|
Arithmetic And Logical Unit
In computing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a combinational digital circuit that performs arithmetic and bitwise operations on integer binary numbers. This is in contrast to a floating-point unit (FPU), which operates on floating point numbers. It is a fundamental building block of many types of computing circuits, including the central processing unit (CPU) of computers, FPUs, and graphics processing units (GPUs). The inputs to an ALU are the data to be operated on, called operands, and a code indicating the operation to be performed (opcode); the ALU's output is the result of the performed operation. In many designs, the ALU also has status inputs or outputs, or both, which convey information about a previous operation or the current operation, respectively, between the ALU and external status registers. Signals An ALU has a variety of input and output nets, which are the electrical conductors used to convey digital signals between the ALU and external circuitry. When an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Digital Signal (electronics)
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete space, discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuity (mathematics), continuous values; at any given time it represents a real number within a continuous range of values. Simple digital signals represent information in discrete bands of levels. All levels within a band of values represent the same information state. In most digital circuits, the signal can have two possible valid values; this is called a binary signal or logic signal. They are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as ''ground'' or zero volts), and the other a value near the supply voltage. These correspond to the two values ''zero'' and ''one'' (or ''false'' and ''true'') of the Boolean domain, so at any given time a binary signal represents one binary digit (bit). Because of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Processor Register
A processor register is a quickly accessible location available to a computer's processor. Registers usually consist of a small amount of fast storage, although some registers have specific hardware functions, and may be read-only or write-only. In computer architecture, registers are typically addressed by mechanisms other than main memory, but may in some cases be assigned a memory address e.g. DEC PDP-10, ICT 1900. Almost all computers, whether load/store architecture or not, load items of data from a larger memory into registers where they are used for arithmetic operations, bitwise operations, and other operations, and are manipulated or tested by machine instructions. Manipulated items are then often stored back to main memory, either by the same instruction or by a subsequent one. Modern processors use either static or dynamic random-access memory (RAM) as main memory, with the latter usually accessed via one or more cache levels. Processor registers are normal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
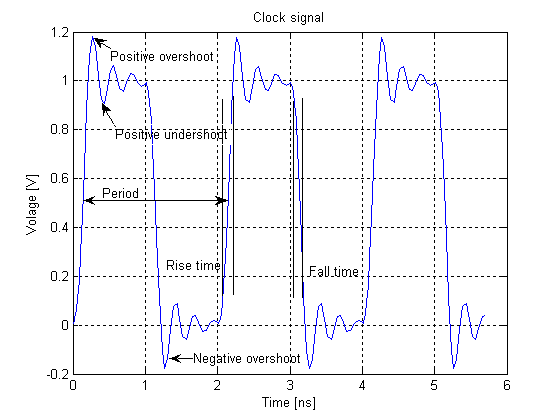
Clock Signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and is used like a metronome to synchronize actions of digital circuits. In a synchronous logic circuit, the most common type of digital circuit, the clock signal is applied to all storage devices, flip-flops and latches, and causes them all to change state simultaneously, preventing race conditions. A clock signal is produced by an electronic oscillator called a clock generator. The most common clock signal is in the form of a square wave with a 50% duty cycle. Circuits using the clock signal for synchronization may become active at either the rising edge, falling edge, or, in the case of double data rate, both in the rising and in the falling edges of the clock cycle. Digital circuits Most integrated circuits (ICs) of suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sequential Logic
In automata theory, sequential logic is a type of logic circuit whose output depends on the present value of its input signals and on the sequence of past inputs, the input history. This is in contrast to '' combinational logic'', whose output is a function of only the present input. That is, sequential logic has ''state'' (''memory'') while combinational logic does not. Sequential logic is used to construct finite-state machines, a basic building block in all digital circuitry. Virtually all circuits in practical digital devices are a mixture of combinational and sequential logic. A familiar example of a device with sequential logic is a television set with "channel up" and "channel down" buttons. Pressing the "up" button gives the television an input telling it to switch to the next channel above the one it is currently receiving. If the television is on channel 5, pressing "up" switches it to receive channel 6. However, if the television is on channel 8, pressing "up" switch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Propagation Delay
Propagation delay is the time duration taken for a signal to reach its destination, for example in the electromagnetic field, a wire, speed of sound, gas, fluid or seismic wave, solid body. Physics * An electromagnetic wave travelling through a medium has a propagation delay determined by the speed of light in that particular medium, or ca. 1 nanosecond per in a vacuum. * An electric signal travelling through a wire has an propagation delay of ca. 1 nanosecond per . See also radio propagation, velocity factor, signal velocity and mechanical wave. Electronics Logic gates can have a gate delay ranging from picoseconds to more than 10 nanoseconds, depending on the technology being used. It is the time between the gate input becoming stable and the gate output becoming stable. Manufacturers often refer to the time from the input changing to 50% of its final input level, to the output reaching 50% of its final output level; this may depend on the direction of the level cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Combinational Logic
In automata theory, combinational logic (also referred to as time-independent logic) is a type of digital logic that is implemented by Boolean circuits, where the output is a pure function of the present input only. This is in contrast to sequential logic, in which the output depends not only on the present input but also on the history of the input. In other words, sequential logic has ''memory'' while combinational logic does not. Combinational logic is used in computer circuits to perform Boolean algebra on input signals and on stored data. Practical computer circuits normally contain a mixture of combinational and sequential logic. For example, the part of an arithmetic logic unit, or ALU, that does mathematical calculations is constructed using combinational logic. Other circuits used in computers, such as half adders, full adders, half subtractors, full subtractors, multiplexers, demultiplexers, encoders and decoders are also made by using combinational logic. Prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parity Flag
In computer processors the parity flag indicates if the numbers of set bits is odd or even in the binary representation of the result of the last operation. It is normally a single bit in a processor status register. For example, assume a machine where a set parity flag indicates even parity. If the result of the last operation were 26 (11010 in binary), the parity flag would be 0 since the number of set bits is odd. Similarly, if the result were 10 (1010 in binary) then the parity flag would be 1. Some microcontrollers, notably the ubiquitous 8051, include a parity flag to help with implementing RS-232 and other serial communication protocols, in lieu of a UART with parity support. x86 processors x86 processors include a parity flag because they are descended (via the Intel 8086, 8080 and 8008) from the Datapoint 2200 terminal, which was designed for serial communication duties. In x86 processors, the parity flag reflects the parity of only the ''least significant byte'' of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arithmetic Overflow
In computer programming, an integer overflow occurs when an arithmetic operation on integers attempts to create a numeric value that is outside of the range that can be represented with a given number of digits – either higher than the maximum or lower than the minimum representable value. The most common result of an overflow is that the least significant representable digits of the result are stored; the result is said to ''wrap'' around the maximum (i.e. modulo a power of the radix, usually two in modern computers, but sometimes ten or other number). On some processors like graphics processing units (GPUs) and digital signal processors (DSPs) which support saturation arithmetic, overflowed results would be ''clamped'', i.e. set to the minimum value in the representable range if the result is below the minimum and set to the maximum value in the representable range if the result is above the maximum, rather than wrapped around. An overflow condition may give results lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carry (arithmetic)
In elementary arithmetic, a carry is a Numerical digit, digit that is transferred from one column of digits to another column of more significant digits. It is part of the standard algorithm to addition, add numbers together by starting with the rightmost digits and working to the left. For example, when 6 and 7 are added to make 13, the "3" is written to the same column and the "1" is carried to the left. When used in subtraction the operation is called a borrow. Carrying is emphasized in traditional mathematics, while curricula based on reform mathematics do not emphasize any specific method to find a correct answer. Carrying makes a few appearances in higher mathematics as well. In computing, carrying is an important function of adder (electronics), adder circuits. Manual arithmetic A typical example of carry is in the following pencil-and-paper addition: 1 27 + 59 ---- 86 7 + 9 = 16, and the digit 1 (number), 1 is the carry. The opposite is a borrow, as in − ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Machine Code
In computer programming, machine code is computer code consisting of machine language instructions, which are used to control a computer's central processing unit (CPU). For conventional binary computers, machine code is the binaryOn nonbinary machines it is, e.g., a decimal representation. representation of a computer program that is actually read and interpreted by the computer. A program in machine code consists of a sequence of machine instructions (possibly interspersed with data). Each machine code instruction causes the CPU to perform a specific task. Examples of such tasks include: # Load a word from memory to a CPU register # Execute an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) operation on one or more registers or memory locations # Jump or skip to an instruction that is not the next one In general, each architecture family (e.g., x86, ARM) has its own instruction set architecture (ISA), and hence its own specific machine code language. There are exceptions, such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |