|
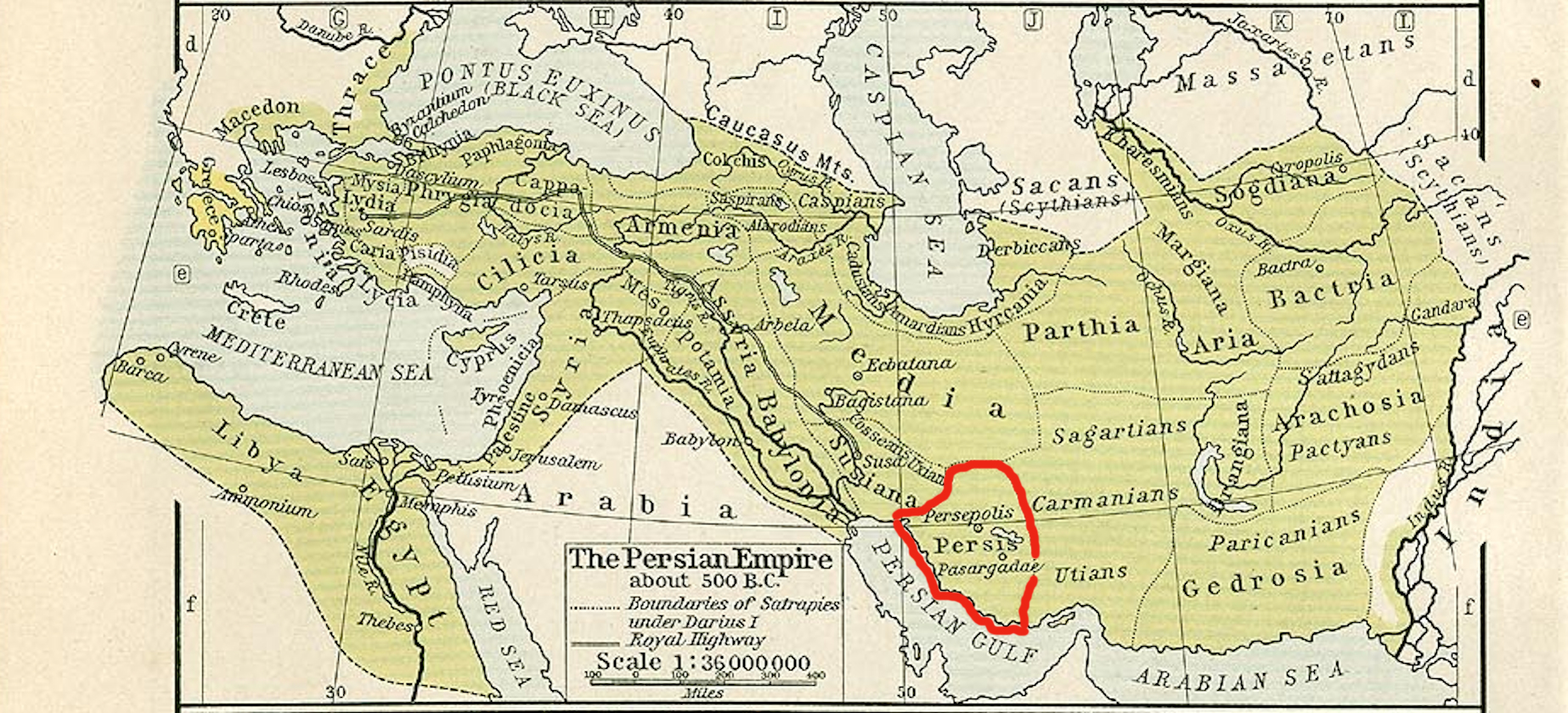
Ariobarzanes (satrap Of Persis)
Ariobarzanes ( peo, *Aryābr̥zaⁿs; grc, Ἀριοβαρζάνης ; fa, آریوبرزن; died 330 BC), was an Achaemenid prince, satrap and a Persian military commander who led an ambush of the Persian army at the Battle of the Persian Gate against Macedonian King Alexander the Great in the winter of 330 BC. Life Though the exact birth date of Ariobarzanes is unknown. His sister was the ancient Persian noblewoman and warrior Youtab. Ariobarzanes was appointed as the first satrap of Persis (the southern province of Fars in present-day Iran) in 335 BC by Darius III Codomannus. Historians are surprised that Darius III appointed a satrap for Persepolis and Persis; apparently, that office did not previously exist. Ariobarzanes commanded part of the Persian Army fighting against the Macedonians at the Battle of Gaugamela in 331 BC. Following the Persian defeat at , Darius III realized he could not aptly defend his capital in Persepolis and traveled east to rebuild his armie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yasuj
Yasuj ( fa, ; also romanized as Yāsūj, Yasooj, and Yesūj; Luri: ''Jasuc'' or ''Jasyç'') is a city and capital of Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 96,786, in 20,297 families. Yasuj is an industrial city in the Zagros Mountains of southwestern Iran. The term ''Yasuj'' is also used to refer to the entire region. Yasuj has a sugar processing plant. History The area of Yasuj has been settled since as early as the Bronze Age. Findings include the Martyrs Hills (dating from 3rd millennium BC), the Khosravi Hill from the Achaemenian period, the ancient site of Gerd, the Pataveh bridge, and the Pay-e Chol cemetery. Yasuj is the place where Alexander III of Macedon and his Macedonian forces stormed the '' Persian Gates'' (''Darvazeh-ye Fars''), and found a way into the Persian heartland (331 BC). The Yasuj Museum, which opened in 2002, displays coins, statues, pottery, and bronze vessels recovered from surrounding archaeological s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Youtab
Youtab meaning "unique" in Old Persian (4th century BC - 330 BC) was an ancient Persian noblewoman. She was the sister of Ariobarzanes, Satrap of Persis. She is notable for fighting alongside her brother against Macedonian King Alexander the Great at the Battle of the Persian Gate The Battle of the Persian Gate was a military conflict between a Persian force, commanded by the satrap of Persis, Ariobarzanes, and the invading Hellenic League, commanded by Alexander the Great. In the winter of 330 BC, Ariobarzanes led a las ... in the winter of 330 BC. References Persian people of the Greco-Persian Wars 330 BC deaths Year of birth unknown 4th-century BC Iranian people Women in ancient Near Eastern warfare 4th-century BC women Opponents of Alexander the Great Iranian princesses Military personnel of the Achaemenid Empire killed in action Women of the Achaemenid Empire People whose existence is disputed {{Iran-mil-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governors Of Fars
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political region or polity, a ''governor'' may be either appointed or elected, and the governor's powers can vary significantly, depending on the public laws in place locally. The adjective pertaining to a governor is gubernatorial, from the Latin root ''gubernare''. Ancient empires Pre-Roman empires Though the legal and administrative framework of provinces, each administrated by a governor, was created by the Romans, the term ''governor'' has been a convenient term for historians to describe similar systems in antiquity. Indeed, many regions of the pre-Roman antiquity were ultimately replaced by Roman 'standardized' provincial governments after their conquest by Rome. Plato used the metaphor of turning the Ship of State with a rudder; the Lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th-century BC Iranian People
The 4th century (per the Julian calendar and Anno Domini/Common era) was the time period which lasted from 301 ( CCCI) through 400 ( CD). In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 (over the current capitals, which had effectively been changed by Diocletian's reforms to Milan in the West, and Nicomedeia in the East) to build the city soon called Nova Roma (New Rome); it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor. The last emperor to control both the eastern and western halves of the empire was Theodosius I. As the century progressed after his death, it became increasingly apparent that the empire had changed in many ways since the time of Augustus. The two emperor system originally established by Diocletian in the previous century fell in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
330 BC Deaths
33 may refer to: *33 (number) *33 BC *AD 33 *1933 * 2033 Music * ''33'' (Luis Miguel album) (2003) * ''33'' (Southpacific album) (1998) * ''33'' (Wanessa album) (2016) *"33 'GOD'", a 2016 song by Bon Iver * "Thirty-Three" (song), a 1995 song by the Smashing Pumpkins *"Thirty Three", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''Almost Heathen'', 2001 *"33", a 2002 song by Coheed and Cambria *"33" a 2020 song by Polo G Television *El 33, a Catalan television channel * "33" (''Battlestar Galactica''), an episode of ''Battlestar Galactica'' Other uses *Los 33, the miners involved in the 2010 Copiapó mining accident **''The 33'', a 2015 film based on the Copiapó mining accident * ''Thirty Three'' (film), a 1965 Soviet comedy film by Georgi Daneliya * +33, the international calling code for France *33, a label printed on Rolling Rock beer bottles See also * (other) * Alfa Romeo 33, an Italian automobile * Club 33, a set of private clubs in Disney Parks * List of highways num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
368 BC Births
Year 368 ( CCCLXVIII) was a leap year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Valens (or, less frequently, year 1121 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 368 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Spring – Emperor Valentinian I and his 8-year-old son, Gratian, cross the Rhine with an army into Alamannic territory. He defeats the Alemanni and burns food stores along the border. A temporary peace is signed with Macrian, king of the Bucinobantes, and Valentinian returns to his capital ''Augusta Treverorum'' (modern Trier). * Great Conspiracy: Picts, Scotti and Saxons reach Roman London and plunder the city. Theodosius, a general (''Comes Britanniarum''), is sent with a relief force to Britannia. He marches from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrasaortes
Phrasaortes was a Persian satrap of Persis under Alexander the Great from circa 330 BCE. He was a son of Rheomithres. Phrasaortes replaced the Achaemenid satrap Ariobarzanes, who had confronted Alexander at the Battle of the Persian Gate, where he was killed. Phrasaortes died at some point before the return of Alexander from India in 324 BCE.Arr. Anab. 6.29.2 He was replaced by Oxines, a Persian noble, without the permission of Alexander, in a direct challenge to Alexander's authority. Oxines was executed by Alexander, and replaced by the Macedonian general Peucestas Peucestas ( grc, Πευκέστας, ''Peukéstas''; lived 4th century BC) was a native of the town of Mieza, in Macedonia, and a distinguished officer in the service of Alexander the Great. His name is first mentioned as one of those appointed t .... References {{Hellenistic satraps Satraps of the Alexandrian Empire 4th-century BC Iranian people Ancient Persian people History of Fars Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Last Stand
A last stand is a military situation in which a body of troops holds a defensive position in the face of overwhelming and virtually insurmountable odds. Troops may make a last stand due to a sense of duty; because they are defending a tactically crucial point; to buy time to enable a trapped army, person, or group of people to escape; due to fear of execution if captured; or to protect their ruler or leader. Last stands loom large in history, as the heroism and sacrifice of the defenders exert a large pull on the public's imagination. Some last stands have become a celebrated part of a fighting force's or a country's history, especially if the defenders accomplished their goals (or in rare cases, defeated their attackers). Tactical significance A "last stand" is a last resort tactic, and is chosen because the defending force realizes or believes the benefits of fighting outweigh the benefits of retreat or surrender. This usually arises from strategic or moral considerations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae ( ; grc, Μάχη τῶν Θερμοπυλῶν, label= Greek, ) was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lasting over the course of three days, it was one of the most prominent battles of both the second Persian invasion of Greece and the wider Greco-Persian Wars. The engagement at Thermopylae occurred simultaneously with the Battle of Artemisium: between July and September 480 BC. The second Persian invasion under Xerxes I was a delayed response to the failure of the first Persian invasion, which had been initiated by Darius I and ended in 490 BC by an Athenian-led Greek victory at the Battle of Marathon. By 480 BC, a decade after the Persian defeat at Marathon, Xerxes had amassed a massive land and naval force, and subsequently set out to conquer all of Greece. In response, the Athenian politician and general Themistocles proposed that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Gates
Persian Gate or the Susian Gate was the ancient name of the pass now known as Tang-e Meyran, connecting Yasuj with Sedeh to the east, crossing the border of the modern Kohgiluyeh va Boyer Ahmad and Fars provinces of Iran, passing south of the Kuh-e-Dinar massif, part of the Zagros Mountains. The pass controls the link between the shore and the central part of Persia. In the early weeks of 330 BC, it was the site of the fierce Battle of the Persian Gate, in which the Macedonian king Alexander the Great faced stiff resistance by the last Achaemenid troops commanded by Ariobarzan Ariobarzanes ( peo, *Aryābr̥zaⁿs; grc, Ἀριοβαρζάνης ; fa, آریوبرزن; died 330 BC), was an Achaemenid prince, satrap and a Persian military commander who led an ambush of the Persian army at the Battle of the Persian Gat .... References Further reading *{{cite journal , first=Henry , last=Speck , title=Alexander at the Persian Gates. A Study in Historiography and Topogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Gaugamela
The Battle of Gaugamela (; grc, Γαυγάμηλα, translit=Gaugámela), also called the Battle of Arbela ( grc, Ἄρβηλα, translit=Árbela), took place in 331 BC between the forces of the Army of Macedon under Alexander the Great and the Persian Army under King Darius III. It was the second and final battle between the two kings, and is considered to be the final blow to the Achaemenid Empire, resulting in its complete conquest by Alexander. The fighting took place in Gaugamela, which literally meant "The Camel's House", a village on the banks of the river Bumodus. The area today would be considered modern-day Erbil, Iraq, according to Urbano Monti's world map. Alexander's army was heavily outnumbered and modern historians say that "the odds were enough to give the most experienced veteran pause". Despite the overwhelming odds, Alexander's army emerged victorious due to the employment of superior tactics and the clever usage of light infantry forces. It was a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Macedonians
The Macedonians ( el, Μακεδόνες, ''Makedónes'') were an ancient tribe that lived on the alluvial plain around the rivers Haliacmon and lower Axios in the northeastern part of mainland Greece. Essentially an ancient Greek people,; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ; . they gradually expanded from their homeland along the Haliacmon valley on the northern edge of the Greek world, absorbing or driving out neighbouring non-Greek tribes, primarily Thracian and Illyrian.. They spoke Ancient Macedonian, which was perhaps a sibling language to Ancient Greek, but more commonly thought to have been a dialect of Northwest Doric Greek; though, some have also suggested an Aeolic Greek classification. However, the prestige language of the region during the Classical era was Attic Greek, replaced by Koine Greek during the Hellenistic era. Their religious beliefs mirrored those of other Greeks, following the main deities of the Greek pantheon, although the Macedonians continued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |