|
Art Gagné
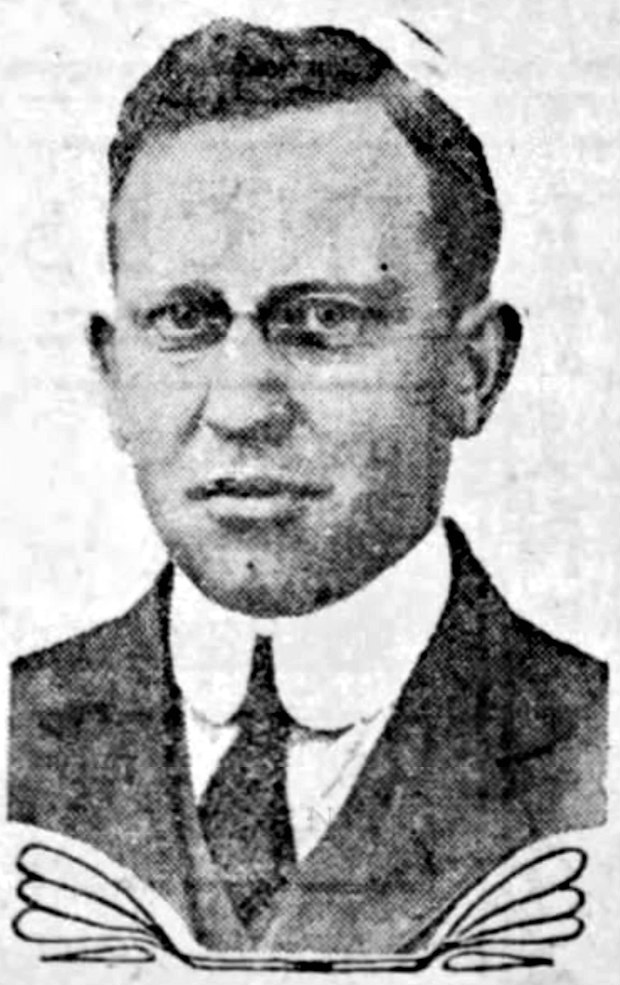
Arthur Edward Joseph Gagné (October 12, 1896 – October 5, 1988) was a Canadian ice hockey forward (ice hockey), forward, born in Ottawa. Career Art Gagné started out his career in the Ottawa City Hockey League, where he played for various teams between 1914–1917. He then played three seasons in Quebec for Laval University, Quebec Sons of Ireland and Quebec Montagnais. Gagné joined the Edmonton Eskimos (ice hockey), Edmonton Eskimos of the Albertan Big-4 League in 1920–21, where he had a productive partnership with centre (ice hockey), centre forward Duke Keats, also when the team moved along to the Western Canada Hockey League. In 1926, he moved to the Montreal Canadiens of the National Hockey League. He also played with the Regina Capitals, Boston Bruins, Ottawa Senators (original), Ottawa Senators, and Detroit Red Wings, Detroit Falcons. Gagné scored 100 points in his 228-game NHL career. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmonton Eskimos (ice Hockey)
The Edmonton Eskimos were a Canadian amateur and later professional men's ice hockey team that existed from 1911 to 1927. After playing in senior hockey in the Alberta-based Big-4 League, the Eskimos joined the Western Canada Hockey League (WCHL) for the inaugural 1921–22 WCHL season, and played for the Stanley Cup against the Ottawa Senators in 1923, as the WCHL Champions. Team alumni include Hockey Hall of Fame members Eddie Shore, Duke Keats and Bullet Joe Simpson. While the Edmonton Eskimos disbanded after the 1926–27 season, the name was adopted by a new team in 1932–33, playing for four years before it disbanded. The name was adopted by another new team for a single 1938–39 season. History The Eskimos club was formed for the 1909–10 season by sports promoter Deacon White, from the remains of the amateur Edmonton Hockey Club, and inherited its predecessor's membership in the Alberta Amateur Hockey Association (AAHA). In 1909–10 and 1911–12 the club was loosely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec Sons Of Ireland
The Quebec Sons of Ireland were a senior amateur ice hockey team from Quebec City that played in various ice hockey leagues in Canada from 1915–1927, such as the Quebec City Hockey League, Quebec Provincial Hockey League and the Eastern Canada Amateur Hockey League. History The team became a member of the Quebec City Hockey League for the 1915–16 season, and was managed and coached by Emmett McDonald, a younger brother of Quebec Bulldogs forward Jack McDonald. With Emmett McDonald as coach the team would capture the Art Ross Cup in 1916, an amateur challenge trophy for teams not eligible to compete for the Allan Cup. McDonald died of pneumonia on February 28, 1919 while serving with the Canadian Expeditionary Force in Siberia. Another brother, Billy McDonald, played defense on the team. Quebec Sons of Ireland defended the Art Ross Cup in 1916–17 by defeating the Montreal Stars, Loyola College and Montreal Vickers. Next season Sons of Ireland lost the Art Ross Cup to Montre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottawa Aberdeens
The Ottawa Aberdeens (or Aberdeen Hockey Club) were an amateur ice hockey team from Ottawa that played in various junior, intermediate and senior amateur leagues from the 1890s to the 1910s. Between 1915–1919 the club figured in the Ottawa City Senior League. For the 1892–93 season the Aberdeens played in the Ottawa Junior City Hockey League against the Rebels, Rideaus, Ottawa Jr., Electrics, and Ottawa College teams, and were captained by Charles T. Moffat. Ottawa Journal. Dec. 21, 1892 (pg. 1). Retrieved 2021-12-06. Several prominent early era hockey players in Ottawa came up through the Aberdeen ranks, such as , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penalty (ice Hockey)
A penalty in ice hockey is a punishment for an infringement of the rules. Most penalties are enforced by sending the offending player to a penalty box for a set number of minutes. During the penalty the player may not participate in play. Penalties are called and enforced by the referee, or in some cases, the linesman. The offending team may not replace the player on the ice (although there are some exceptions, such as fighting), leaving them short-handed as opposed to full strength. When the opposing team is said to be on a ''power play'', they will have one more player on the ice than the short-handed team. The short-handed team is said to be "on the penalty kill" until the penalty expires and the penalized player returns to play. While standards vary somewhat between leagues, most leagues recognize several common varieties of penalties, as well as common infractions. The statistic used to track penalties is called "penalty minutes" and abbreviated to "PIM" (spoken as single w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point (ice Hockey)
In ice hockey, point has three contemporary meanings. Personal stat A point is awarded to a player for each goal scored or assist earned. The total number of goals plus assists equals total points. The Art Ross Trophy is awarded to the National Hockey League (NHL) player who leads the league in scoring points at the end of the regular season. Team stat Points are also awarded to assess standings (or rankings). Historically, teams were awarded two points for each win, one point for each tie and no points for a loss. Such a ranking system, implemented primarily to ensure a tie counted as a "half-win" for each team in the standings, is generally regarded as British and/or European in origin and as such adopted by the National Hockey League which was founded in Canada where leagues generally used ranking systems of British origin. Awarding points in the standings contrasts with traditional American ranking systems favored in sports originating within the United States where today the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assist (ice Hockey)
In ice hockey, an assist is attributed to up to two players of the scoring team who shot, passed or deflected the puck towards the scoring teammate, or touched it in any other way which enabled the goal, meaning that they were "assisting" in the goal. There can be a maximum of two assists per goal. The assists will be awarded in the order of play, with the last player to pass the puck to the goal scorer getting the primary assist and the player who passed it to the primary assister getting the secondary assist. Players who gain an assist will get one point added to their player statistics. Despite the use of the terms "primary assist" and "secondary assist", neither is worth more than the other, and neither is worth more or less than a goal. Assists and goals are added together on a player's scoresheet to display that player's total points. Special cases If a player scores off a rebound given up by a goaltender, assists are still awarded, as long as there is no re-possession by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goal (ice Hockey)
In ice hockey, a goal is scored when the puck entirely crosses the goal line between the two goal posts and below the goal crossbar. A goal awards one point to the team attacking the goal scored upon, regardless of which team the player who actually deflected the puck into the goal belongs to (see also own goal). Typically, a player on the team attempting to score shoots the puck with their stick towards the goal net opening, and a player on the opposing team called a goaltender tries to block the shot to prevent a goal from being scored against their team. The term goal may also refer to the structure in which goals are scored. The ice hockey goal is rectangular in shape; the front frame of the goal is made of steel tube painted red (blue in the ECHL because of a sponsorship deal with GEICO) and consists of two vertical goalposts and a horizontal crossbar. A net is attached to the back of the frame to catch pucks that enter the goal and also to prevent pucks from entering it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Season (sports)
In an organized sports league, a typical season is the portion of one year in which regulated games of the sport are in session: for example, in Major League Baseball the season lasts approximately from the last week of March to the last week of September. In other team sports, like association football or basketball, it is generally from August or September to May although in some countries - such as Northern Europe or East Asia - the season starts in the spring and finishes in autumn, mainly due to weather conditions encountered during the winter. A year can often be broken up into several distinct sections (sometimes themselves called seasons). These are: a preseason, a series of exhibition games played for training purposes; a regular season, the main period of the league's competition; the postseason, a playoff tournament played against the league's top teams to determine the league's champion; and the offseason, the time when there is no official competition. Preseason In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Playoffs
The playoffs, play-offs, postseason or finals of a sports league are a competition played after the regular season by the top competitors to determine the league champion or a similar accolade. Depending on the league, the playoffs may be either a single game, a series of games, or a tournament, and may use a single-elimination system or one of several other different playoff formats. Playoff, in regard to international fixtures, is to qualify or progress to the next round of a competition or tournament. In team sports in the U.S. and Canada, the vast distances and consequent burdens on cross-country travel have led to regional divisions of teams. Generally, during the regular season, teams play more games in their division than outside it, but the league's best teams might not play against each other in the regular season. Therefore, in the postseason a playoff series is organized. Any group-winning team is eligible to participate, and as playoffs became more popular they were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Season
In an organized sports league, a typical season is the portion of one year in which regulated games of the sport are in session: for example, in Major League Baseball the season lasts approximately from the last week of March to the last week of September. In other team sports, like association football or basketball, it is generally from August or September to May although in some countries - such as Northern Europe or East Asia - the season starts in the spring and finishes in autumn, mainly due to weather conditions encountered during the winter. A year can often be broken up into several distinct sections (sometimes themselves called seasons). These are: a preseason, a series of exhibition games played for training purposes; a regular season, the main period of the league's competition; the postseason, a playoff tournament played against the league's top teams to determine the league's champion; and the offseason, the time when there is no official competition. Preseason In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ice hockey league in the world, and is one of the four major professional sports leagues in the United States and Canada. The Stanley Cup, the oldest professional sports trophy in North America, is awarded annually to the league playoff champion at the end of each season. The NHL is the fifth-wealthiest professional sport league in the world by revenue, after the National Football League (NFL), Major League Baseball (MLB), the National Basketball Association (NBA), and the English Premier League (EPL). The National Hockey League was organized at the Windsor Hotel in Montreal on November 26, 1917, after the suspension of operations of its predecessor organization, the National Hockey Association (NHA), which had been founded in 1909 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Canada Hockey League
The Western Canada Hockey League (WCHL), founded in 1921, was a major professional ice hockey league originally based in the prairies of Canada. It was renamed the Western Hockey League (WHL) in 1925 and disbanded in 1926. The WCHL's Victoria Cougars were the last non-NHL team to win the Stanley Cup when they won the 1925 Stanley Cup Finals over the NHL's Montreal Canadiens. History Background The Stanley Cup was donated in 1893 to serve as a trophy to be awarded to the national champion of Canadian amateur ice hockey. The trophy eventually became open to professional teams in 1906 and a new trophy, the Allan Cup was donated to serve as the national amateur trophy. By this time, the Canadian Prairies were being rapidly settled and in 1914 a team based in Saskatchewan (the Regina Victorias) would capture the Allan Cup for the first time. By this time, competition for the Stanley Cup, had evolved into a World Series-inspired "East vs. West" affair to be contested between the win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |