|
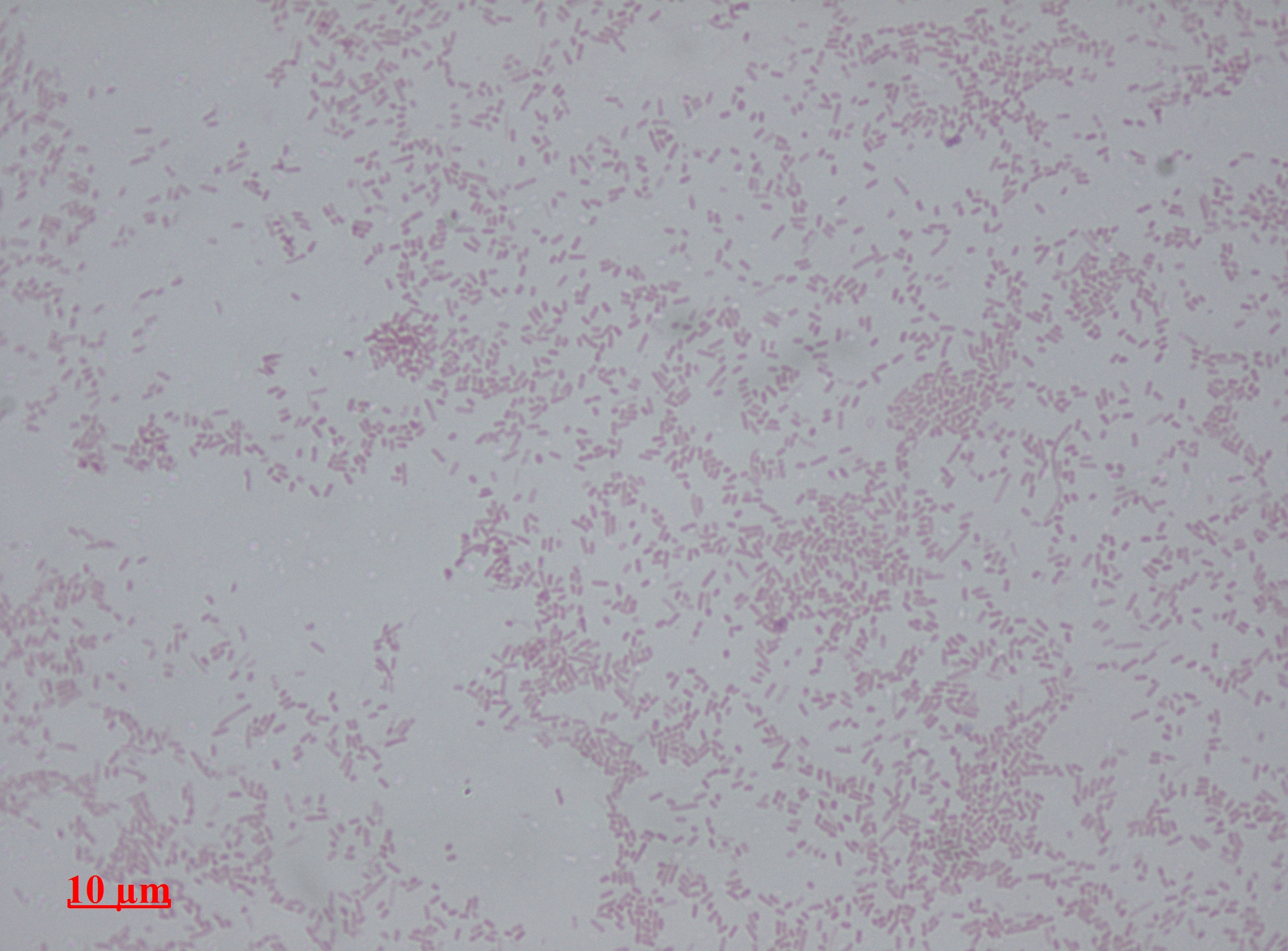
Arsenophonus Nasoniae
''Arsenophonus nasoniae'' is a species of bacterium which was previously isolated from ''Nasonia vitripennis'', a species of parasitoid wasp. These wasps are generalists which afflict the larvae of parasitic carrion flies such as blowflies, houseflies and flesh flies. ''A. nasoniae'' belongs to the phylum Pseudomonadota and family Morganellaceae.The genus ''Arsenophonus'', has a close relationship to the Proteus (bacterium) rather than to that of Salmonella and Escherichia. The genus is composed of gammaproteobacterial, secondary-endosymbionts which are gram-negative. Cells are non-flagellated, non-Motility, motile, non-spore forming and form long to highly Filamentous bacteria, filamentous rods. Cellular division is exhibited through Septate, septation. The name Arsenophonus nasoniae'' gen. nov., sp. nov.' was therefore proposed for the discovered bacterium due to its characteristics and its microbial interaction with ''N. vitripennis''. The type strain of ''A. nasoniae'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a complex lipopol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity due to shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the wings of bats and birds, the arms of primates, the front flippers of whales and the forelegs of four-legged vertebrates like dogs and crocodiles are all derived from the same ancestral tetrapod structure. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures adapted to different purposes as the result of descent with modification from a common ancestor. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this, from Aristotle onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. In developmental biology, organs that developed in the embryo in the same manner and from similar origins, such as from matching p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Reading Frame
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames will be "open" (the "reading", however, refers to the RNA produced by transcription of the DNA and its subsequent interaction with the ribosome in translation). Such an ORF may contain a start codon (usually AUG in terms of RNA) and by definition cannot extend beyond a stop codon (usually UAA, UAG or UGA in RNA). That start codon (not necessarily the first) indicates where translation may start. The transcription termination site is located after the ORF, beyond the translation stop codon. If transcription were to cease before the stop codon, an incomplete protein would be made during translation. In eukaryotic genes with multiple exons, introns are removed and exons are then joined together after transcription to yield the final ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteus Mirabilis
''Proteus mirabilis'' is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It shows swarming motility and urease activity. ''P. mirabilis'' causes 90% of all ''Proteus'' infections in humans. It is widely distributed in soil and water. ''Proteus mirabilis'' can migrate across the surface of solid media or devices using a type of cooperative group motility called swarming. ''Proteus mirabilis'' is most frequently associated with infections of the urinary tract, especially in complicated or catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Diagnosis An alkaline urine sample is a possible sign of ''P. mirabilis''. It can be diagnosed in the lab due to characteristic swarming motility, and inability to metabolize lactose (on a MacConkey agar plate, for example). Also ''P. mirabilis'' produces a very distinct fishy odor. Disease This rod-shaped bacterium has the ability to produce high levels of urease, which hydrolyzes urea to ammonia (NH3), so makes the urine more a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic Analyses
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extrachromosomal DNA
Extrachromosomal DNA (abbreviated ecDNA) is any DNA that is found off the chromosomes, either inside or outside the nucleus of a cell. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes contained in the nucleus. Multiple forms of extrachromosomal DNA exist, and, while some of these serve important biological functions, they can also play a role in diseases, such as ecDNA in cancer. In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids, whereas, in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. The fact that this organelle contains its own DNA supports the hypothesis that mitochondria originated as bacterial cells engulfed by ancestral eukaryotic cells. Extrachromosomal DNA are often used in research of replication because they are easy to identify and isolate. Although extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) is found in normal eukaryotic cells, extrachrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome Assembly
In bioinformatics, sequence assembly refers to aligning and merging fragments from a longer DNA sequence in order to reconstruct the original sequence. This is needed as DNA sequencing technology might not be able to 'read' whole genomes in one go, but rather reads small pieces of between 20 and 30,000 bases, depending on the technology used. Typically, the short fragments (reads) result from shotgun sequencing genomic DNA, or gene transcript ( ESTs). The problem of sequence assembly can be compared to taking many copies of a book, passing each of them through a shredder with a different cutter, and piecing the text of the book back together just by looking at the shredded pieces. Besides the obvious difficulty of this task, there are some extra practical issues: the original may have many repeated paragraphs, and some shreds may be modified during shredding to have typos. Excerpts from another book may also be added in, and some shreds may be completely unrecognizable. Gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrosequencing
Pyrosequencing is a method of DNA sequencing (determining the order of nucleotides in DNA) based on the "sequencing by synthesis" principle, in which the sequencing is performed by detecting the nucleotide incorporated by a DNA polymerase. Pyrosequencing relies on light detection based on a chain reaction when pyrophosphate is released. Hence, the name pyrosequencing. The principle of pyrosequencing was first described in 1993 by, Bertil Pettersson, Mathias Uhlen and Pål Nyren by combining the solid phase sequencing method using streptavidin coated magnetic beads with recombinant DNA polymerase lacking 3´to 5´exonuclease activity (proof-reading) and luminescence detection using the firefly luciferase enzyme. A mixture of three enzymes (DNA polymerase, ATP sulfurylase and firefly luciferase) and a nucleotide (dNTP) are added to single stranded DNA to be sequenced and the incorporation of nucleotide is followed by measuring the light emitted. The intensity of the light determi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septate
In biology, a septum (Latin for ''something that encloses''; plural septa) is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate. Examples Human anatomy * Interatrial septum, the wall of tissue that is a sectional part of the left and right atria of the heart * Interventricular septum, the wall separating the left and right ventricles of the heart * Lingual septum, a vertical layer of fibrous tissue that separates the halves of the tongue. *Nasal septum: the cartilage wall separating the nostrils of the nose * Alveolar septum: the thin wall which separates the alveoli from each other in the lungs * Orbital septum, a palpebral ligament in the upper and lower eyelids * Septum pellucidum or septum lucidum, a thin structure separating two fluid pockets in the brain * Uterine septum, a malformation of the uterus * Vaginal septum, a lateral or transverse partition inside the vagina * Intermuscular sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filamentous Bacteria
Filamentation is the anomalous growth of certain bacteria, such as ''Escherichia coli'', in which cells continue to elongate but do not divide (no septa formation). The cells that result from elongation without division have multiple chromosomal copies. In the absence of antibiotics or other stressors, filamentation occurs at a low frequency in bacterial populations (4–8% short filaments and 0–5% long filaments in 1- to 8-hour cultures). The increased cell length can protect bacteria from protozoan predation and neutrophil phagocytosis by making ingestion of cells more difficult. Filamentation is also thought to protect bacteria from antibiotics, and is associated with other aspects of bacterial virulence such as biofilm formation. The number and length of filaments within a bacterial population increases when the bacteria are exposed to different physical, chemical and biological agents (e.g. UV light, DNA synthesis-inhibiting antibiotics, bacteriophages). This is term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |