|
Arita, Saga
is a town located in Nishimatsuura District, Saga Prefecture, Japan. It is known for producing Arita porcelain, one of the traditional handicrafts of Japan. It also holds the largest ceramic fair in Western Japan, the Arita Ceramic Fair. This event is held from April 29 to May 5 ( Golden Week) every year and has thousands of stores and stalls lining the six-kilometre long main street. On March 1, 2006 the town of Nishiarita, from Nishimatsuura District, was merged into Arita. Geography Arita is located in the western part of Saga Prefecture, bordering Nagasaki Prefecture from its southwest to western sides. About 70% of the town is forest and mountains. Neighbouring municipalities * Saga Prefecture ** Imari ** Takeo History Arita was one of the first sites in Japan to produce porcelain, Arita ware. The discovery of porcelain stone is attributed to a Korean potter named Kanagae Sambe, although most historians consider this a legend. *April 1, 1889 – The modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Towns In Japan
A town (町; ''chō'' or ''machi'') is a local administrative unit in Japan. It is a local public body along with prefecture (''ken'' or other equivalents), city (''shi''), and village (''mura''). Geographically, a town is contained within a district. Note that the same word (町; ''machi'' or ''chō'') is also used in names of smaller regions, usually a part of a ward in a city. This is a legacy of when smaller towns were formed on the outskirts of a city, only to eventually merge into it. Towns See also * Municipalities of Japan * Japanese addressing system The Japanese addressing system is used to identify a specific location in Japan. When written in Japanese characters, addresses start with the largest geographical entity and proceed to the most specific one. When written in Latin alphabet, Lati ... References {{reflist External links DF 7 of 40">"Large City System of Japan"; graphic shows towns compared with other Japanese city types at p. 1 [PDF 7 of 40/now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagasaki Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Kyūshū. Nagasaki Prefecture has a population of 1,314,078 (1 June 2020) and has a geographic area of 4,130 km2 (1,594 sq mi). Nagasaki Prefecture borders Saga Prefecture to the northeast. Nagasaki is the capital and largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture, with other major cities including Sasebo, Isahaya, and Ōmura. Nagasaki Prefecture is located in western Kyūshū with a territory consisting of many mainland peninsulas centered around Ōmura Bay, as well as islands and archipelagos including Tsushima and Iki in the Korea Strait and the Gotō Islands in the East China Sea. Nagasaki Prefecture is known for its century-long trading history with the Europeans and as the sole place of direct trade and exchange between Japan and the outside world during the ''Sakoku'' period. Nagasaki Prefecture is home to several of the Hidden Christian Sites in the Nagasaki Region which have been declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagasaki Airport
is an international airport located west of the railway station in the city of Ōmura and north northeast of the Nagasaki railway station in the city of Nagasaki, Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan. The airport terminal and runway 14/32 are on an island, and the shorter runway 18/36 (now used by the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force for helicopter flights) is on the mainland. History The mainland portion of the airport opened as a military aerodrome in 1923, and commenced civilian joint use as Omura Airport (大村空港) in 1955. The current island runway and terminal opened on May 1, 1975, and became Japan's first full-scale airport built over water. It was also the first airport in the world to be built on the ocean. Although Nagasaki is superficially similar to Japan's other island airports, Kansai International Airport, Kobe Airport, Kitakyushu Airport, and Chūbu Centrair International Airport, Nagasaki Airport was constructed on Mishima Island ( ja, 箕島). Construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saga Airport
is an airport in the Kawasoe area of Saga, Saga Prefecture, Japan. It also uses the unofficial name . Saga Airport is located on the edge of the Ariake Sea, in what is best called a polder, 35 minutes from JR Saga Station by bus. History The governor of Saga Prefecture announced the construction of Saga Airport in January 1969, and after years of studies and negotiations, construction commenced in 1992. The airport opened in July 1998, with hours initially limited to 8.30 a.m. to 8 p.m. At the airport's outset, All Nippon Airways operated flights to Tokyo, Osaka and Nagoya and Japan Air System operated a daily flight to Osaka. JAS suspended service to Osaka in September 2001; ANA suspended service to Nagoya in February 2003 and to Osaka in January 2011. Due to the slump in mainline service to the airport, Saga Prefecture began several programs aimed at promoting usage of the airport, including ground transportation subsidies for local companies that used the airport for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jingdezhen
Jingdezhen is a prefecture-level city, in northeastern Jiangxi province, with a total population of 1,669,057 (2018), bordering Anhui to the north. It is known as the " Porcelain Capital" because it has been producing Chinese ceramics for at least 1,000 years, and for much of that period Jingdezhen porcelain was the most important and finest quality in China. The city has a well-documented history that stretches back over 2,000 years. History Throughout both the Spring and Autumn Period and the Warring States Period, the area of present-day Jingdezhen belonged to the Chu State. After the fall of the Chu, the area was incorporated into the Qin Dynasty as part of Fan County () in . Under the Han Dynasty, the area belonged to Poyang County () in . Under the Han Dynasty, the particular area of future Jingdezhen was known as Xinping (). Historical records show that it was during this time that it began to make porcelain. The town was established during the Jin Dynasty under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meissen
Meissen (in German orthography: ''Meißen'', ) is a town of approximately 30,000 about northwest of Dresden on both banks of the Elbe river in the Free State of Saxony, in eastern Germany. Meissen is the home of Meissen porcelain, the Albrechtsburg castle, the Gothic Meissen Cathedral and the Meissen Frauenkirche. The ''Große Kreisstadt'' is the capital of the Meissen district. Names * german: Meißen * french: Meissen, ou, selon l'orthographe allemande: ''Meißen''; en français suranné: ''Misnie'' * la, Misnia, Misena, Misnensium * pl, Miśnia * cs, Míšeň * hsb, Mišno * dsb, Mišnjo * zh, 迈森 (pinyin: ) History Meissen is sometimes known as the "cradle of Saxony". It grew out of the early West Slavic settlement of ''Misni'' inhabited by Glomatians and was founded as a German town by King Henry the Fowler in 929. In 968, the Diocese of Meissen was founded, and Meissen became the episcopal see of a bishop. The Catholic bishopric was suppressed in 1581 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister City
A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties. While there are early examples of international links between municipalities akin to what are known as sister cities or twin towns today dating back to the 9th century, the modern concept was first established and adopted worldwide during World War II. Origins of the modern concept The modern concept of town twinning has its roots in the Second World War. More specifically, it was inspired by the bombing of Coventry on 14 November 1940, known as the Coventry Blitz. First conceived by the then Mayor of Coventry, Alfred Robert Grindlay, culminating in his renowned telegram to the people of Stalingrad (now Volgograd) in 1942, the idea emerged as a way of establishing solidarity links between cities in allied countries that went through similar devastating events. The comradeshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Japan
Japan has three levels of governments: national, prefectural, and municipal. The nation is divided into 47 prefectures. Each prefecture consists of numerous municipalities, with 1,719 in total (January 2013 figures There are four types of municipalities in Japan: Cities of Japan, cities, towns, villages and special wards (the ''ku'' of Tokyo). In Japanese, this system is known as , where each kanji in the word represents one of the four types of municipalities. Some designated cities also have further administrative subdivisions, also known as wards. But, unlike the Special wards of Tokyo, these wards are not municipalities. Status The status of a municipality, if it is a village, town or city, is decided by the prefectural government. Generally, a village or town can be promoted to a city when its population increases above fifty thousand, and a city can (but need not) be demoted to a town or village when its population decreases below fifty thousand. The least-popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yi Sam-pyeong
Kanagae Sanbee () in historical sources, was a Japanese potter who is said to have moved from Korea. He is often considered the father of Arita ware porcelain, although the narrative is today questioned by historians.Komiya Kiyora 小宮木代良, ''"tōso" gensetsu no rekishiteki zentei'' 「陶祖」言説の歴史的前提, Nitchō kōryū to sōkoku no rekisi 日朝交流と相克の歴史, pp. 363-381, 2009.Komiya Kiyora 小宮木代良, ''"tōso" gensetsu no seiritsu to tenkai'' 「陶祖」言説の成立と展開 (The origins and expansion of the story of ''Touso'', the first ceramist), Kyūshū Shigaku 九州史学, No. 153, pp. 49-74, 2009. He is honored in Sueyama Shrine of Arita as the father of Arita ware. Popular narrative Although there is no doubt that Kanagae Sanbee actually existed, almost no contemporary source mentions him. The story of "Yi Sam-pyeong" as seen today was gradually developed by the late 19th century by various parties with various intentions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
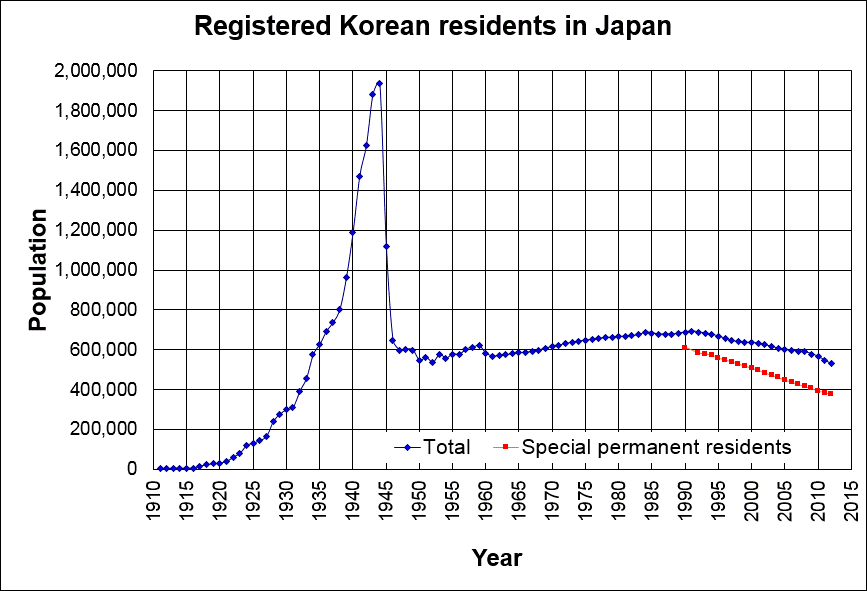
Koreans In Japan
comprise ethnic Koreans who have permanent residency status in Japan or who have become Japanese citizens, and whose immigration to Japan originated before 1945, or who are descendants of those immigrants. They are a group distinct from South Korean nationals who have emigrated to Japan after the end of World War II and the division of Korea. They currently constitute the second largest ethnic minority group in Japan after Chinese immigrants, due to many Koreans assimilating into the general Japanese population. The majority of Koreans in Japan are , often known simply as , who are ethnic Korean permanent residents of Japan. The term Zainichi Korean refers only to long-term Korean residents of Japan who trace their roots to Korea under Japanese rule, distinguishing them from the later wave of Korean migrants who came mostly in the 1980s, and from pre-modern immigrants dating back to antiquity who may themselves be the ancestors of the Japanese people. The Japanese word "Zaini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petuntse
Petuntse (from 白墩子 in pinyin: ), also spelled petunse and ''bai dunzi'', ''baidunzi'', is a historic term for a wide range of micaceous or feldspathic rocks. However, all will have been subject to geological decomposition processes that result in a material which, after processing, is suitable as an ingredient in some ceramic formulations. The name means "little white bricks", referring to the form in which it was transported to the potteries (compare ball clay). It was, and to some extent continues to be, an important raw material for Chinese porcelain, although the terms "porcelain stone", or "pottery stone", are now used. The equivalent term in Chinese is ''cishi''. It is mixed with kaolin in proportions varying according to the grade of porcelain to be produced; equal quantities for the best and two thirds petuntse to one third kaolin for everyday ware. There are large deposits of high quality stone in Jiangxi province in south-eastern China, which became a centre for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arita Ware
is a broad term for Japanese porcelain made in the area around the town of Arita, in the former Hizen Province, northwestern Kyūshū island. It is also known as after the wider area of the province. This was the area where the great majority of early Japanese porcelain, especially Japanese export porcelain, was made. In English usage "Arita ware" was traditionally used for the export wares in blue and white porcelain, mostly copying Chinese styles. The wares with added overglaze colours were called Imari ware or (a sub-group) Kakiemon. It is now recognized that the same kilns often made more than one of these types, and "Arita ware" is more often used as a term for all of them. The brightly coloured Kutani ware is another type that is now recognised as coming from around Arita as well as the Kutani itself, and "Kutani-type" is used as a stylistic description. History According to tradition, the Korean potter Yi Sam-pyeong (d. 1655), or ''Kanagae Sanbee'' (), is oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)