|
Arnulf, Duke Of Bavaria
Arnulf II (birth unknown; died 14 July 937), also known as the Bad (german: der Schlimme), the Evil (''der Böse'') or the Wicked, a member of the Luitpolding dynasty, held the title of Duke of Bavaria from about 907 until his death in 937. He is numbered in succession to Arnulf of Carinthia, counted as Arnulf I. Life The year of Arnulf's birth is unknown, but it is said that he was the namesake of other Arnulfs born around the time of the reign of the seventh-century bishop Arnulf of Metz and the Carolingian king Arnulf of Carinthia. Arnulf was the son of Margrave Luitpold of Bavaria and Cunigunde, herself a member of the Ahalolfing dynasty, daughter of Berthold I, the count palatine of Swabia. Her brother Erchanger assumed the Swabian ducal title in 915. Under the weak rule of the East Frankish king Louis the Child, Margrave Luitpold had already achieved a strong position in the Bavarian lands, succeeding the Wilhelminer margraves. He ruled over extended estates al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rulers Of Bavaria
The following is a list of rulers during the history of Bavaria. Bavaria was ruled by several dukes and Monarch, kings, partitioned and reunited, under several dynasties. Since 1949, Bavaria has been a democratic States of Germany, state in the Federal Republic of Germany. Rulers of Bavaria Ducal Bavaria (also known as the "Old Stem duchy") Agilolfing dynasty Around 548 the kings of the Franks placed the border region of Bavaria under the administration of a duke—possibly Frankish or possibly chosen from amongst the local leading families—who was supposed to act as a regional governor for the Frankish king. The first duke we know of, and likely the first, was Gariwald, or Garibald I of Bavaria, Garibald I, a member of the powerful Agilolfing family. This was the beginning of a series of Agilolfing dukes that was to last until 788. Carolingian dynasty and dominion from the Holy Roman Empire The kings (later emperors) of the Franks now assumed complete control, placing B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Swabia
The Duchy of Swabia ( German: ''Herzogtum Schwaben'') was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German Kingdom. It arose in the 10th century in the southwestern area that had been settled by Alemanni tribes in Late Antiquity. While the historic region of Swabia takes its name from the ancient Suebi, dwelling in the angle formed by the Rhine and the Danube, the stem duchy comprised a much larger territory, stretching from the Alsatian Vosges mountain range in the west to the right bank of the river Lech in the east and up to Chiavenna (''Kleven'') and Gotthard Pass in the south. The name of the larger stem duchy was often used interchangeably with '' Alamannia'' during the High Middle Ages, until about the 11th century, when the form Swabia began to prevail. The Duchy of Swabia was proclaimed by the Ahalolfing count palatine Erchanger in 915. He had allied himself with his Hunfriding rival Burchard II and defeated King Conrad I of Germany in a battle at Wahlwie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
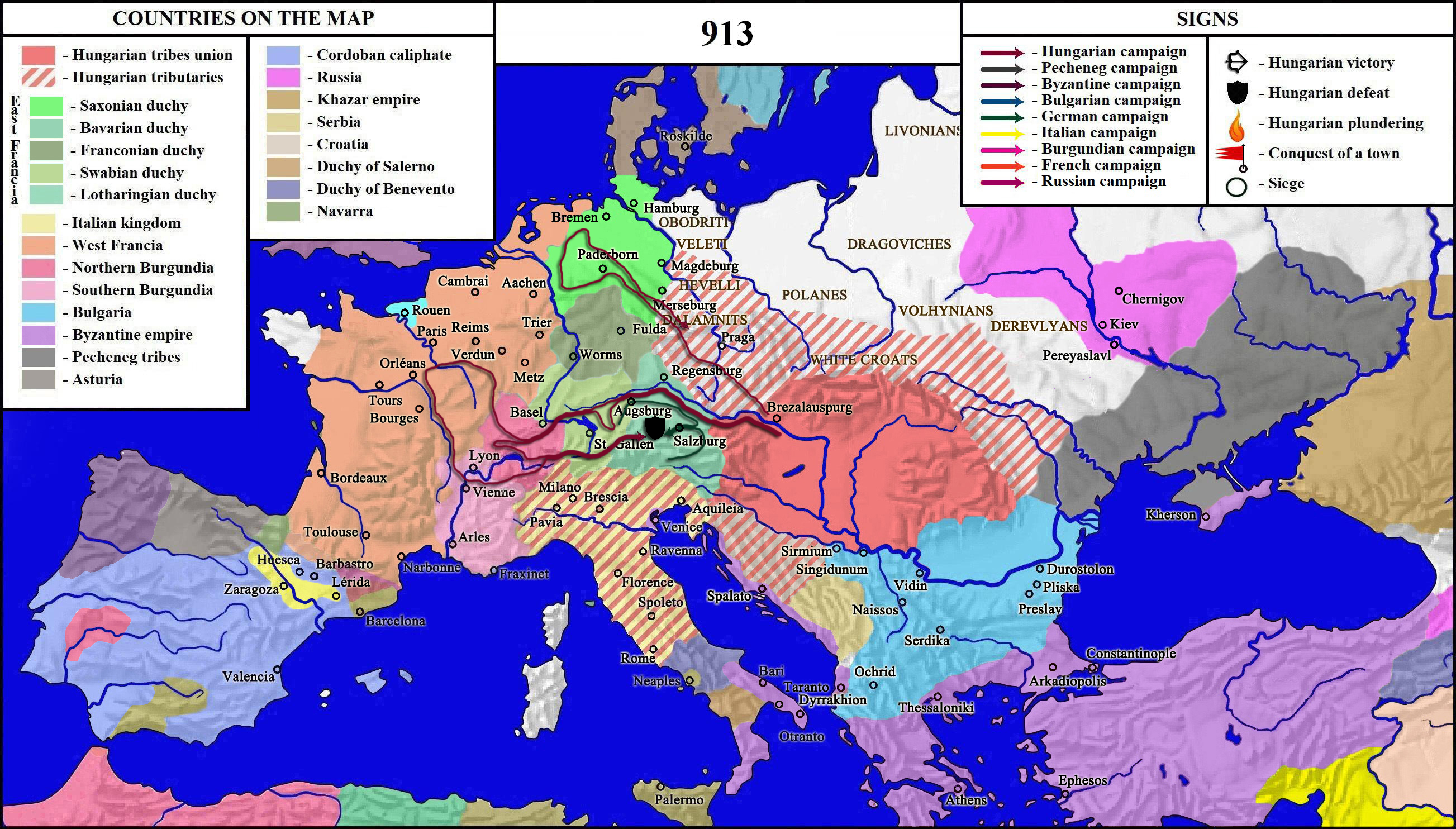
Battle Of Inn
The Battle of the Inn was fought in 913, when a Hungarian raiding army, at their return from plunder attacks against Bavaria, Swabia, and Northern Burgundy, faced the combined army of Arnulf, Duke of Bavaria, Counts Erchanger and Burchard of Swabia, and Lord Udalrich, who defeated them at Aschbach by the River Inn. Sources The skirmish at the Inn River is mentioned by the ''Annales Alamannici'' (continued by Hermann of Reichenau in the 11th century), the ''Annales iuvavenses'', the ''Continuatio Treverensis chronici Reginonis'' (the continuation of Regino of Prüm's ''Chronicon'', who wrote at Trier in 967), and the ''Annales Sangallenses maiores'' (another continuation of the ''Annales Alamannici'', compiled in the Abbey of Saint Gall). The last one suggests that "''the entire'' ungarian''army was destroyed, but thirty men''" ''nisi 30 viros''" Historian Károly Szabó argued this figure is a result of a subsequent insertion. The battle is marginally also mentioned by the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Thuringia
The Duchy of Thuringia was an eastern frontier march of the Merovingian kingdom of Austrasia, established about 631 by King Dagobert I after his troops had been defeated by the forces of the Slavic confederation of Samo at the Battle of Wogastisburg. It was recreated in the Carolingian Empire and its dukes were appointed by the king until it was absorbed by the Saxon dukes in 908. From about 1111/12 the territory was ruled by the Landgraves of Thuringia as Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. History The former kingdom of the Thuringii arose during the Migration Period after the decline of the Hunnic Empire in Central Europe in the mid 5th century, culminating in their defeat in the 454 Battle of Nedao. With Bisinus a first Thuringian king is documented about 500, who ruled overextended estates that stretched beyond the Main River in the south. His son and successor Hermanafrid married Amalaberga, a niece of the Ostrogoth king Theoderic the Great, thereby hedging the threat of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony ( nds, Hartogdom Sassen, german: Herzogtum Sachsen) was originally the area settlement geography, settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 and incorporated into the Carolingian Empire (Francia) by 804. Upon the 843 Treaty of Verdun, Saxony was one of the five German stem duchies of East Francia; Duke Henry the Fowler was elected List of German monarchs, German king in 919. Upon the deposition of the House of Welf, Welf duke Henry the Lion in 1180, the ducal title fell to the House of Ascania, while numerous territories split from Saxony, such as the Principality of Anhalt in 1218 and the Welf Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg in 1235. In 1296 the remaining lands were divided between the Ascanian dukes of Saxe-Lauenburg and Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg, Saxe-Wittenberg, the latter obtaining the title of Electorate of Saxony, Electors of Saxony by the Golden Bull of 1356. Geography The Sax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
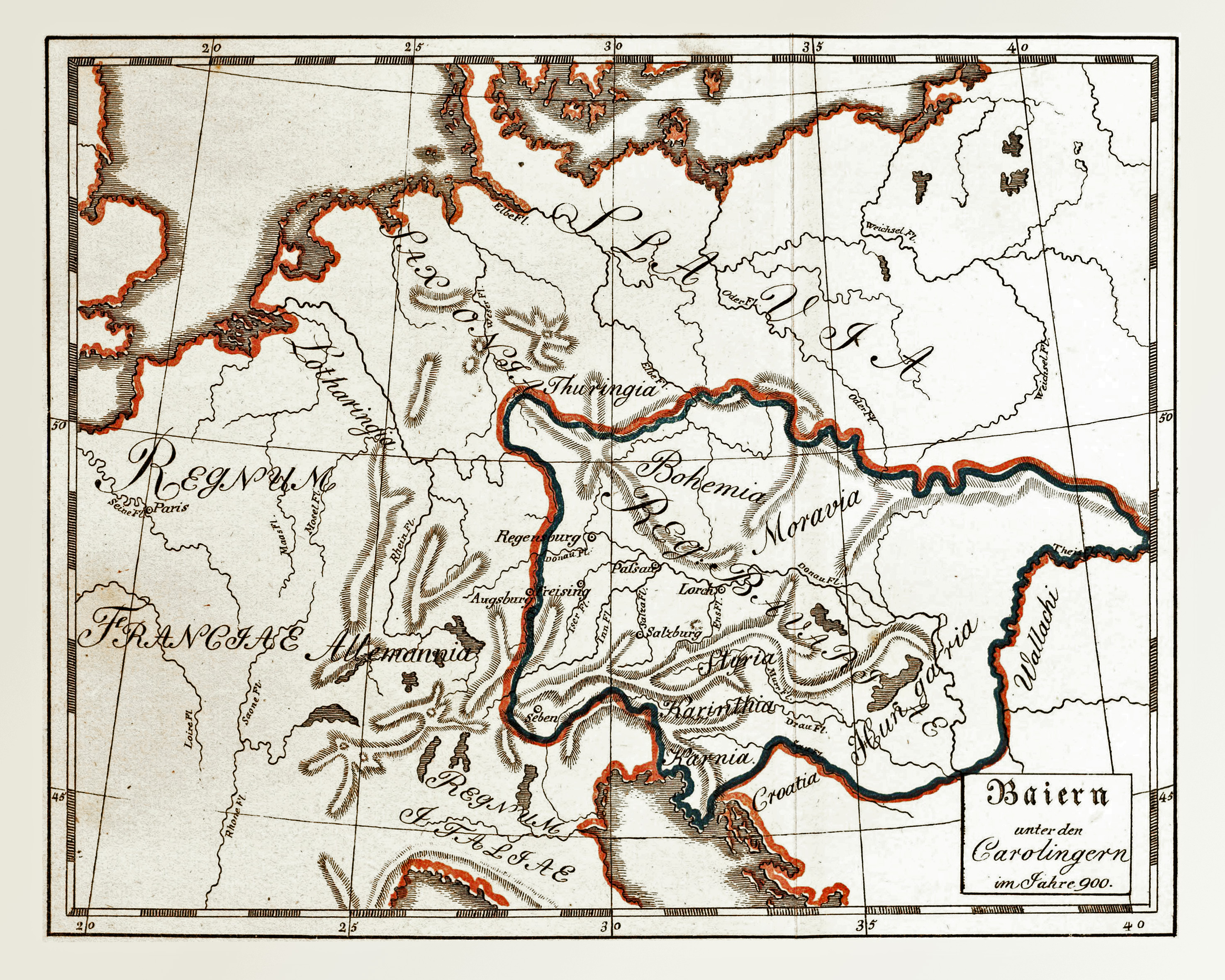
East Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the former empire into three kingdoms. The east–west division, enforced by the Germanic-Latin language split, "gradually hardened into the establishment of separate kingdoms", with East Francia becoming the Kingdom of Germany and West Francia becoming the Kingdom of France. Terminology The term ''orientalis Francia'' originally referred to Franconia and ''orientales Franci'' to its inhabitants, the ethnic Franks living east of the Rhine. The use of the term in a broader sense, to refer to the eastern kingdom, was an innovation of Louis the German's court. Since eastern Francia could be identified with old Austrasia, the Frankish heartland, Louis's choice of terminology hints at his ambitions. Under his grandson, Arnulf of Carinthia, the terminology was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Árpád
Árpád (; 845 – 907) was the head of the confederation of the Magyar tribes at the turn of the 9th and 10th centuries. He might have been either the sacred ruler or '' kende'' of the Hungarians, or their military leader or '' gyula'', although most details of his life are debated by historians, because different sources contain contradictory information. Despite this, many Hungarians refer to him as the "founder of our country", and Árpád's preeminent role in the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin has been emphasized by some later chronicles. The dynasty descending from Árpád ruled the Kingdom of Hungary until 1301. Biography Early life Árpád was the son of Álmos who is mentioned as the first head of the confederation of the Magyar tribes by all Hungarian chronicles. His mother's name and family are unknown. According to historian Gyula Kristó, Árpád was born around 845. His name derived from the Hungarian word for barley, ''árpa''. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Invasions Of Europe
The Hungarian invasions of Europe ( hu, kalandozások, german: Ungarneinfälle) took place in the 9th and 10th centuries, the period of transition in the history of Europe in the Early Middle Ages, when the territory of the former Carolingian Empire was threatened by invasion from multiple hostile forces, the Magyars (Hungarians) from the east, the Viking expansion from the north and the Arabs from the south.Barbara H. Rosenwein, A short history of the Middle Ages, University of Toronto Press, 2009, p. 15/ref> The Magyars successfully Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin, conquered the Carpathian Basin (corresponding to the later Kingdom of Hungary) by the end of the ninth century, and launched a number of plundering raids both westward into former Francia and southward into the Byzantine Empire. The westward raids were stopped only with the Magyar defeat of the Battle of Lechfeld of 955, which led to a new political order in Western Europe centered on the Holy Roman Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heerbann
The ''Heerbann'' (also formerly ''Heermannie'', MHG ''herban'', OHG: ''heriban'', Mid. Latin: ''Heribannus''), in the Imperial Military Constitution (''Reichsheeresverfassung'') of the Holy Roman Empire, was the call to all free landowners capable of bearing arms to participate in a military campaign, i.e. in an imperial war (''Reichskrieg''). According to the original meaning of the word (OHG: ''bannan'' = to 'demand' or 'prohibit', actually 'to speak'), the ''Heerbann'' was a 'call of the king or duke to military service;c.f''Heerbann''at Duden online see also king's ban. However, as the feudal system in the Holy Roman Empire developed in the Early Middle Ages, the ''Heerbann'' became superfluous as a means of raising armies and increasingly fell into disuse after the death of Charlemagne. The ''Heerbann'' was particularly onerous for poorer landowners, several of whom had to equip a knight for war (one for every 3 hides), so they would attempt to withdraw themselves from hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pressburg
The Battle of Pressburg (german: Schlacht von Pressburg) or Battle of Pozsony ( hu, Pozsonyi csata), or Battle of Bratislava ( sk, Bitka pri Bratislave) was a three-day-long battle, fought between 4–6 July 907, during which the East Francian army, consisting mainly of Bavarian troops led by Margrave Luitpold, was annihilated by Hungarian forces. The exact location of the battle is not known. Contemporary sources say it took place at "Brezalauspurc", but where exactly Brezalauspurc was is unclear. Some specialists place it in the vicinity of Zalavár (Mosapurc); others in a location close to Bratislava (Pressburg), the traditional assumption. An important result of the Battle of Pressburg was the Kingdom of East Francia could not regain control over the Carolingian March of Pannonia, including the territory of the later '' marchia orientalis'' (March of Austria), lost in 900. The most significant result of the Battle of Pressburg is that the Hungarians secured the lands the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
March Of The Nordgau
The Margraviate of the Nordgau (german: Markgrafschaft Nordgau) or Bavarian Nordgau () was a medieval administrative unit (''Gau'') on the frontier of the German Duchy of Bavaria. It comprised the region north of the Danube and Regensburg (Ratisbon), roughly covered by the modern Upper Palatinate stretching up to the river Main and, especially after 1061, into the Egerland on the border with Bohemia. History The area east of Franconia proper up to the Bohemian Forest had been settled by Germanic Varisci and Armalausi tribes in ancient times; after the Migration Period, the forces of the proto-Merovingian king Chlodio (died 450) occupied the district. From the mid-6th century onwards, the region was Christianised by several wandering bishops, among them Saints Boniface (lived 675 to 754) and Emmeram of Regensburg. In 739, the Diocese of Regensburg was founded. At the insistence of Saint Boniface, Charles Martel (lived 688 to 741) built the great fortress of Wogastisb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine before draining into the Black Sea. Its drainage basin extends into nine more countries. The largest cities on the river are Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade and Bratislava, all of which are the capitals of their respective countries; the Danube passes through four capital cities, more than any other river in the world. Five more capital cities lie in the Danube's basin: Bucharest, Sofia, Zagreb, Ljubljana and Sarajevo. The fourth-largest city in its basin is Munich, the capital of Bavaria, standing on the Isar River. The Danube is the second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through much of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |