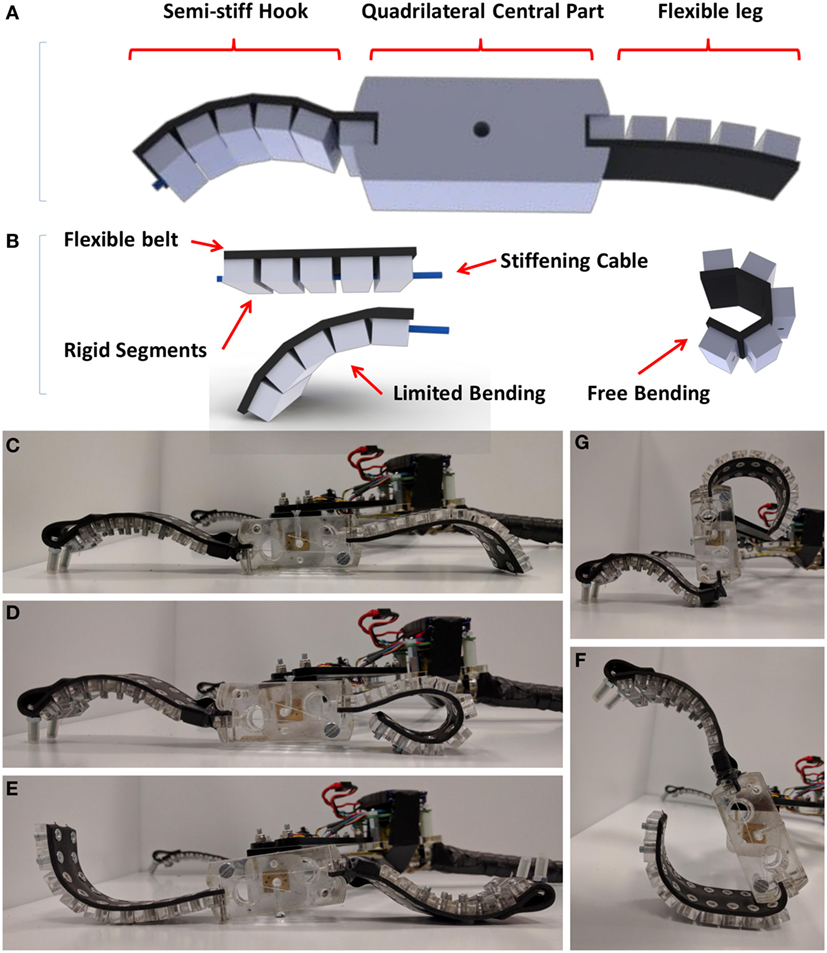
|
Articulated Soft Robotics
The term “soft robots” designs a broad class of robotic systems whose architecture includes soft elements, with much higher elasticity than traditional rigid robots. Articulated Soft Robots are robots with both soft and rigid parts, inspired to the muscle-skeletal system of vertebrate animals – from reptiles to birds to mammalians to humans. Compliance is typically concentrated in actuators, transmission and joints (corresponding to muscles, tendons and articulations) while structural stability is provided by rigid or semi-rigid links (corresponding to bones in vertebrates). The other subgroup in the broad family of soft robots includes continuum soft robots, i.e. robots whose body is a deformable continuum, including its structural, actuating and sensing elements, and take inspiration from invertebrate animals such as octopuses or slugs, or parts of animals, such as an elephant trunk. Soft robots are often designed to exhibit natural behaviours, robustness and adaptivity, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft Robotics
Soft robotics is a subfield of robotics that concerns the design, control, and fabrication of robots composed of compliant materials, instead of rigid links. In contrast to rigid-bodied robots built from metals, ceramics and hard plastics, the compliance of soft robots can improve their safety when working in close contact with humans. Types and designs The goal of soft robotics is the design and construction of robots with physically flexible-bodies and electronics. Sometimes softness is limited to part of the machine. For example, rigid-bodied robotic arms can employ soft end effectors to gently grab and manipulate delicate or irregularly shaped objects. Most rigid-bodied mobile robots also strategically employ soft components, such as foot pads to absorb shock or springy joints to store/release elastic energy. However, the field of soft robotics generally leans toward machines that are predominately or entirely soft. Robots with entirely soft bodies have tremendous potenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actuator
An actuator is a component of a machine that is responsible for moving and controlling a mechanism or system, for example by opening a valve. In simple terms, it is a "mover". An actuator requires a control device (controlled by control signal) and a source of energy. The control signal is relatively low energy and may be electric voltage or current, pneumatic, or hydraulic fluid pressure, or even human power. Its main energy source may be an electric current, hydraulic pressure, or pneumatic pressure. The Control device is usually a valve. When it receives a control signal, an actuator responds by converting the source's energy into mechanical motion. In the ''electric'', ''hydraulic'', and ''pneumatic'' sense, it is a form of automation or automatic control. History The history of the pneumatic actuation system and the hydraulic actuation system dates to around the time of World War II (1938). It was first created by Xhiter Anckeleman who used his knowledge of engines an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Impedance Actuator
{{Disambiguation ...
Variable may refer to: * Variable (computer science), a symbolic name associated with a value and whose associated value may be changed * Variable (mathematics), a symbol that represents a quantity in a mathematical expression, as used in many sciences * Variable (research), a logical set of attributes * Variable star, a type of astronomical star * "The Variable", an episode of the television series ''Lost'' See also * Variability (other) Variability is how spread out or closely clustered a set of data is. Variability may refer to: Biology *Genetic variability, a measure of the tendency of individual genotypes in a population to vary from one another *Heart rate variability, a phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degrees Of Freedom Problem
In neuroscience and motor control , the degrees of freedom problem or motor equivalence problem states that there are multiple ways for humans or animals to perform a movement in order to achieve the same goal. In other words, under normal circumstances, no simple one-to-one correspondence exists between a motor problem (or task) and a motor solution to the problem. The motor equivalence problem was first formulated by the Russian neurophysiologist Nikolai Bernstein: "It is clear that the basic difficulties for co-ordination consist precisely in the extreme abundance of degrees of freedom, with which the ervouscentre is not at first in a position to deal." Although the question of how the nervous system selects which particular degrees of freedom (DOFs) to use in a movement may be a problem to scientists, the abundance of DOFs is almost certainly an advantage to the mammalian and the invertebrate nervous systems. The human body has redundant anatomical DOFs (at muscles and join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humanoid Robot
A humanoid robot is a robot resembling the human body in shape. The design may be for functional purposes, such as interacting with human tools and environments, for experimental purposes, such as the study of bipedal locomotion, or for other purposes. In general, humanoid robots have a torso, a head, two arms, and two legs, though some humanoid robots may replicate only part of the body, for example, from the waist up. Some humanoid robots also have heads designed to replicate human facial features such as eyes and mouths. Androids are humanoid robots built to aesthetically resemble humans. History The concept of a humanoid robot originated in many different cultures around the world. Some of the earliest accounts of the idea of humanoid automata date to the 4th century BCE in Greek mythologies and various religious and philosophical texts from China. Physical prototypes of humanoid automata were later created in the Middle East, Italy, Japan, and France. Greece The Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotic Arm
A robotic arm is a type of mechanical arm, usually programmable, with similar functions to a human arm; the arm may be the sum total of the mechanism or may be part of a more complex robot. The links of such a manipulator are connected by joints allowing either rotational motion (such as in an articulated robot) or translational (linear) displacement. The links of the manipulator can be considered to form a kinematic chain. The terminus of the kinematic chain of the manipulator is called the end effector and it is analogous to the human hand. However, the term "robotic hand" as a synonym of the robotic arm is often proscribed. Types * Cartesian robot / Gantry robot: Used for pick and place work, application of sealant, assembly operations, handling machine tools and arc welding. It is a robot whose arm has three prismatic joints, whose axes are coincident with a Cartesian coordinator. * collaborative robot / Cobot: Cobot applications contrast with traditional industri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industry 4
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, 4IR, or Industry 4.0, conceptualizes rapid change to technology, industries, and societal patterns and processes in the 21st century due to increasing interconnectivity and smart automation. The term has been used widely in scientific literature, and in 2015 was popularized by Klaus Schwab, the World Economic Forum Founder and Executive chairman. Schwab asserts that the changes seen are more than just improvements to efficiency, but express a significant shift in Capitalism, industrial capitalism. A part of this phase of industrial change is the joining of technologies like artificial intelligence, CRISPR gene editing, gene editing, to Robotics, advanced robotics that blur the lines between the physical, digital, and biological worlds. Throughout this, fundamental shifts are taking place in how the global production and supply network operates through ongoing automation of traditional manufacturing and industrial practices, using modern smar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobot
A cobot, or collaborative robot, is a robot intended for direct human-robot interaction within a shared space, or where humans and robots are in close proximity. Cobot applications contrast with traditional industrial robot applications in which robots are isolated from human contact. Cobot safety may rely on lightweight construction materials, rounded edges, and inherent limitation of speed and force, or on sensors and software that ensure safe behavior. The International Federation of Robotics (IFR), a global industry association of robot manufacturers and national robot associations, recognizes two main groups of robots: industrial robots used in automation in an industrial environment and service robots for domestic and professional use. Service robots could be considered to be cobots as they are intended to work alongside humans. Industrial robots have traditionally worked separately from humans behind fences or other protective barriers, but cobots remove that separation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humanoid Robot
A humanoid robot is a robot resembling the human body in shape. The design may be for functional purposes, such as interacting with human tools and environments, for experimental purposes, such as the study of bipedal locomotion, or for other purposes. In general, humanoid robots have a torso, a head, two arms, and two legs, though some humanoid robots may replicate only part of the body, for example, from the waist up. Some humanoid robots also have heads designed to replicate human facial features such as eyes and mouths. Androids are humanoid robots built to aesthetically resemble humans. History The concept of a humanoid robot originated in many different cultures around the world. Some of the earliest accounts of the idea of humanoid automata date to the 4th century BCE in Greek mythologies and various religious and philosophical texts from China. Physical prototypes of humanoid automata were later created in the Middle East, Italy, Japan, and France. Greece The Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomous Robot
An autonomous robot is a robot that acts without recourse to human control. The first autonomous robots environment were known as Elmer and Elsie, which were constructed in the late 1940s by W. Grey Walter. They were the first robots in history that were programmed to "think" the way biological brains do and meant to have free will.Ingalis-Arkell, Esthe"The Very First Robot Brains Were Made of Old Alarm Clocks" 7 March 2012. Elmer and Elsie were often labeled as tortoises because of how they were shaped and the manner in which they moved. They were capable of phototaxis which is the movement that occurs in response to light stimulus. Historic examples include space probes. Modern examples include self-driving vacuums and cars. Industrial robot arms that work on assembly lines inside factories may also be considered autonomous robots, though their autonomy is restricted due to a highly structured environment and their inability to locomote. Components and criteria of rob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |