|
Aristodemus Of Cydathenaeum
Aristodemus of Cydathenaeum (Greek: Ἀριστόδημος Κυδαθηναιεύς ''Aristódēmos Kudathēnaieύs''; fl. c. 5th century BCE) was an ancient Athenian follower of the philosopher Socrates. He is best remembered as a character and narrative source in Plato's ''Symposium'', and is also preserved in Xenophon's ''Memorabilia'' and a fragment from Aristophanes. Life Aristodemus is described as a barefooted runt of low birth in Plato's ''Symposium'',Plato, ''Symposium'', 173b while Xenophon refers to him as Aristodemus the dwarf ("Ἀριστόδημον τὸν μικρόν ''Aristódēmon tón mikrón''"). He was a citizen of the same deme as that of the comedian Aristophanes, with whom he appears in the ''Symposium''. Although little is known of his life, his depiction as a member of an earlier generation of Socratic followers places his birth in the early-mid 5th century BCE,Debra Nails, ''The People of Plato'', Indianapolis: Hackett Publishing, 2002, pp. 52–53 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristodemus
In Greek mythology, Aristodemus (Ancient Greek: Ἀριστόδημος) was one of the Heracleidae, son of Aristomachus and brother of Cresphontes and Temenus. He was a great-great-grandson of Heracles and helped lead the fifth and final attack on Mycenae in the Peloponnese. Aristodemus and his brothers complained to the oracle that its instructions had proved fatal to those who had followed them; the oracle had told Hyllas to attack through the narrow passage when the third fruit was ripe. They received the answer that by the "third fruit" the "third generation" was meant, and that the "narrow passage" was not the isthmus of Corinth, but the straits of Rhium. They accordingly built a fleet at Naupactus, but before they set sail, Aristodemus was struck by lightning (or shot by Apollo) and the fleet destroyed, because one of the Heraclidae had slain an Acarnanian soothsayer. His brothers were later able to conquer the Peloponnese. By his wife Argia, daughter of King Autesion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
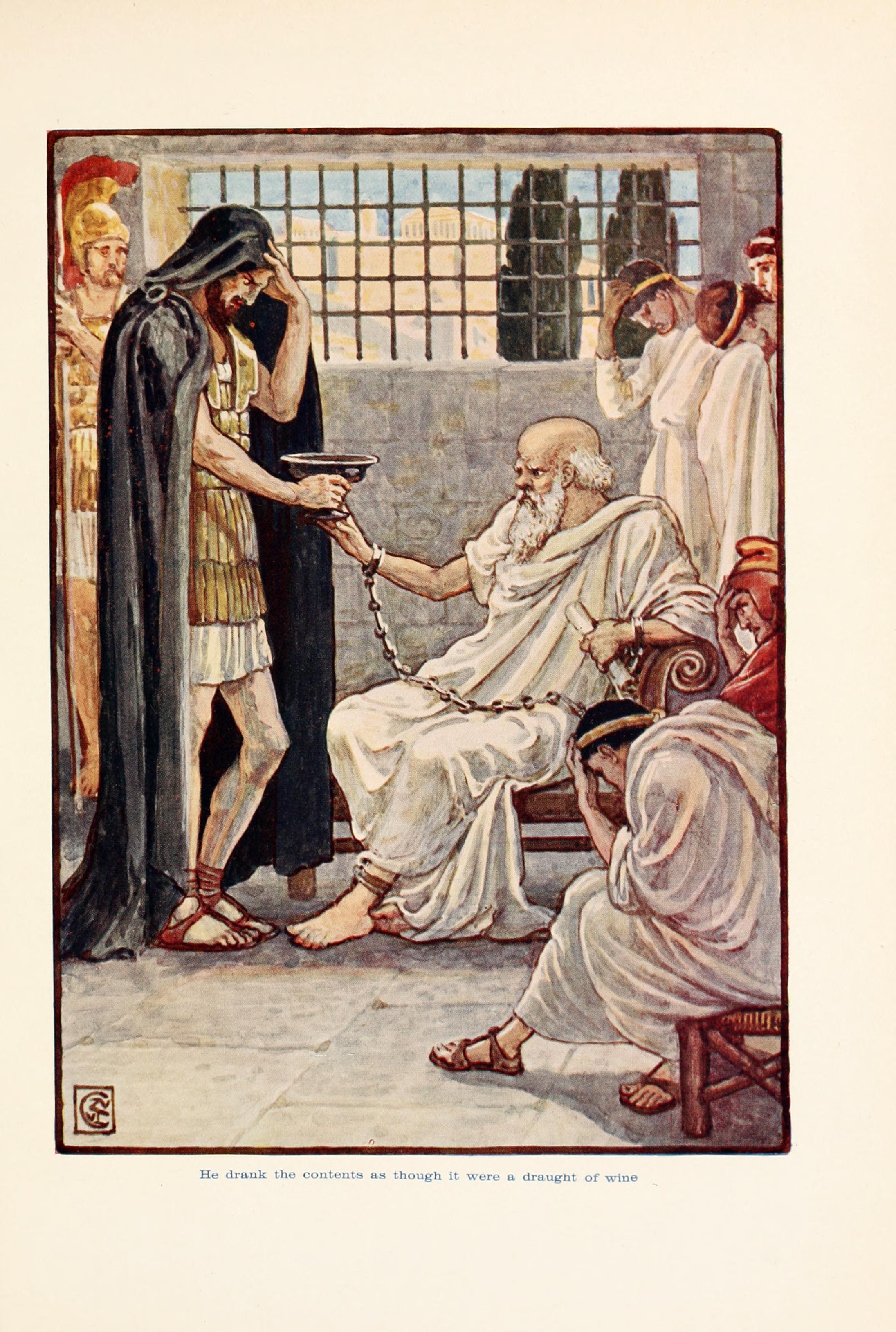
Trial Of Socrates
The trial of Socrates (399 BC) was held to determine the philosopher's guilt of two charges: ''asebeia'' (impiety) against the pantheon of Athens, and corruption of the youth of the city-state; the accusers cited two impious acts by Socrates: "failing to acknowledge the gods that the city acknowledges" and "introducing new deities". The death sentence of Socrates was the legal consequence of asking politico-philosophic questions of his students, which resulted in the two accusations of moral corruption and impiety. At trial, the majority of the ''dikasts'' (male-citizen jurors chosen by lot) voted to convict him of the two charges; then, consistent with common legal practice voted to determine his punishment and agreed to a sentence of death to be executed by Socrates's drinking a poisonous beverage of hemlock. Primary-source accounts of the trial and execution of Socrates are the '' Apology of Socrates'' by Plato and the '' Apology of Socrates to the Jury'' by Xenophon of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Speakers In Plato's Dialogues
following is a list of the speakers found in the dialogues traditionally ascribed to Plato, including extensively quoted, indirect and conjured speakers. Dialogues, as well as Platonic '' Epistles'' and ''Epigrams'', in which these individuals appear dramatically but do not speak are listed separately. ;Unnamed speakers Notes Bibliography * Debra Nails. ''The People of Plato: A Prosopography of Plato and Other Socratics''. Hackett Publishing, 2002. . * Plato Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution .... ''Complete Works''. Ed: John M. Cooper. Hackett Publishing, 1997. {{Socrates navbox * * Platos Dialogues Speakers in Plato's dialogues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eros
In Greek mythology, Eros (, ; grc, Ἔρως, Érōs, Love, Desire) is the Greek god of love and sex. His Roman counterpart was Cupid ("desire").''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. In the earliest account, he is a primordial god, while in later accounts he is described as one of the children of Aphrodite and Ares and, with some of his siblings, was one of the Erotes, a group of winged love gods. Etymology The Greek , meaning 'desire', comes from 'to desire, love', of uncertain etymology. R. S. P. Beekes has suggested a Pre-Greek origin. Cult and depiction Eros appears in ancient Greek sources under several different guises. In the earliest sources (the cosmogonies, the earliest philosophers, and texts referring to the mystery religions), he is one of the primordial gods involved in the coming into being of the cosmos. In later sources, however, Eros is represented as the son of Aphrodite, whose mischievous interventions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seth Benardete
Seth Benardete (April 4, 1930 – November 14, 2001) was an American classicist and philosopher, long a member of the faculties of New York University and The New School. In addition to teaching positions at Harvard, Brandeis, St. John's College, Annapolis and NYU, Benardete was a fellow for the National Endowment for the Humanities and the Carl Friedrich von Siemens Stiftung in Munich. Life and family Benardete was born in Brooklyn into an academic family. His father, Maír José Benardete, was a professor of Spanish at Brooklyn College and expert on Sephardic culture. His older brother José Benardete was a noted philosopher. His younger brother Diego Benardete is a professor of mathematics at the University of Hartford. Seth was married to Jane, a professor of English at Hunter College in Manhattan; and they had two children, Ethan and Alexandra. Career At the University of Chicago in the 1950s he was a student of Leo Strauss, along with Allan Bloom, Stanley Rosen and several o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allan Bloom
Allan David Bloom (September 14, 1930 – October 7, 1992) was an American philosopher, classicist, and academician. He studied under David Grene, Leo Strauss, Richard McKeon, and Alexandre Kojève. He subsequently taught at Cornell University, the University of Toronto, Tel Aviv University, Yale University, École normale supérieure, and the University of Chicago. Bloom championed the idea of Great Books education and became famous for his criticism of contemporary American higher education, with his views being expressed in his bestselling 1987 book, ''The Closing of the American Mind''. Characterized as a conservative in the popular media, Bloom denied the label, asserting that what he sought to defend was the "theoretical life". Saul Bellow wrote ''Ravelstein'', a ''roman à clef'' based on Bloom, his friend and colleague at the University of Chicago. Early life and education Bloom was born in Indianapolis, Indiana to second-generation Jewish parents who were both soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Strauss
Leo Strauss (, ; September 20, 1899 – October 18, 1973) was a German-American political philosopher who specialized in classical political philosophy. Born in Germany to Jewish parents, Strauss later emigrated from Germany to the United States. He spent much of his career as a professor of political science at the University of Chicago, where he taught several generations of students and published fifteen books. Trained in the neo-Kantian tradition with Ernst Cassirer and immersed in the work of the phenomenologists Edmund Husserl and Martin Heidegger, Strauss established his fame with path-breaking books on Spinoza and Hobbes, then with articles on Maimonides and Al-Farabi. In the late 1930s his research focused on the rediscovery of esoteric writing, thereby a new illumination of Plato and Aristotle, retracing their interpretation through medieval Islamic and Jewish philosophy, and encouraging the application of those ideas to contemporary political theory. Early life and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atheism
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no deities. Atheism is contrasted with theism, which in its most general form is the belief that at least one deity exists. The first individuals to identify themselves as atheists lived in the 18th century during the Age of Enlightenment. The French Revolution, noted for its "unprecedented atheism", witnessed the first significant political movement in history to advocate for the supremacy of human reason.Extract of page 22 In 1967, Albania declared itself the first official atheist coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Gods
The following is a list of gods, goddesses, and many other divine and semi-divine figures from ancient Greek mythology and ancient Greek religion. Immortals The Greeks created images of their deities for many purposes. A temple would house the statue of a god or goddess, or multiple deities, and might be decorated with relief scenes depicting myths. Divine images were common on coins. Drinking cups and other vessels were painted with scenes from Greek myths. Major gods and goddesses Greek primordial deities Titans and Titanesses The Titan gods and goddesses are depicted in Greek art less commonly than the Olympians. File:Eos Memnon Louvre G115.jpg, Eos (Dawn) and the hero Memnon (490–480 BC) File:Ilion---metopa.jpg, Helios in his four-horse chariot (3rd century BC) File:0029MAN-Themis.jpg, Themis, from the Temple of Nemesis (ca. 300 BC) File:Antakya Arkeoloji Muzesi 02366 nevit.jpg, Oceanus wearing crab-claw horns, with Tethys ( Roman-era mosaic) File:Creation Promethe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debra Nails
Debra Nails (born November 15, 1950) is an American philosophy professor who taught at Michigan State University. Nails earned her M.A. in philosophy and classical Greek from Louisiana State University before going on to earn a Ph.D. in philosophy at the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg in 1993.Michigan State University/philosophy/Debra Nails (accessed July 11, 2016) Previously, she taught in the Department of Classics, Philosophy, and Religion at . Nails taught courses on the history of philosophy, continental rationalism, metaphysics, and modern philosophy. Contributions to philosophy Nails' work primarily focuses on ancient Gre ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Comedy
Old Comedy (''archaia'') is the first period of the ancient Greek comedy, according to the canonical division by the Alexandrian grammarians.Mastromarco (1994) p.12 The most important Old Comic playwright is Aristophanes – whose works, with their daring political commentary and abundance of sexual innuendo, effectively define the genre today. Origins and history The Greek word for comedy (''kōmōidía'') derives from the words for 'revel' and 'song' (''kōmos'' and ''ōdē'') and according to Aristotle comic drama actually developed from song. The first official comedy at the City Dionysia was not staged until 487/6 BC, by which time tragedy had already been long established there. The first comedy at the Lenaia was staged later still, only about 20 years before the performance there of ''The Acharnians'', the first of Aristophanes' surviving plays. According to Aristotle, comedy was slow to gain official acceptance because nobody took it seriously, yet only 60 years after come ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |