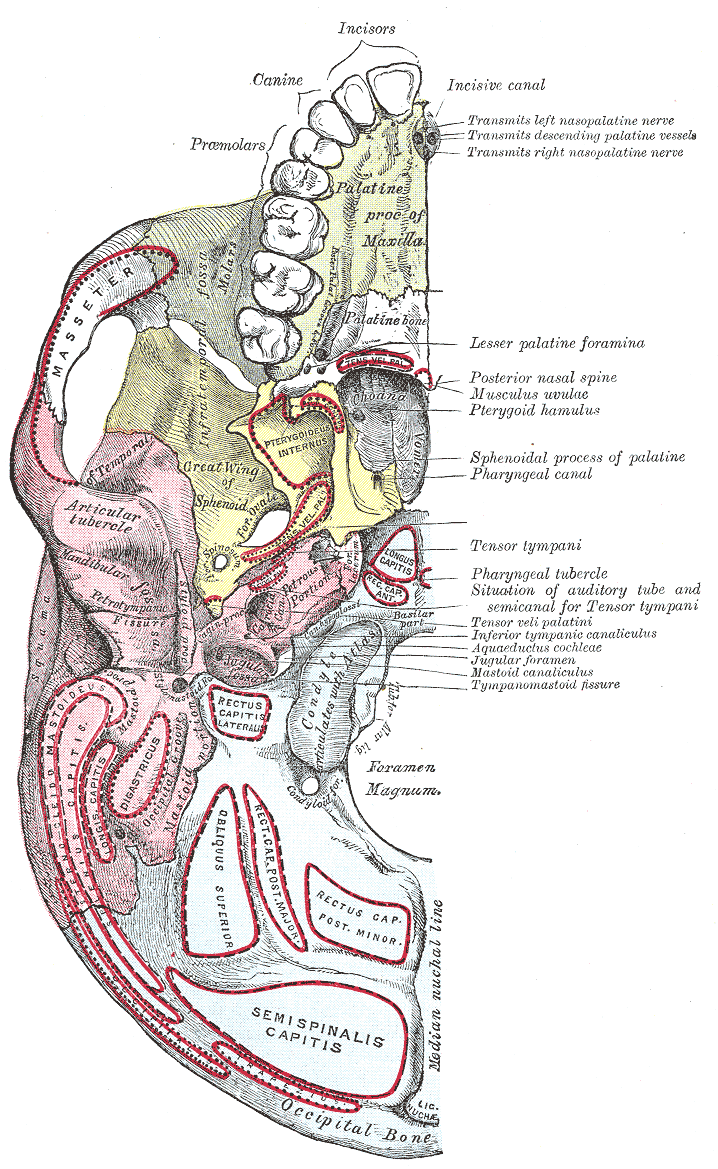
Medial Pterygoid Muscle
The medial pterygoid muscle (or internal pterygoid muscle), is a thick, quadrilateral muscle of the face. It is supplied by the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (V). It is important in mastication (chewing). Structure The medial pterygoid muscle consists of two heads. The bulk of the muscle arises as a deep head from just above the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate. The smaller, superficial head originates from the maxillary tuberosity and the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. Its fibers pass downward, lateral, and posterior, and are inserted, by a strong tendinous lamina, into the lower and back part of the medial surface of the ramus and angle of the mandible, as high as the mandibular foramen. The insertion joins the masseter muscle to form a common tendinous sling which allows the medial pterygoid and masseter to be powerful elevators of the jaw. Nerve supply The medial pterygoid muscle is supplied by the medial pterygoid nerve, a branch of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW) is an American imprint of the American Dutch publishing conglomerate Wolters Kluwer. It was established by the acquisition of Williams & Wilkins and its merger with J.B. Lippincott Company in 1998. Under the LWW brand, Wolters Kluwer, through its Health Division, publishes scientific, technical, and medical content such as textbooks, reference works, and over 275 scientific journals (most of which are medical or other public health journals). Publications are aimed at physicians, nurses, clinicians, and students. Overview LWW grew out of the gradual consolidation of various earlier independent publishers by Wolters Kluwer. Predecessor Wolters Samson acquired Raven Press of New York in 1986. Wolters Samson merged with Kluwer in 1987. The merged company bought J. B. Lippincott & Co. of Philadelphia in 1990; it merged Lippincott with the Raven Press to form Lippincott-Raven in 1995. In 1997 and 1998, Wolters Kluwer acquired Thomson Science (owner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Descending Palatine Artery
The descending palatine artery is a branch of the third part of the maxillary artery supplying the hard and soft palate. Course It descends through the greater palatine canal with the greater and lesser palatine branches of the pterygopalatine ganglion, and, emerging from the greater palatine foramen, runs forward in a groove on the medial side of the alveolar border of the hard palate to the incisive canal; the terminal branch of the artery passes upward through this canal to anastomose with the sphenopalatine artery. Branches Branches are distributed to the gums, the palatine glands, and the mucous membrane of the roof of the mouth; while in the pterygopalatine canal it gives off twigs which descend in the lesser palatine canals to supply the soft palate and palatine tonsil, anastomosing with the ascending palatine artery. According to Terminologia Anatomica, the descending palatine artery branches into the greater palatine artery and lesser palatine arteries The lesser pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascending Pharyngeal Artery
The ascending pharyngeal artery is an artery in the neck that supplies the pharynx, developing from the proximal part of the embryonic second aortic arch. It is the smallest branch of the external carotid and is a long, slender vessel, deeply seated in the neck, beneath the other branches of the external carotid and under the stylopharyngeus muscle. It lies just superior to the bifurcation of the common carotid arteries. The artery most typically bifurcates into embryologically distinct pharyngeal and neuromeningeal trunks. The pharyngeal trunk usually consists of several branches which supply the middle and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles and the stylopharyngeus, ramifying in their substance and in the mucous membranes lining them. These branches are in hemodynamic equilibrium with contributors from the internal maxillary artery. The neuromeningeal trunk classically consists of jugular and hypoglossal divisions, which enter the jugular and hypoglossal foramina to supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonsillar Branch Of The Facial Artery
The tonsillar branch of the facial artery ascends between the pterygoideus internus and styloglossus muscles, and then along the side of the pharynx, perforating the constrictor pharyngis superior, to ramify in the substance of the palatine tonsil and root of the tongue The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste .... References External links Arteries of the head and neck {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Tonsil
Palatine tonsils, commonly called the tonsils and occasionally called the faucial tonsils, are tonsils located on the left and right sides at the back of the throat, which can often be seen as flesh-colored, pinkish lumps. Tonsils only present as "white lumps" if they are inflamed or infected with symptoms of exudates (pus drainage) and severe swelling. Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils and will often, but not necessarily, cause a sore throat and fever. In Chronic (medicine), chronic cases tonsillectomy may be indicated. Structure The palatine tonsils are located in the isthmus of the fauces, between the palatoglossal arch and the palatopharyngeal arch of the soft palate. The palatine tonsil is one of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues (MALT), located at the entrance to the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts to protect the body from the entry of exogenous material through mucosal sites. In consequence it is a site of, and potential focus for, infection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxillary Artery
The maxillary artery supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible. Structure The maxillary artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery, arises behind the neck of the mandible, and is at first imbedded in the substance of the parotid gland; it passes forward between the ramus of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, and then runs, either superficial or deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle, to the pterygopalatine fossa. It supplies the deep structures of the face, and may be divided into mandibular, pterygoid, and pterygopalatine portions. First portion The ''first'' or ''mandibular '' or ''bony'' portion passes horizontally forward, between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, where it lies parallel to and a little below the auriculotemporal nerve; it crosses the inferior alveolar nerve, and runs along the lower border of the lateral pte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Glands
The palatine glands form a continuous layer on the posterior surface of the mucous membrane of the soft palate and around the uvula The palatine uvula, usually referred to as simply the uvula, is a conic projection from the back edge of the middle of the soft palate, composed of connective tissue containing a number of racemose glands, and some muscular fibers. It also conta .... They are pure mucous glands. References External links * Glands {{Anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levator Veli Palatini
The levator veli palatini () is the elevator muscle of the soft palate in the human body. It is supplied via the pharyngeal plexus. During swallowing, it contracts, elevating the soft palate to help prevent food from entering the nasopharynx. Structure The levator veli palatini muscle is found in the soft palate of the mouth. It arises from the under surface of the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone, and from the surface inferolateral to the medial lamina of the cartilage of the Eustachian tube. It does not connect with the medial lamina. It passes above the upper concave margin of the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. It spreads out in the palatine velum, its fibers extending obliquely downward and medially to the middle line, where they blend with those of the opposite side. It lies lateral to the choana. Nerve supply The levator veli palatini muscle is supplied by the pharyngeal plexus, which is supplied by the vagus nerve (CN X). Function The levat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Of The Skull
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria. Structure Structures found at the base of the skull are for example: Bones There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: *Ethmoid bone * Sphenoid bone * Occipital bone *Frontal bone *Temporal bone Sinuses *Occipital sinus * Superior sagittal sinus *Superior petrosal sinus Foramina of the skull * Foramen cecum *Optic foramen *Foramen lacerum *Foramen rotundum * Foramen magnum * Foramen ovale *Jugular foramen *Internal auditory meatus *Mastoid foramen *Sphenoidal emissary foramen *Foramen spinosum Sutures *Frontoethmoidal suture *Sphenofrontal suture *Sphenopetrosal suture *Sphenoethmoidal suture * Petrosquamous suture *Sphenosquamosal suture Other *Sphenoidal lingula *Subarcuate fossa *Dorsum sellae *Jugular process *Petro-occipital fissure *Condylar canal * Jugular tubercle * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food and air to the esophagus and larynx respectively. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. It is also important in vocalization. In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen. They are arranged as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)