|
Arthur Addison 2
Arthur is a masculine given name of uncertain etymology. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur. A common spelling variant used in many Slavic, Romance, and Germanic languages is Artur. In Spanish and Italian it is Arturo. Etymology The earliest attestation of the name Arthur is in the early 9th century Welsh-Latin text ''Historia Brittonum'', where it refers to a circa 5th century Romano-British general who fought against the invading Saxons, and who later gave rise to the famous King Arthur of medieval legend and literature. A possible earlier mention of the same man is to be found in the epic Welsh poem ''Y Gododdin'' by Aneirin, which some scholars assign to the late 6th century, though this is still a matter of debate and the poem only survives in a late 13th century manuscript entitled the Book of Aneirin. A 9th-century Breton landowner named Arthur witnessed several charters collected in the '' Cartulary of Redon''. The Irish borro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
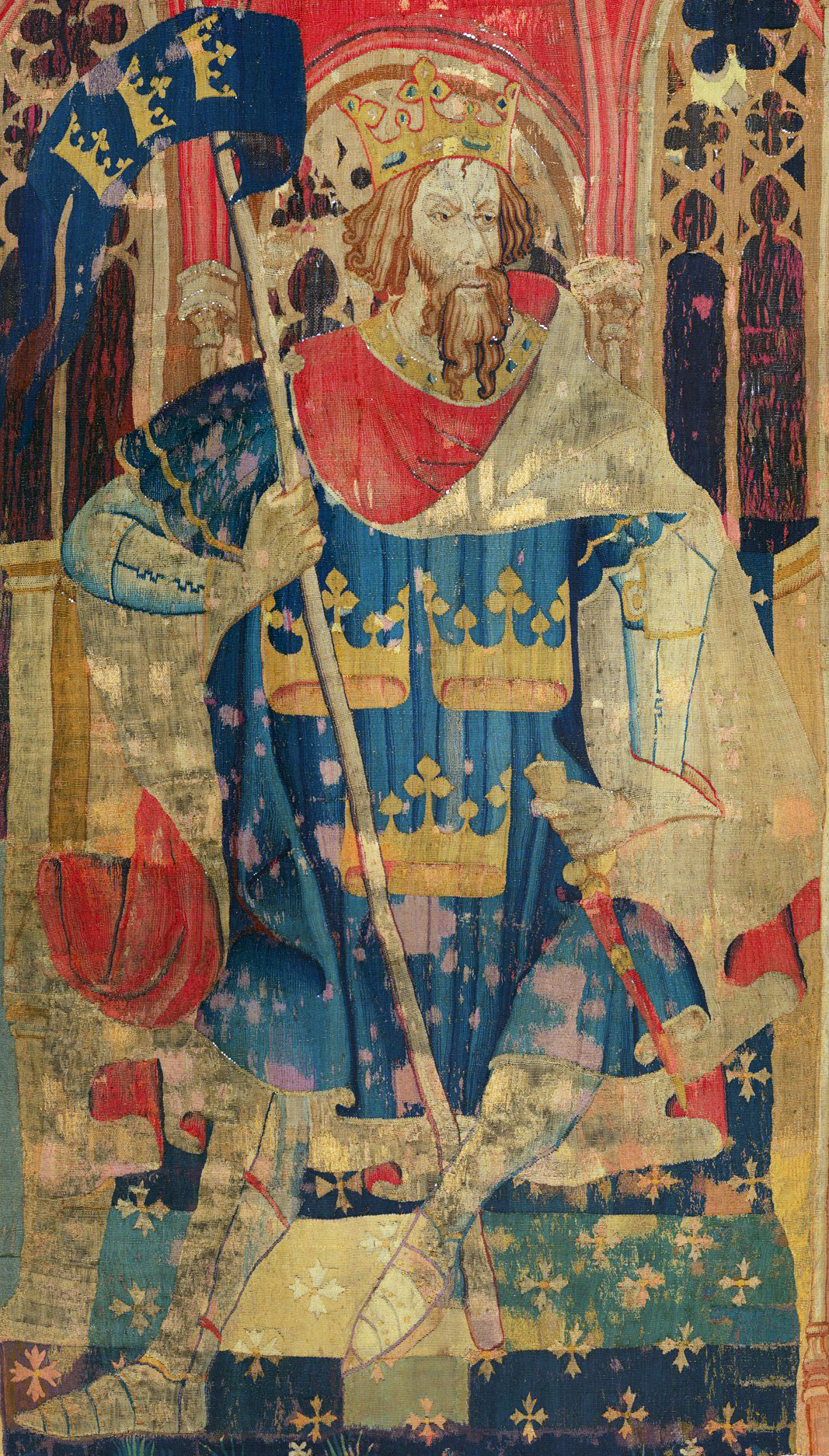
King Arthur
According to legends, King Arthur (; ; ; ) was a king of Great Britain, Britain. He is a folk hero and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain. In Wales, Welsh sources, Arthur is portrayed as a leader of the Sub-Roman Britain, post-Roman Britons in battles against the Anglo-Saxons in the late-5th and early-6th centuries. He first appears in two early medieval historical sources, the ''Annales Cambriae'' and the ''Historia Brittonum'', but these date to 300 years after he is supposed to have lived, and most historians who study the period Historicity of King Arthur, do not consider him a historical figure.Tom Shippey, "So Much Smoke", ''review'' of , ''London Review of Books'', 40:24:23 (20 December 2018) His name also occurs in early Welsh-language literature, Welsh poetic sources, such as ''Y Gododdin''. The character developed through Welsh mythology, appearing either as a great warrior defending Britain from human and supernatura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
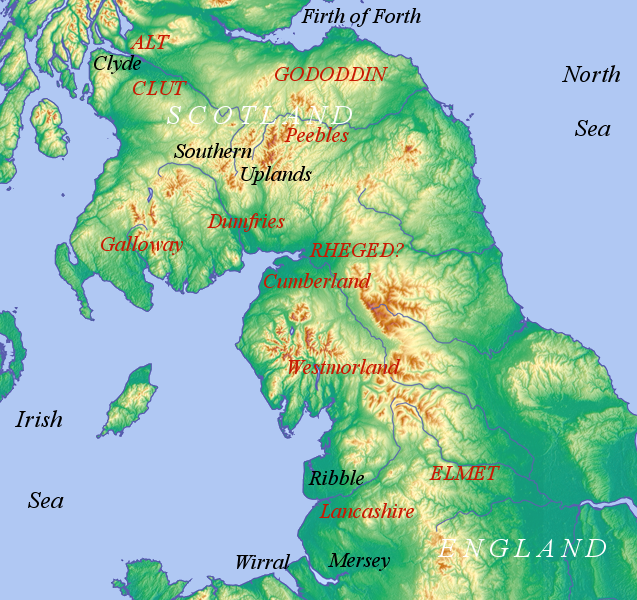
Cumbric Language
Cumbric is an extinct Celtic languages, Celtic language of the Brittonic languages, Brittonic subgroup spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North", in Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands. It was closely related to Old Welsh and the other Brittonic languages. Place-name evidence suggests Cumbric may also have been spoken as far south as Borough of Pendle, Pendle and the Yorkshire Dales. The prevailing view is that it became extinct in the 12th century, after the incorporation of the Kingdom of Strathclyde into the Kingdom of Scotland. Problems with terminology Dauvit Broun sets out the problems with the various terms used to describe the Cumbric language and its speakers.Broun, Dauvit (2004): 'The Welsh identity of the kingdom of Strathclyde, ca 900-ca 1200', ''Innes Review'' 55, pp 111–80. The people seem to have called themselves the same way that the Welsh called themselves (most likely from reconstructed Brittonic meaning "f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonology
Phonology (formerly also phonemics or phonematics: "phonemics ''n.'' [''obsolescent''] 1. Any procedure for identifying the phonemes of a language from a corpus of data. 2. (formerly also phonematics) A former synonym for phonology, often preferred by the American Structuralists and reflecting the importance in structuralist work of phonemics in sense 1.": "phonematics ''n.'' 1. [''obsolete''] An old synonym for phonemics (sense 2).") is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages systematically organize their phonemes or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but now it may relate to any Linguistic description, linguistic analysis either: Sign languages have a phonological system equivalent to the system of sounds in spoken languages. The buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patronym
A patronymic, or patronym, is a component of a personal name based on the given name of one's father, grandfather (more specifically an avonymic), or an earlier male ancestor. It is the male equivalent of a matronymic. Patronymics are used, by custom or official policy, in many countries worldwide, although elsewhere their use has been replaced by or transformed into patronymic surnames. Examples of such transformations include common English surnames such as Johnson (son of John). Origins of terms The usual noun and adjective in English is ''patronymic'', but as a noun this exists in free variation alongside ''patronym''. The first part of the word ''patronym'' comes from Greek πατήρ ''patēr'' 'father' ( GEN πατρός ''patros'' whence the combining form πατρο- ''patro''-); the second part comes from Greek ὄνυμα ''onyma'', a variant form of ὄνομα ''onoma'' 'name'. In the form ''patronymic'', this stands with the addition of the suffix -ικός ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celticist
Celtic studies or Celtology is the academic discipline occupied with the study of any sort of cultural output relating to the Celtic-speaking peoples (i.e. speakers of Celtic languages). This ranges from linguistics, literature and art history, archaeology and history, the focus lying on the study of the various Celtic languages, living and extinct.Wiley, "Celtic studies, early history of the field" (2006). The primary areas of focus are the six Celtic languages currently in use: Irish, Scottish Gaelic, Manx, Welsh, Cornish, and Breton. As a university subject, it is taught at a number of universities, most of them in Ireland, the United Kingdom, or France, but also in the United States, Canada, Australia, Germany, Poland, Austria and the Netherlands. History Written studies of the Celts, their cultures, and their languages go back to classical Greek and Latin accounts, possibly beginning with Hecataeus in the 6th century BC and best known through such authors as Polybi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kemp Malone
Kemp Malone (March 14, 1889 – October 13, 1971) was an American medievalist, etymology, etymologist, philologist, and specialist in Geoffrey Chaucer, Chaucer. He was a lecturer and then professor of English literature at Johns Hopkins University from 1924 to 1956. Life and career Born in Minter City, Mississippi, to an academic family, Kemp Malone graduated from Emory University, Emory College (as it then was) in 1907, with the ambition of mastering all the languages that impinged upon the development of Middle English. He spent several years in Germany, Denmark and Iceland. When World War I broke out, he served two years in the United States Army and was discharged with the rank of captain. Malone was elected to the American Philosophical Society in 1945. He served as president of the Modern Language Association, and other philological associations and was etymology editor of the ''American College Dictionary'', 1947. With Louise Pound and Arthur G. Kennedy, he founded the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscan Language
Etruscan ( ) was the language of the Etruscan civilization in the ancient region of Etruria, in Etruria Padana and Etruria Campana in what is now Italy. Etruscan influenced Latin but was eventually superseded by it. Around 13,000 Etruscan epigraphy, inscriptions have been found so far, only a small minority of which are of significant length; some bilingual inscriptions with texts also in Latin, Ancient Greek, Greek, or Phoenician language, Phoenician; and a few dozen purported loanwords. Attested from 700 BC to AD 50, the relation of Etruscan to other languages has been a source of long-running speculation and study. Nowadays, it is generally agreed to be in the Tyrsenian language family, but before it gained currency as one of the Tyrsenian languages, it was commonly treated as an Language isolate, isolate, although there were also a number of other less well-known hypotheses. The consensus among linguists and Etruscologists is that Etruscan was a Pre-Indo-European languages, Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
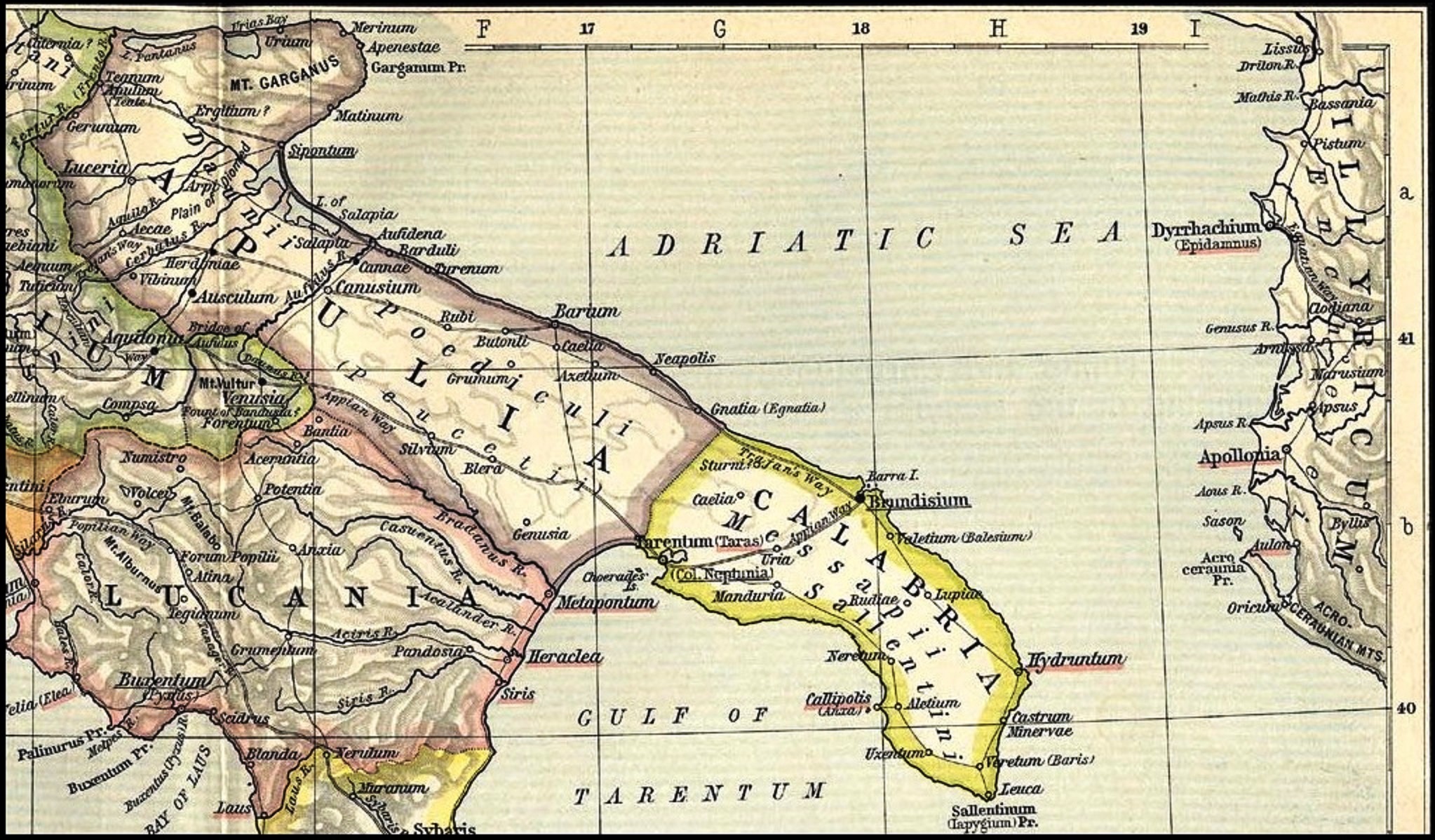
Messapian Language
Messapic (; also known as Messapian; or as Iapygian) is an extinct Indo-European languages, Indo-European Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkanic language of the southeastern Italian Peninsula, once spoken in Salento by the Iapygians, Iapygian peoples of the region: the Calabri and Salentini (known collectively as the Messapians), the Peucetians and the Daunians. Messapic was the pre-Roman Republic, Roman, non-Italic languages, Italic language of Apulia. It has been preserved in about 600 inscriptions written in an alphabet derived from a Archaic Greek alphabets, Western Greek model and dating from the mid-6th to at least the 2nd century BC, when it went extinct following the Roman Republic, Roman conquest of the region. Name The term 'Messapic' or 'Messapian' is traditionally used to refer to a group of languages spoken by the Iapygians, a "relatively homogeneous linguistic community" of non-Italic languages, Italic-speaking tribes (Messapii, Messapians, Peucetians and Daunians) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artoria Gens
The gens Artoria was a minor plebeian family at ancient Rome. Few members of this gens are mentioned in history, but a number are known from inscriptions. Under the later Empire at least some of them were of senatorial rank. Origin At least two distinct linguistic origins have been proposed for the nomen ''Artorius''. Schulze, Herbig, and Salomies propose that the name is derived from the Etruscan praenomen ''Arnthur'', perhaps Latinized as ''Artor''. Other scholars have proposed a Messapic origin, identifying a nomen ''Artorres'', "descendant of ''Artas''", with a Messapic possessive suffix ''-orres'', indicating filiation. Some scholars have suggested that ''Artorius'' might be the origin of the Welsh name ''Arthur''. Praenomina The chief praenomina of the Artorii were '' Lucius'', '' Gaius'', '' Marcus'', and '' Quintus'', four of the most common names throughout Roman history. Lesser-used praenomina of the Artorii included '' Gnaeus'', '' Sextus'', and '' Titus'', and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomen Gentile
The (; or simply ) was a hereditary name borne by the peoples of Roman Italy and later by the citizens of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. It was originally the name of one's (family or clan) by patrilineal descent. However, as Rome expanded its frontiers and non-Roman peoples were progressively granted citizenship and concomitant , the latter lost its value in indicating patrilineal ancestry. For men, the was the middle of the ("three names"), after the and before the . For women, the was often the only name used until the late Republic. For example, three members of gens ''Julia'' were Gaius ''Julius'' Caesar and his sisters ''Julia'' Major and ''Julia'' Minor ("Julia the elder" and "Julia the younger"). History The ''nomen gentilicium'', or "gentile name" designated a Roman citizen as a member of a ''gens''. A ''gens'', which may be translated as "race", "family", or "clan", constituted an extended Roman family, all of whom shared the same ''nomen'' and cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
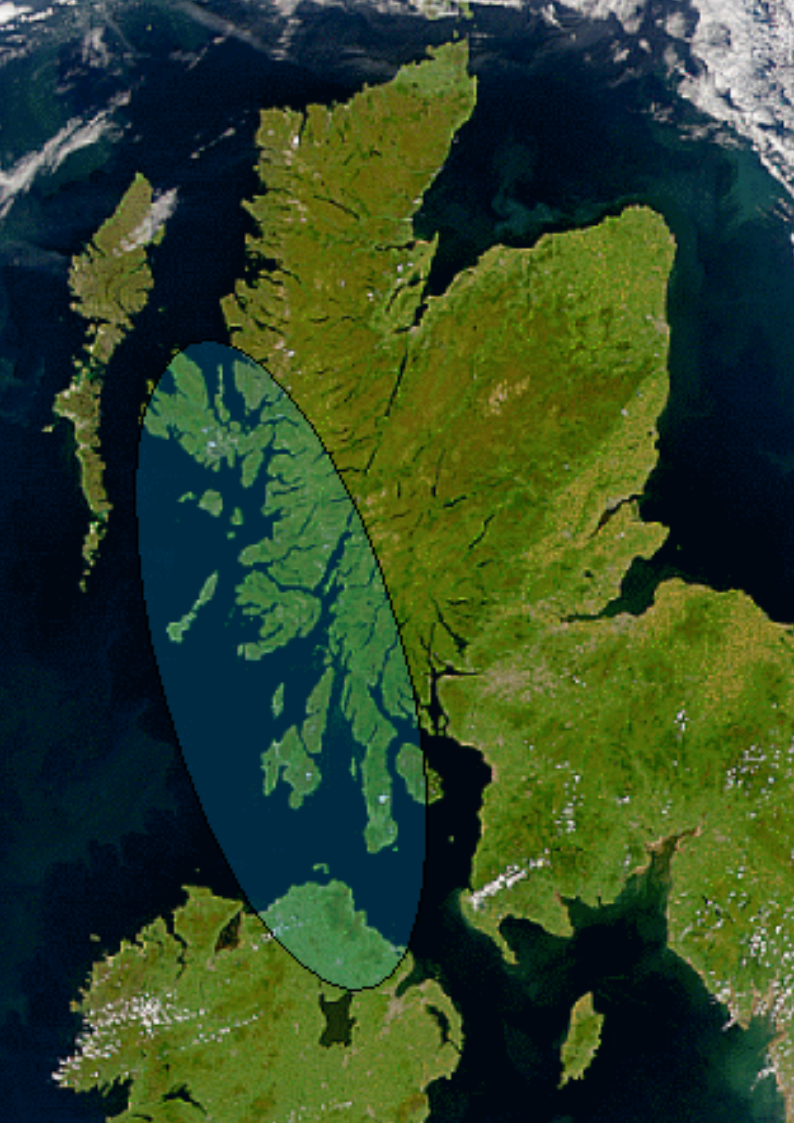
Áedán Mac Gabráin
Áedán mac Gabráin (; ), also written as Aedan, was a king of Dál Riata from 574 until c. 609 AD. The kingdom of Dál Riata was situated in modern Argyll and Bute, Scotland, and parts of County Antrim, Ireland. Genealogies record that Áedán was a son of Gabrán mac Domangairt. He was a contemporary of Saint Columba, and much that is recorded of his life and career comes from hagiography such as Adomnán of Iona's ''Life of Saint Columba''. Áedán appears as a character in Old Irish and Middle Irish language works of prose and verse, some now lost. The Irish annals record Áedán's campaigns against his neighbours, in Ireland, and in northern Britain, including expeditions to the Orkney Islands, the Isle of Man, and the east coast of Scotland. As recorded by Bede, Áedán was decisively defeated by Æthelfrith of Bernicia at the Battle of Degsastan. Áedán may have been deposed, or have abdicated, following this defeat. His date of death is recorded by one source a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columba
Columba () or Colmcille (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is today Scotland at the start of the Hiberno-Scottish mission. He founded the important abbey on Iona, which became a dominant religious and political institution in the region for centuries. He is the patron saint of Derry. He was highly regarded by both the Gaels of Dál Riata and the Picts, and is remembered today as a Catholic saint and one of the Twelve Apostles of Ireland. Columba studied under some of Ireland's most prominent church figures and founded several monasteries in the country. Around 563 AD he and his twelve companions crossed to Dunaverty near Southend, Argyll, in Kintyre before settling in Iona in Scotland, then part of the Ulster kingdom of Dál Riata, where they founded a new abbey as a base for spreading Celtic Christianity among the pagan Northern Pictish kingdoms. He remained active in Irish politics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |