|
Arthur Bambridge Wyse
Arthur Bambridge Wyse (June 25, 1909 – June 8, 1942) was an American astronomer. He was killed in a U.S. Navy airship accident during World War II. Biography Wyse was born in Blairstown, Iowa, the son of Charles M. Wyse and Celia J. Bambridge. His father was a Prebyterian minister. At the age of sixteen, he matriculated to the private liberal arts College of Wooster in Ohio. While there, he received the John H. Moreland prize for his work in Greek studies, and was elected to the Phi Beta Kappa honor society. At Wooster, Wyse met his future wife, Marylyn Crandell. He graduated in 1929 with an A.B. ''cum laude'', then went work as an accountant for the Bell Telephone Company for a year. Wyse entered graduate school at the University of Michigan, where he decided on Astronomy as his profession. He received his A.M. in 1931 with studies in astronomy, physics, and mathematics. In August 1931, Wyse transferred to the University of California, Berkeley to study astrophysics. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy (IPA: ), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224 and originally the Andromeda Nebula, is a barred spiral galaxy with the diameter of about approximately from Earth and the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. The galaxy's name stems from the area of Earth's sky in which it appears, the constellation of Andromeda, which itself is named after the princess who was the wife of Perseus in Greek mythology. The virial mass of the Andromeda Galaxy is of the same order of magnitude as that of the Milky Way, at . The mass of either galaxy is difficult to estimate with any accuracy, but it was long thought that the Andromeda Galaxy is more massive than the Milky Way by a margin of some 25% to 50%. This has been called into question by a 2018 study that cited a lower estimate on the mass of the Andromeda Galaxy, combined with preliminary reports on a 2019 study estimating a higher mass of the Milky Way. The Andromeda Galaxy has a diameter of about , making it the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-class Blimp
The ''G''-Class Blimps were a series of non-rigid airships (blimps) used by the United States Navy. In 1935, instead of developing a new design airship, the Navy purchased the Goodyear Blimp ''Defender'' for use as a trainer and utility airship assigning it the designator ''G-1''. ''Defender'' was built by the Goodyear Aircraft Company of Akron, Ohio and was the largest blimp in the company’s fleet of airships that were used for advertising and as passenger airships. Goodyear built additional ''G''-class airships for the Navy during World War II to support training needs. Operational history After purchase on September 23, 1935, ''G-1'' was in constant use until it was lost in a mid-air collision on 8 June 1942 with another blimp, the ''L-2''. The two blimps were conducting experimental visual and photographic observations during night flight. Although twelve people were killed in the crash, ''G-1'' had demonstrated her capabilities as a trainer and utility blimp. As the Nav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manasquan, New Jersey
Manasquan (, ) is a borough in Monmouth County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey, on the Jersey Shore. As of the 2020 United States census, the borough's population was 5,938, an increase of 41 (+.7%) from the 2010 census count of 5,897, which in turn reflected a decline of 413 (−6.5%) from the 6,310 counted at the 2000 Census. The borough's name is of Lenape Native American origin, deriving from "Mënàskunk" meaning "Place to Gather Grass or Reeds". Manasquan, Maniquan, Mannisquan, Manasquam, Squan, and Squan Village are variations on the original pronunciation and spelling. The borough's name has also been described as deriving from "Man-A-Squaw-Han" meaning "stream of the island of squaws", "an island with enclosure for squans", "island door" or "point" / "top". Manasquan, Maniquan, Mannisquan, Manasquam, Squan, and Squan Village are variations on the original pronunciation and spelling. Manasquan was formed as a borough by an act of the New Jersey Legislature on Decemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-class Blimp
The L-class blimps were training airships operated by the United States Navy during World War II. In the mid-1930s, the Goodyear Aircraft Company built a family of small non-rigid airships that the company used for advertising the Goodyear name. In 1937 the United States Navy awarded a contract for two different airships, K-class blimp designated K-2 and a smaller blimp based upon Goodyear's smaller commercial model airship used for advertising and passenger carrying. The smaller blimp was designated by the Navy as L-1. It was delivered in April 1938 and operated from the Navy's lighter-than-air facility at Lakehurst, New Jersey. In the meantime, the Navy ordered two more L-Class blimps, the L-2 and L-3, on September 25, 1940. These were delivered in 1941. L-2 was lost in a nighttime mid-air collision with the G-1 on June 8, 1942. When the United States entered World War II, the Navy took over the operation of Goodyear's five commercial blimps. These were the ''Resolute'', ''En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Of Scientific Research And Development
The Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) was an agency of the United States federal government created to coordinate scientific research for military purposes during World War II. Arrangements were made for its creation during May 1941, and it was created formally by Executive Order 8807 on June 28, 1941. It superseded the work of the National Defense Research Committee (NDRC), was given almost unlimited access to funding and resources, and was directed by Vannevar Bush, who reported only to President Franklin Delano Roosevelt. The research was widely varied, and included projects devoted to new and more accurate bombs, reliable detonators, work on the proximity fuze, guided missiles, radar and early-warning systems, lighter and more accurate hand weapons, more effective medical treatments (including work to make penicillin at scale, which was necessary for its use as a drug), more versatile vehicles, and, the most secret of all, the S-1 Section, which later be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Defense Research Committee
The National Defense Research Committee (NDRC) was an organization created "to coordinate, supervise, and conduct scientific research on the problems underlying the development, production, and use of mechanisms and devices of warfare" in the United States from June 27, 1940, until June 28, 1941. Most of its work was done with the strictest secrecy, and it began research of what would become some of the most important technology during World War II, including radar and the atomic bomb. It was superseded by the Office of Scientific Research and Development in 1941, and reduced to merely an advisory organization until it was eventually terminated during 1947. Organization The NDRC was created by an order of President Franklin Delano Roosevelt on June 27, 1940. It was part of the Council of National Defense, which had been created during 1916 to coordinate industry and resources for national security purposes. Vannevar Bush, the director of the Carnegie Institution, had pressed for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allegheny Observatory
The Allegheny Observatory is an American astronomical research institution, a part of the Department of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Pittsburgh. The facility is listed on the National Register of Historic Places (ref. # 79002157, added June 22, 1979) and is designated as a Pennsylvania state and Pittsburgh History and Landmarks Foundation historic landmark. History The observatory was founded on February 15, 1859, in the city of Allegheny, Pennsylvania (incorporated into the City of Pittsburgh in 1907) by a group of wealthy industrialists calling themselves the Allegheny Telescope Association. The observatory's initial purpose was for general public education as opposed to research, but by 1867 the revenues derived from this had receded. The facility was then donated to the Western University of Pennsylvania, today known as the University of Pittsburgh. The University hired Samuel Pierpont Langley to be the first director. One of the research programs initiate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Pittsburgh
The University of Pittsburgh (Pitt) is a public state-related research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The university is composed of 17 undergraduate and graduate schools and colleges at its urban Pittsburgh campus, home to the university's central administration and around 28,000 undergraduate and graduate students. The 132-acre Pittsburgh campus includes various historic buildings that are part of the Schenley Farms Historic District, most notably its 42-story Gothic revival centerpiece, the Cathedral of Learning. Pitt is a member of the Association of American Universities and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". It is the second-largest non-government employer in the Pittsburgh metropolitan area. Pitt traces its roots to the Pittsburgh Academy founded by Hugh Henry Brackenridge in 1787. While the city was still on the edge of the American frontier at the time, Pittsburgh's rapid growth meant that a proper university was so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limb Darkening
Limb darkening is an optical effect seen in stars (including the Sun), where the central part of the disk appears brighter than the edge, or ''limb''. Its understanding offered early solar astronomers an opportunity to construct models with such gradients. This encouraged the development of the theory of radiative transfer. Basic theory Optical depth, a measure of the opacity of an object or part of an object, combines with effective temperature gradients inside the star to produce limb darkening. The light seen is approximately the integral of all emission along the line of sight modulated by the optical depth to the viewer (i.e. 1/e times the emission at 1 optical depth, 1/e2 times the emission at 2 optical depths, etc.). Near the center of the star, optical depth is effectively infinite, causing approximately constant brightness. However, the effective optical depth decreases with increasing radius due to lower gas density and a shorter line of sight distance through the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ira Sprague Bowen
Ira Sprague Bowen (December 21, 1898 – February 6, 1973) was an American physicist and astronomer. In 1927 he discovered that nebulium was not really a chemical element but instead doubly ionized oxygen. Life and work Bowen was born in Seneca Falls, New York in 1898 to Philinda Sprague and James Bowen. Due to frequent moves of his family he was home schooled until his father died in 1908. From that point on he attended Houghton College where his mother worked as teacher. After graduation from high school in 1915 Bowen stayed at the junior college of Houghton College, and later joined Oberlin College from which he graduated in 1919. During his time at Oberlin, Bowen did some research on the properties of steel for the scientist Robert Hadfield. Their results were published in 1921. Bowen began studying physics at the University of Chicago in fall 1919. By 1921 he took a position in the research group of Robert Andrews Millikan. He was assigned to do ultraviolet spectrosco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
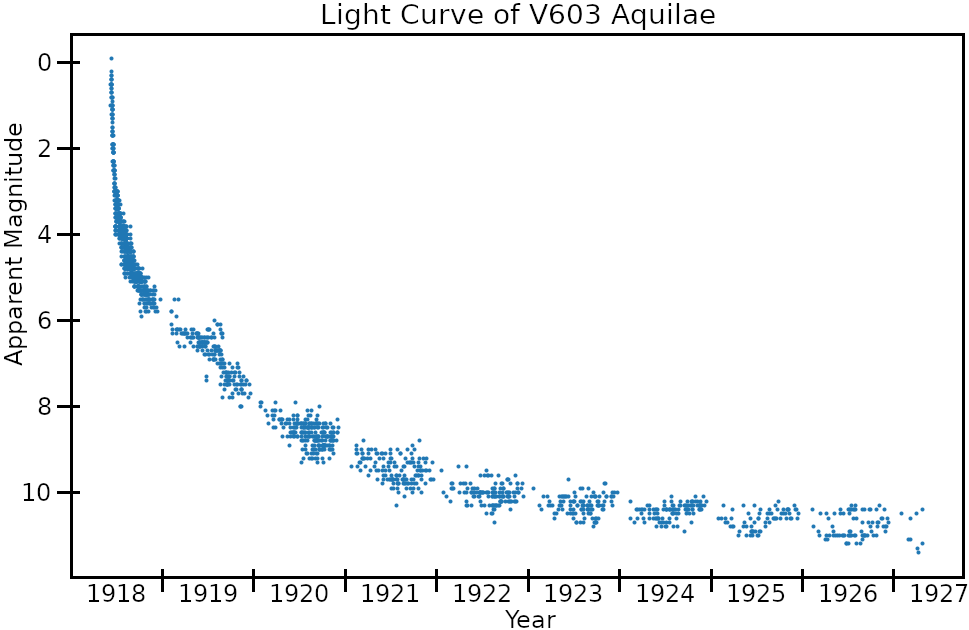
Nova Aquilae 1918
V603 Aquilae (or Nova Aquilae 1918) was a bright nova first observed (from Earth) in the constellation Aquila in 1918. It was the brightest "new star" to appear in the sky since Kepler's Supernova in 1604. Like all novae, it is a binary system, comprising a white dwarf and donor low-mass star in close orbit to the point of being only semidetached. The white dwarf sucks matter off its companion, which has filled its Roche lobe, onto its accretion disk and surface until the excess material is blown off in a thermonuclear event. This material then forms an expanding shell, which eventually thins out and disappears. First seen by Zygmunt Laskowski, a medical professor and amateur astronomer, and then confirmed on the night of 8 June 1918 by the UK amateur astronomer Grace Cook, Nova Aquilae reached a peak magnitude of −0.5; it was the brightest nova recorded in the era of the telescope. It was brighter than all stars but Sirius and Canopus. Tycho's and Kepler's supernova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)