|
Armstrong-Siddeley Lynx
The Armstrong Siddeley Lynx is a British seven-cylinder aero engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley. Testing began in 1920 and 6,000 had been produced by 1939. In Italy Alfa Romeo built a licensed version of this engine named the Alfa Romeo Lynx. Variants ;Lynx I :1920, . ;Lynx II :1920, . ;Lynx III :1924, . ;Lynx IV :1929, . ;Lynx IVA :1930, . ;Lynx IVC :1929, . ;Lynx IV(G) :1929, Geared propeller drive. ;Lynx IV(MOD) :1929, , reconditioned and modified Lynx IV. ;Lynx IV(S) :1928, , fully supercharged. ;Lynx V (Lynx Major) :1930, increased bore and stroke, name changed from Lynx V to Lynx Major then Cheetah. Effectively half a Panther ;Piaggio P.II: Licence production in Italy by Piaggio. Applications * Airspeed Courier * Airspeed Envoy *Albatros L 68 *Avro 504 *Avro 618 Ten * Avro Avocet * Avro 641 Commodore *Avro 626 * Avro 642/4m Eighteen * Avro Sea Tutor *Avro Tutor *BAT Bantam * Blackburn Lincock *Boulton Paul Bittern *Canadian Vickers Vanessa *Canadian Vickers Var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shuttleworth Collection
The Shuttleworth Collection is a working aeronautical and automotive collection located at the Old Warden Aerodrome, Old Warden in Bedfordshire, England. It is the oldest in the world and one of the most prestigious, due to the variety of old and well-preserved aircraft. History The collection was founded in 1928 by aviator Richard Ormonde Shuttleworth. While flying a Fairey Battle at night on 2 August 1940, Shuttleworth fatally crashed. His mother, in 1944, formed the Richard Ormonde Shuttleworth Remembrance Trust "for the teaching of the science and practice of aviation and of afforestation and agriculture." Collection Restoration and maintenance work is carried out by a staff of 12 full-time and many volunteer engineers. These volunteers are all members of the 3,000-strong Shuttleworth Veteran Aeroplane Society (SVAS). These dedicated enthusiasts are crucial to the preservation and restoration of the collection. In addition to the aircraft, the collection houses a nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avro 626
The Avro 626 is a single-engined British biplane trainer aircraft produced by Avro during the (1918-1939) inter-war period. Design and development The Model 626 was developed by Avro from the company's Model 621 (Tutor) for export to smaller air forces, the idea being that the 626 would be a single aircraft that could carry out general aircrew training as well as a number of other roles. The types 621 and 626 were both two-seaters, but the latter had an additional cockpit behind the rear seat of the 621 and accessible from it. This additional cockpit was fitted with a Scarff ring for a machine gun and carried equipment for air navigation, wireless and gunnery training. Structurally and aerodynamically, it was almost identical to the Tutor: it had a conventional fabric-covered, metal airframe with single-bay wings. Most of the 626s, like the Tutors had an Armstrong Siddeley Lynx IVC engine of 240 hp (180 kW), but most of those supplied to the Egyptian and Brazilian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fokker C
Fokker was a Dutch aircraft manufacturer named after its founder, Anthony Fokker. The company operated under several different names. It was founded in 1912 in Berlin, Germany, and became famous for its fighter aircraft in World War I. In 1919 the company moved its operations to the Netherlands. During its most successful period in the 1920s and 1930s, it dominated the civil aviation market. Fokker went into bankruptcy in 1996, and its operations were sold to competitors. History Fokker in Germany At age 20, while studying in Germany, Anthony Fokker built his initial aircraft, the ''Spin'' (Spider)—the first Dutch-built plane to fly in his home country. Taking advantage of better opportunities in Germany, he moved to Berlin, where in 1912, he founded his first company, Fokker Aeroplanbau, later moving to the Görries suburb just southwest of Schwerin (at ), where the current company was founded, as Fokker Aviatik GmbH, on 12 February 1912. World War I Fokker capitalized o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild FC-2
The Fairchild FC-1 and its derivatives were a family of light, single-engine, high-wing utility monoplanes produced in the United States in the 1920s and 1930s. The aircraft was originally designed to provide a camera platform for Sherman Fairchild's aerial photography and survey business, Fairchild Aerial Surveys. Design and development Fairchild had approached a number of aircraft builders with specifications for what he considered to be an ideal aircraft for this type of work, with which he hoped to replace the variety of types that his firm then operated. Believing the quotes he received to be excessive, Fairchild opted to produce the aircraft in-house, purchasing facilities at Farmingdale, New York for the purpose. The design was for a conventional high-wing, strut-braced monoplane with a fully enclosed cabin and tailwheel undercarriage. The wooden wings were able to be folded back against the tail for storage. To facilitate its intended role, the cabin was extensively glazed, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
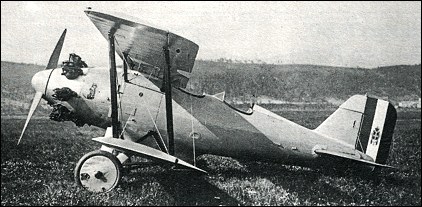
Armstrong-Siddeley Lynx IV On Avro 504N
Armstrong Siddeley was a British engineering group that operated during the first half of the 20th century. It was formed in 1919 and is best known for the production of luxury vehicles and aircraft engines. The company was created following the purchase by Armstrong Whitworth of Siddeley-Deasy, a manufacturer of fine motor cars that were marketed to the top echelon of society. After the merge of companies, this focus on quality continued throughout in the production of cars, aircraft engines, gearboxes for tanks and buses, rocket and torpedo motors, and the development of railcars. Company mergers and takeovers with Hawker Aviation and Bristol Aero Engines saw the continuation of the car production which ceased in August 1960. The company was absorbed into the Rolls-Royce conglomerate which was interested in the aircraft and aircraft engine business. Eventually, the remaining spares and all motor car interests were sold to the Armstrong Siddeley Owners Club Ltd, which now own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Havilland Hawk Moth
The de Havilland DH.75 Hawk Moth was a 1920s British four-seat cabin monoplane built by de Havilland at Stag Lane Aerodrome, Edgware. Design and development The DH.75 Hawk Moth was the first of a family of high-wing monoplane Moths, and was designed as a light transport or air-taxi for export. The aircraft had a fabric-covered steel-tube fuselage and wooden wings. The Hawk Moth was first flown on 7 December 1928 from Stag Lane.Jackson 1987, p.284. The first aircraft used a 200 hp (149 kW) de Havilland Ghost engine. This engine comprised two de Havilland Gipsys mounted on a common crankcase to form an air-cooled V-8. With the Ghost, the aircraft was underpowered and a Armstrong Siddeley Cheetah 7-cylinder radial engine was fitted to it and all but one production aircraft. Changes were also made to the structure including increased span and chord wings and the aircraft was redesignated the DH.75A. In December 1929 the first aircraft was demonstrated in Canada wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cierva C
The Cierva Autogiro Company was a British firm established in 1926 to develop the autogyro. The company was set up to further the designs of Juan de la Cierva, a Spanish engineer and pilot, with the financial backing of James George Weir, a Scottish industrialist and aviator. History Juan de la Cierva's first British-built autogyro was the C.8 design. It and some other designs were built in conjunction with Avro. The pre-war Cierva C.30 proved popular. Nearly 150 were built under licence in the United Kingdom by Avro, in Germany by Focke-Wulf, and in France by Lioré-et-Olivier. On 9 December 1936, Cierva was killed in the Croydon KLM airliner accident when the aircraft in which he was a passenger crashed after taking off in fog. Dr. James Allan Jamieson Bennett was promoted to Chief Technical Officer of the company and remained in the position until leaving in 1939. In addition to making important contributions to autogyro controls while at Cierva Autogyro, Bennett carried th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Vickers Vedette
The Canadian Vickers Vedette was the first aircraft designed and built in Canada to meet a specification for Canadian conditions. It was a single-engine biplane flying boat purchased to meet a Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) demand for a smaller aircraft than the Vickers Viking with a much greater rate of climb, to be suitable for forestry survey and fire protection work. The type went on to have a long and distinguished career in civil operations in Canada. Most of the topographical maps in use in Canada today are based on photos taken from these aircraft. Design and development Based on a preliminary design in early 1924 for a "flying boat" by R.K.Pierson of the British company Vickers, the Canadian Vickers Vedette was a two/three-seat single-engine pusher aircraft. The design was passed over to the subsidiary Canadian Vickers Limited of Longueuil, Quebec (formed in 1911) where Wilfrid Thomas Reid served as Chief Engineer. The prototype Vedette I was first flown on 4 Nove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Vickers Varuna
The Canadian Vickers Varuna was a Canadian flying boat of the 1920s built by Canadian Vickers as a twin-engined, unequal-span biplane, with a wooden hull and steel tube structure. Design and development The Varuna was developed in response to a Royal Canadian Air Force requirement for a flying boat to transport men and equipment to forest fires. It was a large-scale twin-engined version of the Vedette. Operational history Most Varunas spent their service in Manitoba operating in their intended role; all Varuna IIs were withdrawn in 1930 and the sole Varuna I was struck off in 1932 Variants * Varuna I - with Wright J-6 Whirlwind radial engines, one built. * Varuna II - with Armstrong Siddeley Lynx IV radial engines. Specifications (Varuna II) References External links {{Portal bar, Aviation 1920s Canadian military transport aircraft Flying boats Varuna Varuna (; sa, वरुण, , Malay: ''Baruna'') is a Vedic deity associated initially with the sky, later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Vickers Vanessa
The Canadian Vickers Vanessa was a Canadian biplane transport seaplane of the 1920s. It was a single-engine, twin-float biplane of mixed construction, evaluated by the Royal Canadian Air Force and used for experimental air-mail services.. Design and development The Vanessa was developed as a private venture commercial seaplane. The Canadian Vickers Chief Engineer based his design on the contemporary Stinson cabin biplane which had been introduced in the United States. The one feature that was a departure from the Stinson was the use of interplane struts which formed an "X" (when viewed from the front), thus eliminating the need for traditional wire bracing and allowing easy access to the cabin. The enclosed cabin fuselage was constructed of steel tubing as were various support structures along with the tail surfaces. The remainder of the aircraft was of wood construction and the entire aircraft was fabric covered. Ailerons and flaps, the latter being an unusual feature in ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulton Paul Bittern
The Boulton Paul Bittern was a 1920s British night-fighter aircraft built by Boulton Paul Limited of Norwich, named after the marsh bird of the same name. Design and development Designed to Air Ministry Specification 27/24, which called for a single-seat night fighter for use against enemy bomber aircraft, the Bittern design was unusual for its time in that it was a twin- engined shoulder wing monoplane rather than a single-engine biplane. Two prototypes were built. The first was a cantilever wing design with the engines - 214 hp Armstrong-Siddeley Lynx - on the leading edge of the wing. However initial trials showed that the wing was too flexible and so wing struts were added fixed between the bottom of the fuselage and the engine installations. However this added weight and drag with a commensurate effect on performance. The second prototype had the engines suspended from the wings on the struts. The first prototype had two fixed .303 in (7.7 mm) Vickers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackburn Lincock
The Blackburn F.2 Lincock was a British single-seat lightweight fighter produced by Blackburn Aircraft Limited. Design and development In 1928 Blackburn designed and built a private venture lightweight biplane fighter powered by an Armstrong Siddeley Lynx IVC engine. The Blackburn F.2 Lincock was of wooden construction and first appeared in May 1928. It performed well in demonstrations but failed to gain any orders. The Canadian government showed an interest in the design, and a metal construction variant (the Lincock II) was built. It was tested in Canada at Camp Borden in 1930 where there was interest in using the Lincock as an advanced trainer, but the type was not ordered. It was later used to perform public aerobatic displays in 1933 and 1934. The final version was the Lincock III of which five were produced, two were delivered to China, two to Japan and one retained as a demonstrator. Interest from Italy resulted in Piaggio acquiring a licence to produce a two-seat versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |